The four types of foreign exchange market participants are – The foreign exchange market, a bustling hub of global finance, is orchestrated by a diverse ensemble of participants, each playing a pivotal role in shaping its dynamics. From commercial banks to non-financial corporations, central banks to governments, these entities form the four pillars of the forex market, their interactions driving its liquidity, efficiency, and overall health.
As we delve into the intricacies of each participant’s role, we will uncover the strategies they employ to manage currency risk, facilitate international trade, and influence economic conditions. Join us on this enlightening journey into the heart of the forex market, where the actions of these four key players paint a vibrant tapestry of global financial activity.
Four Types of Foreign Exchange Market Participants: The Four Types Of Foreign Exchange Market Participants Are
The foreign exchange market is a global decentralized market for the trading of currencies. It involves the exchange of one currency for another, and participants in this market play crucial roles in facilitating these transactions.
There are four main types of participants in the foreign exchange market:
- Commercial Banks
- Central Banks
- Investment Firms
- Retail Traders
Commercial Banks
Commercial banks are the primary participants in the foreign exchange market, accounting for the majority of transactions. They facilitate currency exchange for their customers, which include individuals, businesses, and other financial institutions.
Get the entire information you require about foreign exchange market ppt presentation on this page.
Commercial banks offer a range of foreign exchange services, including currency conversion, hedging, and trade finance. They also play a role in setting exchange rates and providing liquidity to the market.
You also can investigate more thoroughly about foreign exchange market business example to enhance your awareness in the field of foreign exchange market business example.
Central Banks
Central banks are government agencies responsible for managing a country’s monetary policy and financial system. They participate in the foreign exchange market to influence exchange rates, manage foreign reserves, and maintain economic stability.
Central banks intervene in the market by buying or selling currencies to influence their value. They also set interest rates and implement other monetary policies to manage inflation, economic growth, and other macroeconomic factors.
Investment Firms
Investment firms are financial institutions that manage investments for their clients. They participate in the foreign exchange market to execute currency transactions for their investment portfolios.
Investment firms include hedge funds, mutual funds, and pension funds. They use foreign exchange transactions to diversify their portfolios, hedge against currency risk, and speculate on currency movements.
Retail Traders
Retail traders are individuals who trade currencies in the foreign exchange market for profit. They typically trade smaller amounts of currency compared to other participants and often use leverage to increase their potential returns.
Retail traders use various trading strategies and platforms to speculate on currency movements. They can trade currencies through online brokers or directly in the interbank market.
Commercial Banks and Other Financial Institutions
Commercial banks are central players in the foreign exchange market, facilitating transactions for businesses and individuals. They offer a range of services, including currency exchange, hedging, and international payments.
Find out about how foreign exchange market course can deliver the best answers for your issues.
Other financial institutions, such as investment banks and hedge funds, also participate in the foreign exchange market. Investment banks act as intermediaries between borrowers and lenders, while hedge funds engage in speculative trading to generate profits.
Contribution to Liquidity and Efficiency
These institutions contribute significantly to the liquidity and efficiency of the foreign exchange market. Commercial banks provide a large pool of liquidity, enabling businesses and individuals to buy and sell currencies at competitive rates. Investment banks facilitate large-scale transactions and provide access to specialized products, such as currency forwards and options.
Hedge funds, by actively trading in the market, create price discovery and arbitrage opportunities. They help stabilize prices and ensure that currencies are fairly valued.
3. Non-Financial Corporations
Non-financial corporations actively participate in the foreign exchange market to facilitate their international operations and manage currency risk. They engage in various transactions that require currency conversion, such as importing raw materials, exporting finished goods, and investing in foreign subsidiaries.
Corporations use the foreign exchange market to mitigate currency fluctuations that can impact their profitability and cash flows. By employing hedging strategies, such as forward contracts, options, and currency swaps, they can lock in exchange rates and reduce the uncertainty associated with currency movements.
Hedging Strategies
* Forward Contracts: Corporations can enter into forward contracts to fix the exchange rate for a future transaction, ensuring a predetermined rate for the conversion of a specific currency amount on a specific date.
* Options: Corporations can purchase currency options to give them the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specified amount of currency at a predetermined exchange rate within a specific time frame.
* Currency Swaps: Corporations can engage in currency swaps to exchange one currency for another at an agreed-upon exchange rate, with the obligation to reverse the transaction at a later date.
4. Central Banks and Governments
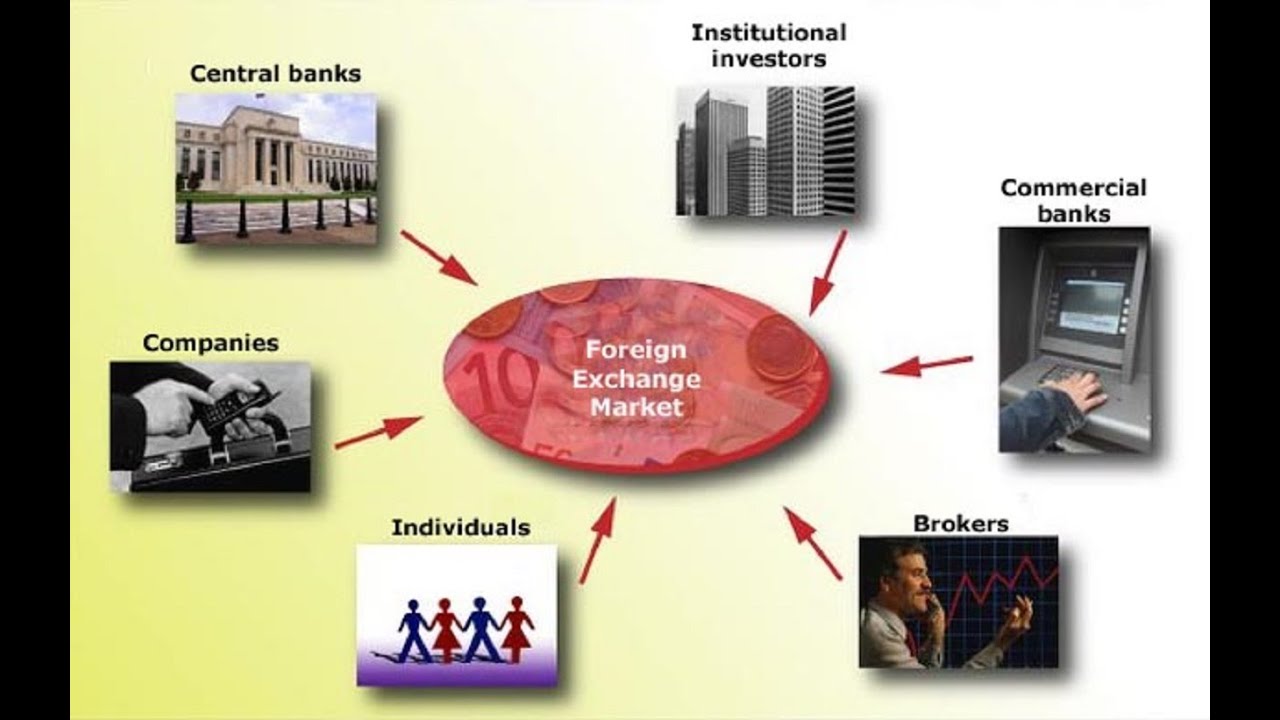
Central banks play a crucial role in the foreign exchange market as they are responsible for managing monetary policy and influencing exchange rates. Governments also have a significant impact on the market through their economic policies and regulations.
Central Bank Interventions
Central banks use foreign exchange interventions to influence exchange rates and manage economic conditions. They can buy or sell foreign currencies in the market to affect the supply and demand of currencies, thereby influencing their values. This is done to achieve various objectives, such as:
- Stabilizing exchange rates to reduce volatility and uncertainty.
- Managing inflation by influencing the value of the domestic currency relative to foreign currencies.
- Supporting economic growth by promoting exports or reducing imports.
Government Policies and Regulations, The four types of foreign exchange market participants are
Government policies and regulations can also impact the foreign exchange market. For instance, trade policies, such as tariffs or quotas, can affect the demand for currencies used in international trade. Similarly, fiscal policies, such as changes in taxes or government spending, can influence economic growth and the value of the domestic currency.
Closure

In the intricate ballet of the foreign exchange market, the four types of participants – commercial banks, non-financial corporations, central banks, and governments – each contribute a unique step, shaping the market’s rhythm and tempo. Their decisions, strategies, and interactions weave a complex web of financial activity that spans borders and influences economies worldwide. Understanding their roles is akin to deciphering the score of this global symphony, allowing us to appreciate the harmony and occasional dissonance that drive the ever-evolving foreign exchange market.
