Foreign exchange controls market definition – Defining foreign exchange controls market, this comprehensive guide delves into the intricate world of currency regulations, exploring their history, types, economic implications, and future trends. Join us as we uncover the complexities of foreign exchange controls and their impact on global markets.
Foreign exchange controls are government-imposed regulations that restrict the conversion of domestic currency into foreign currencies and vice versa. Their primary objectives include managing balance of payments, stabilizing exchange rates, and preventing capital flight. Historically, foreign exchange controls have been implemented during periods of economic instability, wars, and financial crises.
Market Overview

Foreign exchange controls refer to regulations and measures implemented by governments or central banks to influence or restrict the flow of foreign currencies into and out of a country. These controls aim to manage the exchange rate, stabilize the financial system, and achieve specific economic or political objectives.
Examine how foreign exchange market risks can boost performance in your area.
The purpose of foreign exchange controls is multifaceted. They can be used to protect a country’s foreign reserves, prevent currency speculation, support domestic industries, and influence the exchange rate to promote exports or discourage imports.
Historical Evolution of Foreign Exchange Controls
Foreign exchange controls have existed for centuries, with early examples dating back to the Middle Ages. However, they became more prevalent during the 20th century, particularly during times of economic crisis or political instability.
In the post-World War II era, many countries adopted foreign exchange controls to manage the reconstruction process and stabilize their economies. These controls often included restrictions on currency convertibility, exchange rate controls, and limits on foreign investment.
Do not overlook explore the latest data about foreign exchange market what.
In recent decades, there has been a gradual trend towards liberalization of foreign exchange controls. This has been driven by globalization, the rise of international trade and investment, and the adoption of floating exchange rate regimes by many countries.
Types of Foreign Exchange Controls: Foreign Exchange Controls Market Definition
Foreign exchange controls are government regulations that restrict the exchange of domestic currency for foreign currencies and vice versa. These controls can take various forms, each with its unique impact on the economy.
Direct Controls
Direct controls involve explicit government restrictions on foreign exchange transactions. These include:
- Exchange Rate Pegging: Fixing the value of the domestic currency to a foreign currency or a basket of currencies.
- Multiple Exchange Rates: Establishing different exchange rates for different types of transactions.
- Foreign Exchange Quotas: Limiting the amount of foreign exchange that individuals and businesses can purchase or sell.
Countries that have implemented direct controls include China, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela.
Indirect Controls
Indirect controls use monetary or fiscal policies to influence foreign exchange transactions. These include:
- Capital Controls: Restricting the movement of capital into and out of the country.
- Interest Rate Controls: Setting interest rates to influence the demand for foreign exchange.
li>Reserve Requirements: Requiring banks to hold a certain percentage of their deposits in foreign exchange.
Countries that have implemented indirect controls include the United States, the European Union, and Japan.
Impact of Foreign Exchange Controls
The impact of foreign exchange controls on the economy depends on the type and severity of the controls. Direct controls can distort the foreign exchange market and create inefficiencies. Indirect controls can affect economic growth, investment, and inflation.
In general, foreign exchange controls can have the following effects:
- Stabilize exchange rates and prevent currency crises.
- Protect domestic industries from foreign competition.
- Manage capital flows and prevent capital flight.
- Influence inflation and economic growth.
- Create distortions in the foreign exchange market.
Economic Impact of Foreign Exchange Controls
Foreign exchange controls can have a significant impact on a country’s economy. They can affect economic growth, trade, investment, and the value of a country’s currency.
Impact on Economic Growth
Foreign exchange controls can hinder economic growth by making it more difficult for businesses to import goods and services. This can lead to higher prices for consumers and businesses, which can reduce demand and slow economic growth. Additionally, foreign exchange controls can make it more difficult for businesses to invest in new equipment and technology, which can also slow economic growth.
Impact on Trade and Investment
Foreign exchange controls can also affect trade and investment. They can make it more difficult for businesses to export goods and services, which can lead to a decline in exports and a loss of foreign exchange earnings. Additionally, foreign exchange controls can make it more difficult for foreign investors to invest in a country, which can lead to a decline in investment and economic growth.
Impact on the Value of a Country’s Currency
Foreign exchange controls can also affect the value of a country’s currency. If a country imposes foreign exchange controls, it can lead to a decrease in the demand for the country’s currency, which can cause the currency to depreciate. This can make it more expensive for businesses to import goods and services, which can lead to higher prices for consumers and businesses.
Implementation and Enforcement of Foreign Exchange Controls

The implementation and enforcement of foreign exchange controls involve various methods, each with its own advantages and challenges.
Governments typically employ a combination of administrative, legal, and market-based measures to implement and enforce foreign exchange controls.
Administrative Measures
Administrative measures include the establishment of regulatory bodies, such as central banks or foreign exchange commissions, to oversee and enforce foreign exchange regulations.
- These bodies may issue licenses or permits for foreign exchange transactions, set limits on the amount of foreign currency that can be bought or sold, and monitor compliance with regulations.
- Administrative measures can be relatively easy to implement, but they may also be subject to corruption and favoritism.
Legal Measures
Legal measures involve the enactment of laws and regulations that prohibit or restrict certain types of foreign exchange transactions.
Get the entire information you require about foreign exchange market videos on this page.
- These laws may impose penalties for violations, such as fines or imprisonment.
- Legal measures can be effective in deterring illegal foreign exchange transactions, but they can also be difficult to enforce in practice.
Market-Based Measures
Market-based measures use economic incentives to encourage compliance with foreign exchange regulations.
- For example, governments may impose taxes on foreign exchange transactions or adjust the exchange rate to make it more expensive to buy or sell foreign currency.
- Market-based measures can be effective in reducing the demand for foreign currency, but they can also have negative consequences for the economy.
Challenges and Obstacles, Foreign exchange controls market definition
The implementation and enforcement of foreign exchange controls can face several challenges and obstacles, including:
- Black markets: Foreign exchange controls can create black markets where foreign currency is traded illegally.
- Smuggling: Individuals and businesses may attempt to smuggle foreign currency across borders to avoid controls.
- Corruption: Officials may be bribed to allow illegal foreign exchange transactions.
- Lack of resources: Governments may not have the resources to effectively enforce foreign exchange controls.
Case Studies
There have been both successful and unsuccessful implementations of foreign exchange controls.
- Successful implementation: China has successfully used foreign exchange controls to manage its currency and prevent capital flight.
- Unsuccessful implementation: Argentina’s implementation of foreign exchange controls in the early 2000s led to a sharp decline in investment and economic growth.
Emerging Trends in Foreign Exchange Controls
The global landscape of foreign exchange controls is undergoing significant transformations, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing interconnectedness of the world economy.
Impact of Technology
Technological advancements, such as blockchain and artificial intelligence, are revolutionizing the way foreign exchange controls are implemented and enforced. Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and immutable nature, has the potential to enhance the transparency and efficiency of foreign exchange transactions. Artificial intelligence can be used to automate monitoring and compliance processes, reducing the need for manual intervention and increasing the effectiveness of foreign exchange controls.
Impact of Globalization
Globalization has led to increased cross-border trade and investment, making it more challenging for countries to maintain strict foreign exchange controls. The free flow of capital across borders has put pressure on governments to relax or eliminate foreign exchange restrictions to attract foreign investment and promote economic growth.
Future of Foreign Exchange Controls
The future of foreign exchange controls is likely to be characterized by a greater reliance on technology and a shift towards more flexible and targeted measures. Governments will continue to explore innovative ways to implement and enforce foreign exchange controls while balancing the need for macroeconomic stability with the benefits of financial liberalization.
Wrap-Up
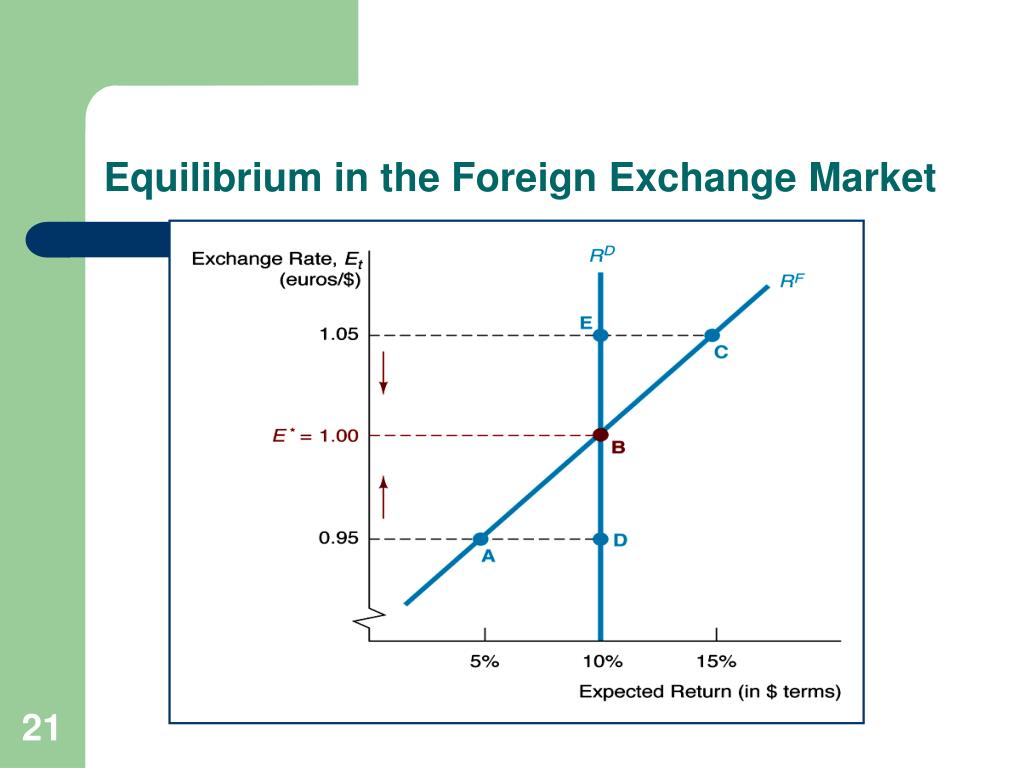
In conclusion, foreign exchange controls market definition remains a complex and evolving field, influenced by economic conditions, technological advancements, and globalization. As we navigate the ever-changing landscape of international finance, understanding the intricacies of foreign exchange controls becomes paramount for businesses, investors, and policymakers alike.
