Capital flight in foreign exchange market, a complex and multifaceted phenomenon, takes center stage as we delve into its intricate web of economic and political factors. This movement of capital across borders, driven by a myriad of motivations, has profound implications for exchange rates, economic growth, and societal stability. Join us as we unravel the causes, consequences, and policy responses surrounding this enigmatic topic.
From currency controls to exchange rate regimes, we will explore the mechanisms that shape capital flight. We will examine how it impacts exchange rates, investment, employment, and social harmony. Moreover, we will analyze the effectiveness and limitations of various policy options aimed at addressing capital flight, highlighting the delicate balance between mitigating capital flight and achieving other economic objectives.
Causes of Capital Flight in Foreign Exchange Market

Capital flight, the movement of funds from one country to another, can be triggered by various economic and political factors. These factors can create uncertainty and instability, leading investors and businesses to seek safer havens for their capital.
Discover more by delving into foreign exchange market pdf further.
Economic Factors
Economic factors that can contribute to capital flight include:
- Economic instability: A weak or declining economy, characterized by high inflation, low growth, and high unemployment, can lead to a loss of confidence in the country’s currency and economy.
- Currency devaluation: A sharp decline in the value of a country’s currency can prompt investors to move their funds to countries with more stable currencies.
- High interest rates in other countries: If interest rates are higher in other countries, investors may be tempted to move their funds to earn higher returns.
Political Factors
Political factors that can contribute to capital flight include:
- Political instability: Political unrest, wars, or revolutions can create uncertainty and fear, leading to capital flight.
- Government policies: Government policies that are seen as unfavorable to businesses, such as high taxes, restrictive regulations, or expropriation of assets, can drive capital out of the country.
- Currency controls: Currency controls, such as restrictions on foreign exchange transactions, can make it difficult for investors to move their funds out of the country, leading to capital flight.
Role of Currency Controls and Exchange Rate Regimes
Currency controls and exchange rate regimes can play a role in capital flight:
- Currency controls: Strict currency controls can make it difficult for investors to move their funds out of the country, leading to capital flight through informal channels, such as the black market.
- Fixed exchange rates: Fixed exchange rates can create overvaluation or undervaluation of the currency, making it more or less attractive to investors, leading to capital flight.
Consequences of Capital Flight in Foreign Exchange Market
Capital flight, the sudden outflow of large sums of money from a country, can have severe consequences for the foreign exchange market and the economy as a whole.
Remember to click role of participants in foreign exchange market to understand more comprehensive aspects of the role of participants in foreign exchange market topic.
Impact on Exchange Rates and Currency Stability
Capital flight can lead to a sharp depreciation of the domestic currency, as the increased demand for foreign currencies drives up their value. This depreciation can make it more expensive for the country to import goods and services, leading to higher inflation and a decline in living standards.
Remember to click foreign exchange artinya to understand more comprehensive aspects of the foreign exchange artinya topic.
Impact on Economic Growth, Investment, and Employment
Capital flight can also stifle economic growth by reducing investment and employment opportunities. As capital leaves the country, businesses have less access to funding, which can lead to a slowdown in economic activity. Additionally, the loss of capital can reduce tax revenues, making it difficult for governments to provide essential services.
Social and Political Consequences
Capital flight can have significant social and political consequences as well. The economic instability caused by capital flight can lead to social unrest and political instability. In extreme cases, it can even lead to the collapse of governments.
Measurement and Monitoring of Capital Flight in Foreign Exchange Market
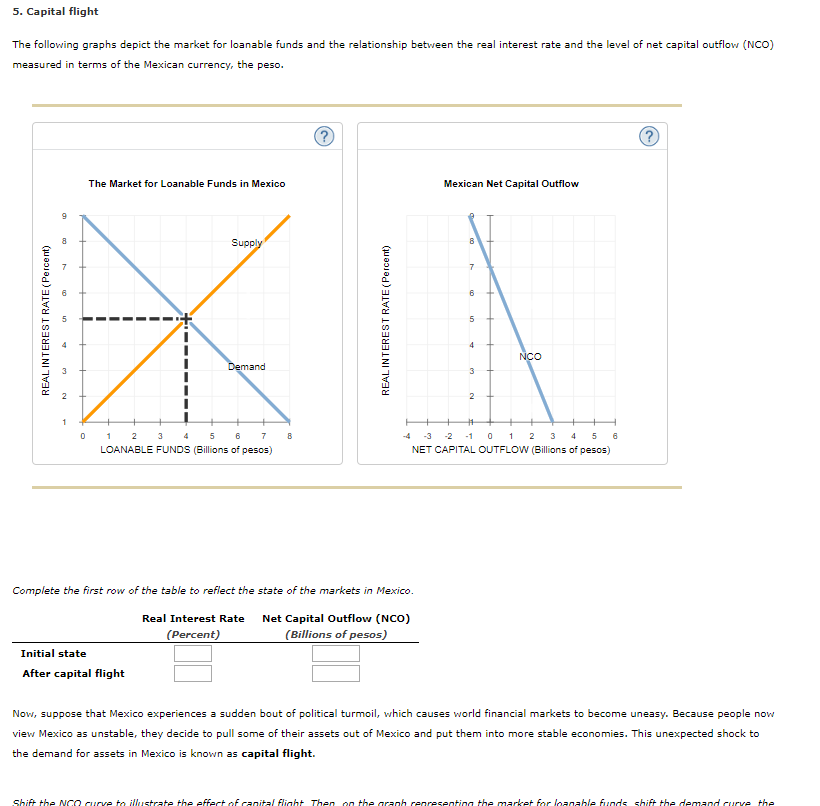
Measuring and monitoring capital flight in the foreign exchange market presents challenges due to its clandestine nature. However, several methods are employed to estimate its magnitude and track its trends.
Methods of Measurement, Capital flight in foreign exchange market
- Balance of Payments Discrepancy: Comparing the recorded balance of payments with actual capital flows can reveal discrepancies attributed to capital flight.
- Residual Approach: Estimating capital flight as the residual in the overall balance of payments equation.
- Sudden Stop Analysis: Identifying sharp declines in capital inflows or increases in capital outflows that may indicate capital flight.
- Currency Demand Analysis: Monitoring the demand for foreign currency as an indicator of capital flight.
- Asset Price Analysis: Tracking the prices of domestic assets, such as real estate and stocks, which may reflect capital flight if they decline.
Challenges and Limitations
Measuring capital flight accurately is difficult due to:
- Data Availability: Accurate and timely data on capital flows is often limited.
- Illicit Transactions: Capital flight often involves illicit transactions, making it challenging to track.
- Misinvoicing: Trade misinvoicing can be used to disguise capital flight.
- Multiple Exchange Rates: In countries with multiple exchange rates, capital flight can occur through arbitrage.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations, such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank, play a crucial role in monitoring capital flight. They:
- Provide Technical Assistance: Help countries improve their data collection and analysis capabilities.
- Conduct Research: Study the causes and consequences of capital flight.
- Offer Policy Advice: Advise countries on policies to address capital flight.
Policy Responses to Capital Flight in Foreign Exchange Market
Policymakers can implement various measures to address capital flight in the foreign exchange market. These policy options include exchange rate management, capital controls, and macroeconomic policies.
Exchange Rate Management
Exchange rate management involves intervening in the foreign exchange market to influence the value of the domestic currency. By stabilizing or appreciating the currency, policymakers can reduce the incentive for capital outflows. However, this policy option can be costly and ineffective in the long run.
Capital Controls
Capital controls restrict the movement of capital across borders. By imposing limits on capital outflows, policymakers can directly address capital flight. However, capital controls can distort investment decisions and hinder economic growth.
Macroeconomic Policies
Macroeconomic policies aim to address the underlying causes of capital flight, such as high inflation, political instability, or economic uncertainty. By implementing sound fiscal and monetary policies, policymakers can create a stable economic environment that reduces the incentive for capital outflows. However, macroeconomic policies can take time to have an impact and may not be effective in all situations.
The effectiveness of each policy option depends on the specific circumstances of the country experiencing capital flight. Policymakers must carefully consider the trade-offs between addressing capital flight and other economic objectives, such as economic growth, investment, and financial stability.
Case Studies of Capital Flight in Foreign Exchange Market
Capital flight has been a significant issue for many countries, leading to economic instability and currency depreciation. By examining case studies of countries that have experienced capital flight, we can better understand the causes, consequences, and policy responses to this phenomenon.
Case Study: Argentina
In 2001, Argentina experienced a severe financial crisis, characterized by massive capital flight. The causes of the crisis included high inflation, unsustainable government debt, and a lack of confidence in the government’s economic policies. The consequences of capital flight were devastating, leading to a sharp decline in economic growth, a sharp devaluation of the peso, and a banking crisis. The government responded to the crisis by implementing a series of austerity measures, including spending cuts and tax increases. However, these measures were not sufficient to stem the tide of capital flight, and the country eventually defaulted on its foreign debt.
Case Study: Greece
Greece experienced a severe debt crisis in 2010, which led to a large-scale capital flight. The causes of the crisis included high government debt, unsustainable fiscal deficits, and a lack of competitiveness. The consequences of capital flight were severe, leading to a sharp decline in economic growth, a sharp devaluation of the euro, and a banking crisis. The Greek government responded to the crisis by implementing a series of austerity measures, including spending cuts and tax increases. These measures helped to stabilize the economy, but they also led to a sharp increase in unemployment and poverty.
Lessons Learned
The case studies of Argentina and Greece provide valuable lessons about the causes, consequences, and policy responses to capital flight. These lessons include the importance of maintaining fiscal discipline, ensuring the sustainability of government debt, and promoting economic growth. Additionally, it is important to have a credible and consistent economic policy framework in place to maintain investor confidence and prevent capital flight.
Ultimate Conclusion: Capital Flight In Foreign Exchange Market
In the tapestry of international finance, capital flight in foreign exchange market stands as a force that can both build and dismantle economies. Understanding its causes, consequences, and policy responses is crucial for policymakers, economists, and anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of global financial markets. As we conclude our exploration, we leave you with a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of capital flight and its far-reaching effects.
