At the heart of global finance, the foreign exchange market and balance of payment are intricately intertwined, influencing international trade, economic growth, and the value of currencies. This exploration delves into their multifaceted relationship, shedding light on the dynamics that shape our financial landscape.
The foreign exchange market, a global marketplace for currencies, facilitates the exchange of goods and services across borders. It enables businesses to conduct international transactions, manage risk, and hedge against currency fluctuations. The balance of payment, on the other hand, records the financial transactions between a country and the rest of the world, providing insights into its economic health and external position.
Definition of Foreign Exchange Market: Foreign Exchange Market And Balance Of Payment
The foreign exchange market (Forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized market for the trading of currencies. It is the largest financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume exceeding $5 trillion.
Participants in the foreign exchange market include banks, corporations, governments, and individual traders. Banks act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers of currencies, while corporations use the foreign exchange market to facilitate international trade and investment. Governments use the foreign exchange market to manage their currencies and influence their economies. Individual traders participate in the foreign exchange market for speculation and profit.
Functions of the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market plays a crucial role in facilitating international trade and managing financial risks. It serves as a global marketplace where currencies are bought, sold, and exchanged, enabling businesses and individuals to conduct transactions across borders.
Facilitating International Trade
The foreign exchange market provides a platform for businesses to convert their domestic currency into foreign currency when importing or exporting goods and services. This allows them to settle payments with their foreign counterparts and eliminates the need for direct barter arrangements.
Discover how role of rbi in foreign exchange market ppt has transformed methods in RELATED FIELD.
Risk Management
The foreign exchange market also enables businesses to manage foreign exchange risk. Companies operating internationally face the risk of currency fluctuations, which can impact their profits and financial stability. By using the foreign exchange market, they can hedge against currency risks through forward contracts, options, and other financial instruments.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Rates
Foreign exchange rates are influenced by a myriad of economic and political factors that can cause currency values to fluctuate significantly. These factors include:
Economic Factors
- Interest rates: Higher interest rates in a country make its currency more attractive to investors, leading to an appreciation in its value.
- Inflation: High inflation can erode the value of a currency, making it less desirable to hold and leading to its depreciation.
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth prospects can boost demand for a country’s currency, resulting in its appreciation.
- Trade balance: A trade deficit, where imports exceed exports, can put downward pressure on a currency’s value.
Political Factors
- Political stability: Political instability and uncertainty can lead to investors fleeing a country’s currency, causing its value to depreciate.
- Government policies: Government policies, such as exchange rate controls or fiscal stimulus, can influence the demand and supply of a currency.
- International relations: Diplomatic tensions or conflicts can affect investor sentiment towards a country’s currency.
Balance of Payments
The balance of payments (BOP) is a summary of a country’s economic transactions with the rest of the world over a certain period, typically a year. It records all international financial transactions involving goods, services, and financial assets between residents of a country and residents of other countries.
The BOP is divided into two main accounts: the current account and the capital and financial account. The current account records the value of goods and services exported and imported, as well as net income from abroad and net unilateral transfers. The capital and financial account records the net change in a country’s external assets and liabilities.
Components of the Balance of Payments
- Current Account: Includes trade in goods and services, net income from abroad, and net unilateral transfers.
- Capital and Financial Account: Records the net change in a country’s external assets and liabilities.
Relationship between Foreign Exchange Market and Balance of Payments
The foreign exchange market and the balance of payments are two closely intertwined aspects of international finance. The foreign exchange market facilitates the exchange of currencies between countries, while the balance of payments records the flow of money into and out of a country.
You also can understand valuable knowledge by exploring foreign exchange market presentation.
How the Foreign Exchange Market Affects the Balance of Payments
The foreign exchange market plays a crucial role in determining the balance of payments. When a country’s currency appreciates (increases in value), it becomes more expensive for foreigners to buy goods and services from that country. This leads to a decrease in exports and an increase in imports, resulting in a deficit in the balance of payments.
Conversely, when a country’s currency depreciates (decreases in value), it becomes cheaper for foreigners to buy goods and services from that country. This leads to an increase in exports and a decrease in imports, resulting in a surplus in the balance of payments.
How Imbalances in the Balance of Payments Can Impact Foreign Exchange Rates
Imbalances in the balance of payments can put pressure on foreign exchange rates. A persistent deficit in the balance of payments can lead to a depreciation of the currency, while a persistent surplus can lead to an appreciation of the currency.
For example, if a country consistently imports more goods and services than it exports, it will have a deficit in its balance of payments. This can lead to a decrease in demand for the country’s currency, causing it to depreciate. A depreciated currency makes imports more expensive and exports cheaper, helping to correct the imbalance.
Conversely, if a country consistently exports more goods and services than it imports, it will have a surplus in its balance of payments. This can lead to an increase in demand for the country’s currency, causing it to appreciate. An appreciated currency makes imports cheaper and exports more expensive, helping to correct the imbalance.
Further details about functions of foreign exchange market pdf notes is accessible to provide you additional insights.
Role of Central Banks in the Foreign Exchange Market

Central banks play a critical role in managing foreign exchange reserves and intervening in the foreign exchange market to influence exchange rates and maintain financial stability.
Managing Foreign Exchange Reserves
Central banks hold foreign exchange reserves to facilitate international trade, support the value of their domestic currency, and intervene in the foreign exchange market. These reserves consist of various currencies, gold, and other assets. Central banks can accumulate reserves through foreign exchange interventions, trade surpluses, or other means.
Intervention in the Foreign Exchange Market
Central banks intervene in the foreign exchange market by buying or selling foreign currencies to influence exchange rates. They may intervene to:
– Stabilize the value of their domestic currency against other currencies
– Manage inflation or deflation
– Influence economic growth and employment
– Support the stability of the financial system
Central banks can use various intervention techniques, such as:
– Direct intervention: Buying or selling currencies directly in the market
– Indirect intervention: Using monetary policy tools (e.g., interest rates) to influence exchange rates
– Verbal intervention: Issuing statements or making announcements to influence market sentiment
Impact of Foreign Exchange Market on Economic Growth
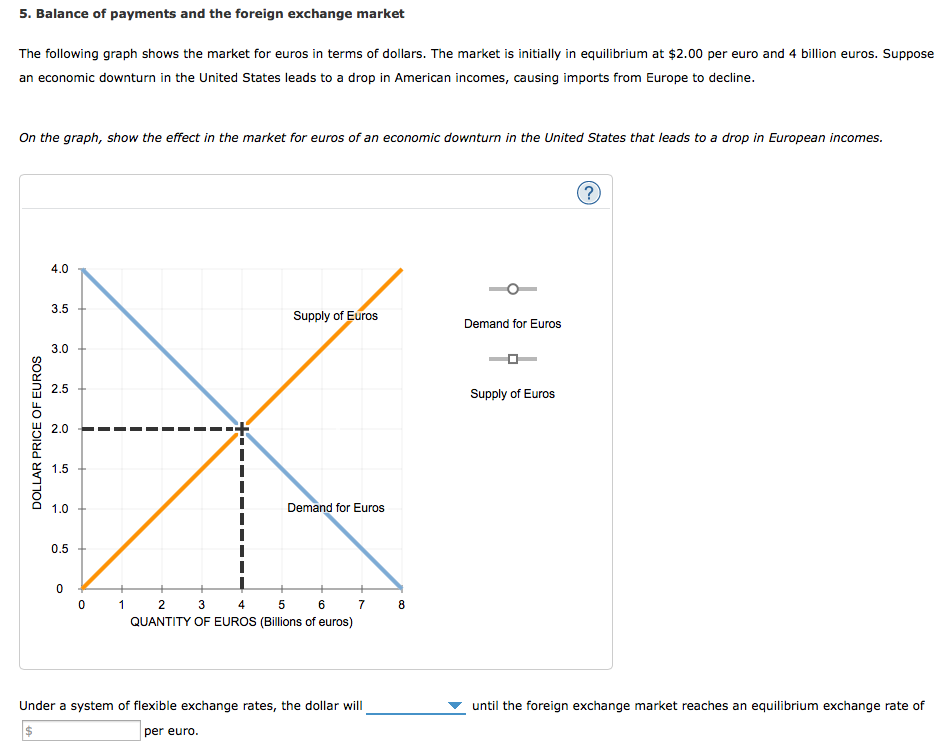
The foreign exchange market, where currencies are traded, plays a pivotal role in shaping the economic growth of nations. Its fluctuations can have both positive and negative impacts, affecting various aspects of the economy.
Positive Impacts
- Export competitiveness: When a country’s currency depreciates against other currencies, its exports become cheaper in the global market, boosting demand and export earnings.
- Tourism: A weaker currency makes a country more attractive to foreign tourists, as their spending power increases, leading to increased tourism revenue.
- Foreign direct investment: A stable and predictable foreign exchange market attracts foreign investors seeking opportunities in emerging markets, bringing in capital and creating jobs.
Negative Impacts, Foreign exchange market and balance of payment
- Inflation: Currency depreciation can lead to higher import prices, contributing to inflation and reducing the purchasing power of consumers.
- Debt burden: Countries with significant foreign currency-denominated debt may face increased debt servicing costs if their currency depreciates.
- Economic uncertainty: Excessive volatility in the foreign exchange market can create uncertainty and discourage investment, hindering economic growth.
Examples
Economic Growth: China’s rapid economic growth in the past decades has been partly attributed to its managed currency devaluation, which boosted exports and attracted foreign investment.
Economic Challenges: Turkey’s economic crisis in 2018 was partly caused by a sharp depreciation of the Turkish lira, leading to high inflation and a decline in foreign investment.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Foreign Exchange Market

The foreign exchange market presents both challenges and opportunities for businesses and individuals.
Challenges
- Exchange rate volatility: Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact the value of investments, exports, and imports, creating uncertainty for businesses and individuals.
- Transaction costs: Converting currencies involves fees and spreads, which can add to the overall cost of foreign exchange transactions.
- Regulatory complexities: Different countries have varying regulations governing foreign exchange transactions, which can be challenging to navigate for businesses and individuals.
- Political and economic risks: Political instability or economic downturns in foreign countries can affect exchange rates and impact businesses and individuals with exposure to those countries.
Opportunities
- Investment diversification: Investing in foreign markets through the foreign exchange market can provide diversification benefits and reduce portfolio risk.
- Hedging risks: Businesses and individuals can use foreign exchange derivatives to hedge against exchange rate risks, protecting their financial positions.
- Trading opportunities: Traders can capitalize on exchange rate fluctuations by buying and selling currencies for profit.
- Access to global markets: The foreign exchange market facilitates global trade and investment, allowing businesses and individuals to access markets beyond their home countries.
Ending Remarks
The interplay between the foreign exchange market and balance of payment is a complex and ever-evolving dance. Understanding their relationship is crucial for businesses, investors, and policymakers alike. By navigating the intricacies of currency exchange and international trade, we can harness the opportunities and mitigate the risks associated with this dynamic financial ecosystem.
