The BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market, a financial hub of global significance, serves as the backbone of international trade and investment. This intricate network connects central banks, commercial banks, hedge funds, and corporations, facilitating the exchange of currencies and shaping the global economy. With its vast size and complex dynamics, the BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market warrants our attention as we delve into its intricacies, unraveling its history, participants, instruments, and the myriad factors that influence its ever-evolving landscape.
The BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market has witnessed remarkable growth over the years, evolving from humble beginnings to become the largest and most liquid financial market globally. Its sheer size, coupled with the diverse range of participants and instruments traded, makes it a fascinating subject of study for economists, financial professionals, and anyone seeking to understand the inner workings of the global financial system.
Overview of the BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market
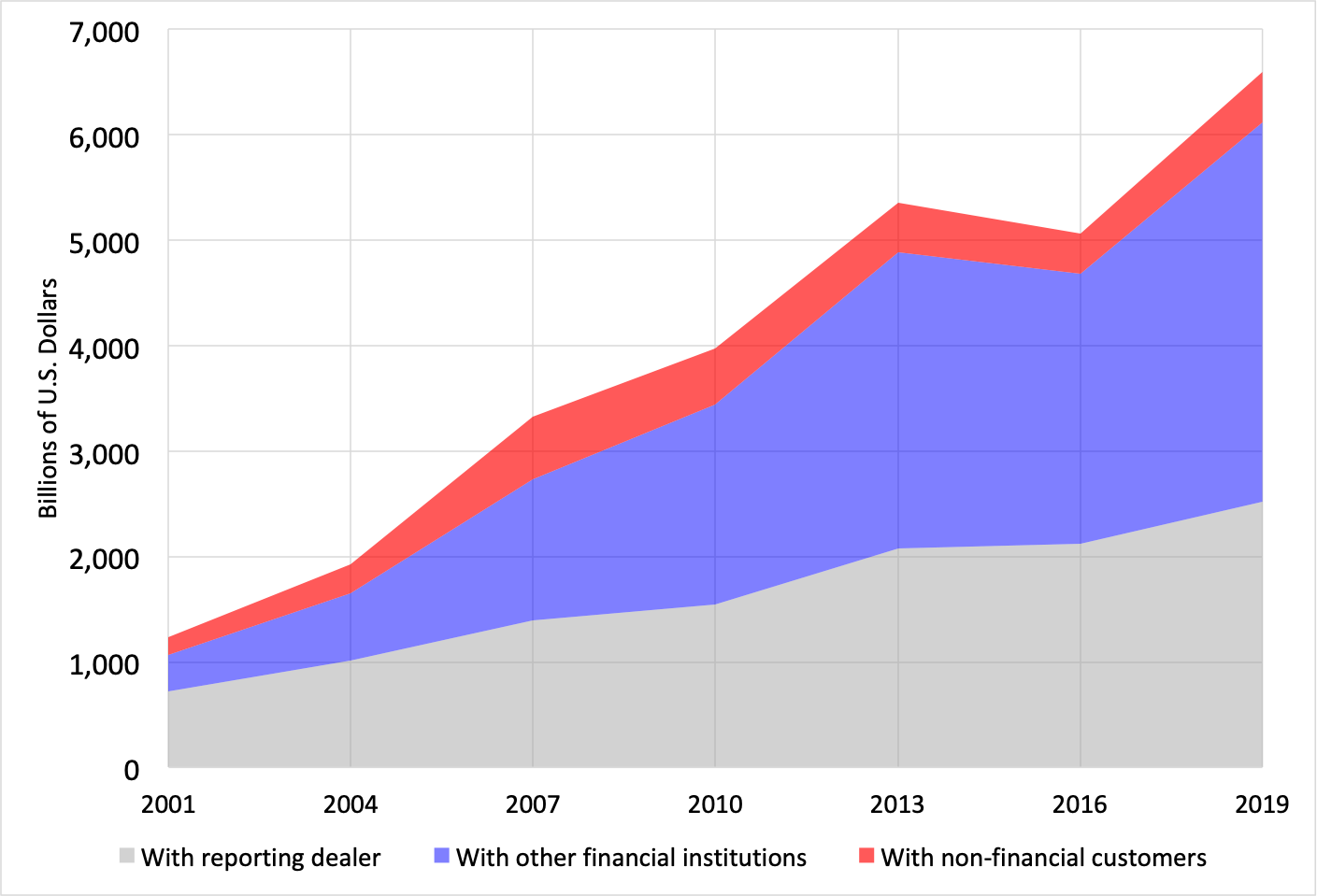
The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) Global Foreign Exchange Market is the world’s largest and most liquid financial market, facilitating the exchange of currencies between participants around the globe. It serves as a central hub for the trading of foreign exchange (forex) and plays a crucial role in international trade, investment, and economic stability.
History and Evolution
The BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market traces its roots back to the early 20th century when central banks and commercial banks began to trade currencies directly with each other. Over time, the market evolved and expanded, with the establishment of electronic trading platforms and the participation of a wider range of market participants, including hedge funds, asset managers, and retail investors.
Size and Volume
The BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market is the largest financial market globally, with an estimated daily trading volume of over $6.6 trillion. This volume is significantly higher than that of other financial markets, such as the stock or bond markets.
Participants in the BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market
The BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market is a complex and dynamic ecosystem, with a diverse range of participants playing significant roles. These participants include banks, hedge funds, corporations, and other financial institutions, each with unique strategies and motivations.
The largest and most active participants in the FX market are banks. They act as intermediaries, facilitating currency exchange transactions between other market participants. Banks also engage in proprietary trading, speculating on currency movements for their own profit.
Hedge Funds
Hedge funds are investment vehicles that employ complex trading strategies, including currency trading. They are often highly leveraged and take both long and short positions in currency pairs, seeking to profit from market volatility.
Corporations
Corporations participate in the FX market to manage their foreign exchange risk. When they engage in international trade or have overseas operations, they need to convert currencies to facilitate transactions and protect against currency fluctuations.
Impact of Different Participants on Market Dynamics
The diverse range of participants in the FX market contributes to its liquidity and volatility. Banks provide the infrastructure and liquidity necessary for efficient currency trading, while hedge funds and corporations introduce demand and supply imbalances that drive price movements. The strategies and risk appetites of these participants shape market dynamics, influencing currency values and exchange rates.
Obtain access to three functions of a foreign exchange market to private resources that are additional.
Products and Instruments Traded in the BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market
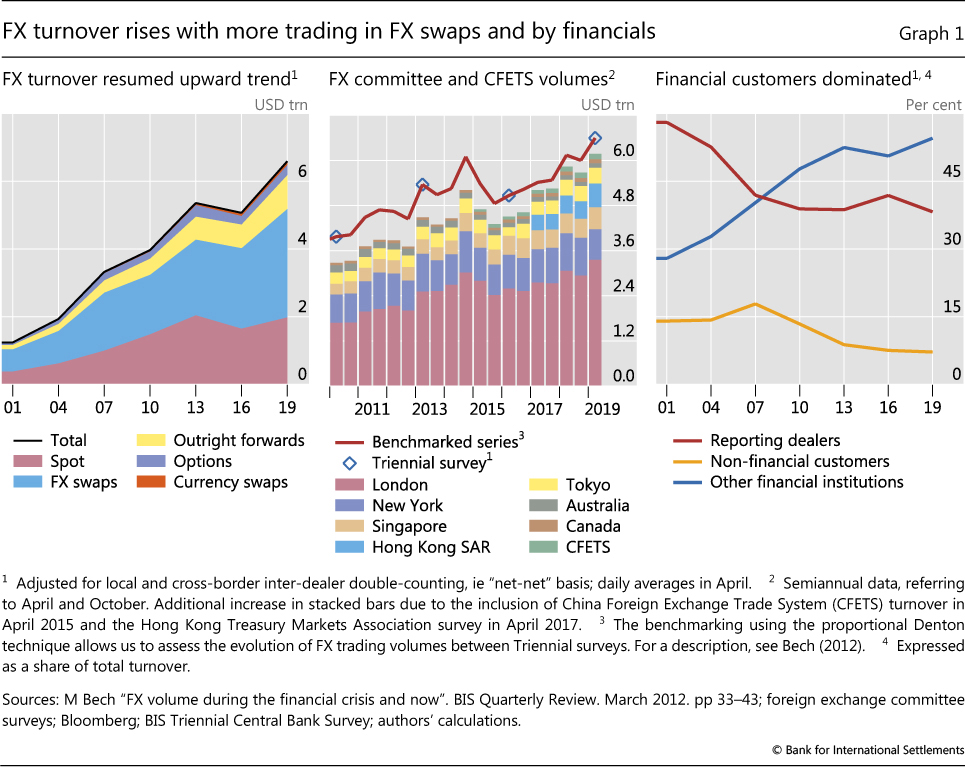
The BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market facilitates the trading of various foreign exchange products, each serving specific purposes and catering to different market participants’ needs. These products include spot FX, forwards, and options, which are briefly explained below:
Spot FX
Spot FX transactions involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the prevailing market rate. They are typically settled within two business days and are commonly used for short-term currency needs, such as making international payments or covering foreign exchange risk.
Forwards
Forward contracts are agreements to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date. They are used to hedge against future currency fluctuations and lock in exchange rates for upcoming transactions. Forwards are customizable in terms of the contract size, currency pair, and settlement date.
Discover the crucial elements that make foreign exchange market between countries the top choice.
Options
Options provide the buyer with the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific currency at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a specified date (expiration date). Options are used for speculation or hedging purposes, depending on the buyer’s market outlook and risk appetite.
Trading Mechanisms in the BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market
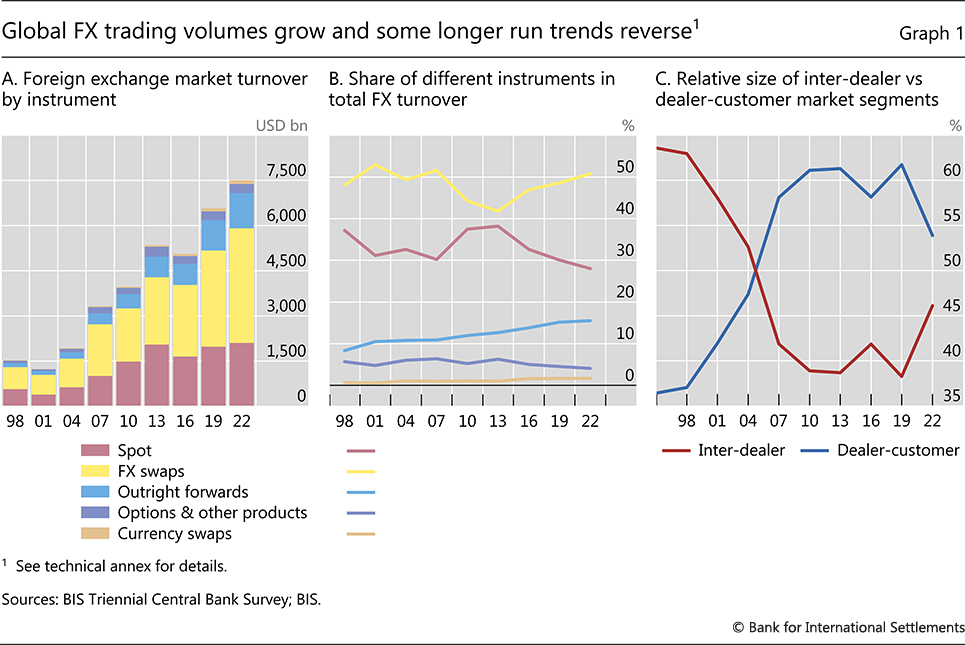
The BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market employs various trading mechanisms to facilitate the exchange of currencies. These mechanisms can be broadly categorized into over-the-counter (OTC) trading and electronic trading platforms.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Trading
OTC trading involves direct negotiations between two parties, without the involvement of an exchange or a central platform. It is a flexible and customizable mechanism that allows participants to tailor transactions to their specific needs. Advantages of OTC trading include:
– Flexibility: Parties can negotiate terms, including price, quantity, and settlement date, to suit their individual requirements.
– Confidentiality: Transactions are private and not publicly disclosed, ensuring anonymity and discretion.
– Access to a wider pool of liquidity: OTC trading connects participants with a vast network of market makers and liquidity providers, offering a broader range of trading opportunities.
However, OTC trading also has disadvantages:
– Counterparty risk: Since transactions are bilateral, there is a risk of default by the counterparty, especially in volatile market conditions.
– Lack of transparency: The absence of a central platform makes it difficult to track market prices and liquidity in real-time.
Electronic Trading Platforms
Electronic trading platforms, also known as foreign exchange (FX) exchanges, provide a centralized marketplace where participants can trade currencies electronically. These platforms offer several advantages:
– Transparency: Market prices and liquidity are displayed in real-time, ensuring transparency and reducing information asymmetry.
– Efficiency: Automated order matching and execution systems enable faster and more efficient trading.
– Reduced counterparty risk: Platforms act as intermediaries, reducing the risk of default by individual counterparties.
However, electronic trading platforms also have some drawbacks:
– Limited customization: Transactions are typically standardized, offering less flexibility compared to OTC trading.
– Access restrictions: Access to certain platforms may be restricted to specific types of participants, such as banks or large institutions.
– Technical issues: Platform outages or technical glitches can disrupt trading activities.
In practice, both OTC trading and electronic trading platforms coexist in the BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market. Participants choose the trading mechanism that best suits their specific needs, considering factors such as flexibility, transparency, counterparty risk, and efficiency. For example, large banks and institutional investors often engage in OTC trading to customize large-volume transactions, while retail traders may prefer electronic trading platforms for their transparency and ease of use.
Factors Influencing the BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market
The BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market is influenced by a complex interplay of economic, political, and social factors. These factors affect the value of currencies and the behavior of market participants, shaping the overall dynamics of the market.
Economic Factors
- Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates by central banks impact the demand for currencies, as investors seek higher returns.
- Inflation: Rising inflation erodes the value of a currency, making it less desirable in the market.
- Economic Growth: Positive economic growth prospects attract foreign investment and boost currency demand.
- Trade Balances: Countries with large trade surpluses tend to have stronger currencies, while those with deficits may experience currency depreciation.
Political Factors
- Political Stability: Political uncertainty and instability can lead to currency volatility and reduced market confidence.
- Government Policies: Fiscal and monetary policies can impact currency values, such as exchange rate interventions or capital controls.
- International Relations: Diplomatic tensions or conflicts can affect currency demand and market sentiment.
Social Factors
- Cultural Trends: Cultural events or shifts in consumer preferences can influence demand for certain currencies, such as for tourism or luxury goods.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in payment systems and cross-border transactions can impact currency flows and market liquidity.
- Natural Disasters: Major natural disasters can affect economic activity and currency values, particularly in emerging markets.
Regulation of the BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market
The BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market is subject to a comprehensive regulatory framework designed to maintain market stability, protect investors, and prevent financial crime. This framework involves central banks, financial regulators, and other international organizations.
Central banks play a crucial role in regulating the foreign exchange market by setting monetary policy, managing foreign exchange reserves, and intervening in the market to maintain exchange rate stability. They also issue regulations and guidelines to ensure the orderly functioning of the market.
Role of Central Banks
- Set monetary policy to influence exchange rates
- Manage foreign exchange reserves to stabilize currencies
- Intervene in the market to prevent excessive volatility
- Issue regulations and guidelines for market participants
Financial regulators, such as the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the United Kingdom and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States, oversee the activities of market participants and enforce regulations to prevent fraud, manipulation, and other illegal activities.
Obtain direct knowledge about the efficiency of various participants in the foreign exchange market for successfully executing his task through case studies.
Role of Financial Regulators
- Oversee the activities of market participants
- Enforce regulations to prevent fraud and manipulation
- Investigate and prosecute violations of regulations
International organizations, such as the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF), play a role in promoting cooperation and coordination among central banks and financial regulators worldwide.
Role of International Organizations
- Promote cooperation and coordination among central banks
- Develop and implement international standards and guidelines
- Monitor and assess global financial markets
Regulation has a significant impact on the BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market. It helps to ensure market stability, protect investors, and prevent financial crime. Regulations have also influenced the development of new products and instruments, such as electronic trading platforms, which have made the market more efficient and accessible.
Emerging Trends and Innovations in the BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market
The BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging all the time. Two of the most important trends in recent years have been the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain technology.
Artificial Intelligence, Bis global foreign exchange market
AI is being used in a variety of ways in the FX market, including:
- Fraud detection: AI can be used to identify and flag suspicious transactions, helping to protect market participants from fraud.
- Risk management: AI can be used to help market participants manage their risk by identifying potential risks and developing mitigation strategies.
- Trade execution: AI can be used to automate the execution of trades, helping to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger system that allows for the secure and transparent recording of transactions. It is being used in a variety of ways in the FX market, including:
- Settlement: Blockchain can be used to streamline the settlement of FX trades, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
- Transparency: Blockchain can provide greater transparency into the FX market, helping to reduce risk and improve confidence.
- New products: Blockchain is enabling the development of new FX products, such as tokenized FX swaps.
The use of AI and blockchain technology is still in its early stages, but these technologies have the potential to revolutionize the FX market. They can help to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase transparency. As these technologies continue to develop, we can expect to see even more innovation in the FX market in the years to come.
Final Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of the BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market, it is evident that this dynamic and ever-changing market plays a pivotal role in the global economy. Its participants, products, and trading mechanisms are constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the ever-changing global economic landscape. Understanding the BIS Global Foreign Exchange Market is essential for anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of international finance and stay abreast of the forces that shape our interconnected world.
