Foreign exchange market definition in business, also known as forex, is a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It’s the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $6 trillion. Forex plays a vital role in international trade and investment, facilitating the exchange of currencies for businesses, individuals, and governments.
The foreign exchange market operates 24 hours a day, 5 days a week, across the globe. It involves a wide range of participants, including commercial banks, investment banks, hedge funds, and retail traders. These participants contribute to the liquidity and stability of the market by buying and selling currencies.
Foreign Exchange Market Definition
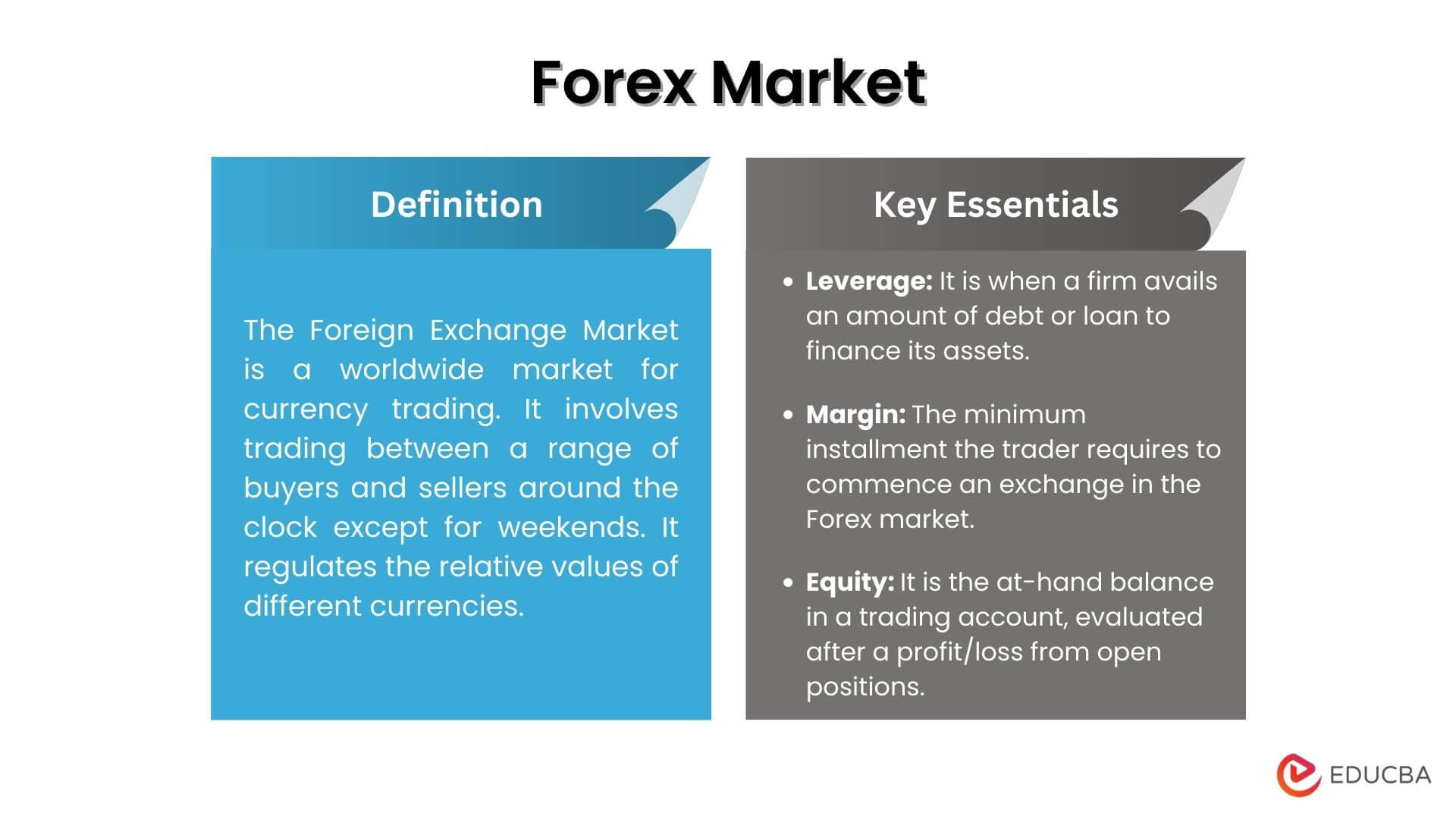
The foreign exchange market (forex market or FX market) is a global decentralized marketplace for trading currencies. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
The forex market is open 24 hours a day, five days a week, and it allows participants to buy, sell, and exchange currencies from all over the world. The market is made up of a network of banks, brokers, and other financial institutions that facilitate the trading of currencies.
Role of Central Banks and Other Financial Institutions
Central banks play a significant role in the forex market by setting monetary policy and managing the supply of money in their respective countries. They also intervene in the forex market to influence the value of their currencies.
Other financial institutions, such as banks, brokers, and investment funds, also play a significant role in the forex market. They provide liquidity to the market and facilitate the trading of currencies for their clients.
You also will receive the benefits of visiting foreign exchange market daily turnover today.
Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is a global, decentralized market where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion. The major participants in the foreign exchange market include commercial banks, investment banks, hedge funds, and retail traders.
Commercial banks are the largest participants in the foreign exchange market. They provide foreign exchange services to their customers, such as businesses and individuals. Commercial banks also trade foreign currencies for their own account, in order to manage their risk and to profit from changes in currency prices.
Investment banks are another major participant in the foreign exchange market. They provide foreign exchange services to their clients, such as institutional investors and hedge funds. Investment banks also trade foreign currencies for their own account, in order to manage their risk and to profit from changes in currency prices.
Hedge funds are actively managed pooled investment funds that use a wide range of strategies to generate capital gains for investors. Hedge funds are major participants in the foreign exchange market, and they often use sophisticated trading strategies to profit from changes in currency prices.
Retail traders are individuals who trade foreign currencies for their own account. Retail traders can trade foreign currencies through online platforms or through brokers.
These participants contribute to the liquidity and stability of the foreign exchange market by providing a continuous supply of buyers and sellers of foreign currencies. The liquidity of the foreign exchange market makes it possible for businesses and individuals to exchange currencies quickly and easily, and the stability of the foreign exchange market helps to ensure that businesses and individuals can rely on the value of their currencies.
Commercial Banks
Commercial banks are the largest participants in the foreign exchange market. They provide foreign exchange services to their customers, such as businesses and individuals. Commercial banks also trade foreign currencies for their own account, in order to manage their risk and to profit from changes in currency prices.
Commercial banks play a vital role in the foreign exchange market by providing liquidity and stability. They are able to provide liquidity because they have access to large pools of capital. They are able to provide stability because they are able to hedge their risk by trading in both the spot and forward markets.
Investment Banks
Investment banks are another major participant in the foreign exchange market. They provide foreign exchange services to their clients, such as institutional investors and hedge funds. Investment banks also trade foreign currencies for their own account, in order to manage their risk and to profit from changes in currency prices.
Investment banks play a vital role in the foreign exchange market by providing liquidity and stability. They are able to provide liquidity because they have access to large pools of capital. They are able to provide stability because they are able to hedge their risk by trading in both the spot and forward markets.
Hedge Funds
Hedge funds are actively managed pooled investment funds that use a wide range of strategies to generate capital gains for investors. Hedge funds are major participants in the foreign exchange market, and they often use sophisticated trading strategies to profit from changes in currency prices.
Hedge funds play a vital role in the foreign exchange market by providing liquidity and stability. They are able to provide liquidity because they have access to large pools of capital. They are able to provide stability because they are able to hedge their risk by trading in both the spot and forward markets.
Retail Traders
Retail traders are individuals who trade foreign currencies for their own account. Retail traders can trade foreign currencies through online platforms or through brokers.
Retail traders play a vital role in the foreign exchange market by providing liquidity. They are able to provide liquidity because they are willing to trade small amounts of foreign currencies.
Factors Influencing Foreign Exchange Rates

Foreign exchange rates are constantly fluctuating, influenced by a complex interplay of economic and political factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses and individuals involved in international trade or investment.
Economic Factors
- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates make a currency more attractive to foreign investors, leading to an appreciation in its value. For example, when the US Federal Reserve raises interest rates, the US dollar tends to strengthen against other currencies.
- Inflation: High inflation erodes the purchasing power of a currency, making it less valuable. Persistent inflation can lead to currency depreciation, as investors seek more stable currencies.
- Economic Growth: A strong and growing economy attracts foreign investment, boosting demand for its currency and leading to appreciation. For example, the Chinese yuan has appreciated significantly over the past decade due to China’s rapid economic growth.
Political Factors
- Political Stability: Currency values are influenced by the perceived political stability of a country. Uncertainty and political unrest can lead to currency depreciation, as investors seek safer havens.
- Government Policies: Government policies, such as fiscal and monetary policies, can impact foreign exchange rates. For example, expansionary fiscal policies can lead to currency depreciation by increasing government borrowing and inflation.
- International Relations: Diplomatic tensions and trade disputes can affect currency values. For instance, the US-China trade war has contributed to fluctuations in the exchange rate between the US dollar and the Chinese yuan.
Supply and Demand
Ultimately, foreign exchange rates are determined by the forces of supply and demand. When there is a high demand for a currency (e.g., due to increased foreign investment), its value will rise. Conversely, when there is a low demand for a currency, its value will fall.
Get the entire information you require about foreign exchange student on this page.
Types of Foreign Exchange Transactions
Foreign exchange transactions involve the exchange of currencies between parties in different countries. These transactions can take various forms, each with its own purpose and mechanics.
Spot Transactions
Spot transactions are the most common type of foreign exchange transaction. They involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the current market rate. These transactions are typically used for small amounts of currency and are settled within two business days.
For descriptions on additional topics like foreign exchange market the bauer college of business is houston’s, please visit the available foreign exchange market the bauer college of business is houston’s.
For example, a U.S. importer may need to purchase euros to pay for goods imported from France. The importer would enter into a spot transaction with a bank or currency broker to exchange U.S. dollars for euros at the current exchange rate.
Forward Transactions, Foreign exchange market definition in business
Forward transactions are agreements to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date. These transactions are used to hedge against currency fluctuations and lock in a favorable exchange rate. Forward transactions are typically used for larger amounts of currency and are settled on a specific future date.
For example, a U.S. exporter may be expecting to receive payment in euros in six months. To protect against the risk of the euro depreciating against the U.S. dollar, the exporter may enter into a forward contract to sell euros at a fixed rate in six months.
Swap Transactions
Swap transactions are agreements to exchange currencies and then exchange them back at a later date. These transactions are used to hedge against currency fluctuations and can also be used for speculation. Swap transactions are typically used for large amounts of currency and are settled on two different future dates.
For example, a U.S. investor may want to invest in a euro-denominated bond but does not want to bear the risk of the euro depreciating against the U.S. dollar. The investor may enter into a currency swap with a bank to exchange U.S. dollars for euros and then exchange them back at a later date.
Risks and Rewards of Foreign Exchange Trading: Foreign Exchange Market Definition In Business
Foreign exchange trading, also known as forex trading, involves buying and selling currencies to capitalize on exchange rate fluctuations. While it offers the potential for significant returns, it also comes with inherent risks that traders must carefully consider.
Exchange Rate Volatility
One of the primary risks in forex trading is exchange rate volatility. Currency values are constantly fluctuating due to various factors such as economic data, political events, and market sentiment. These fluctuations can lead to substantial losses if traders do not manage their risk effectively.
Strategies for Managing Risk
To mitigate the risks associated with forex trading, traders can employ various strategies:
– Stop-loss orders: These orders automatically close a position when the market price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses.
– Hedging: Traders can reduce risk by using hedging strategies, which involve entering into offsetting positions in different currencies to reduce exposure to unfavorable market movements.
– Diversification: Diversifying a portfolio by trading multiple currency pairs can help spread risk and reduce the impact of losses in any one pair.
Maximizing Returns
While managing risk is crucial, traders also aim to maximize returns in forex trading. Strategies for enhancing returns include:
– Technical analysis: Studying historical price charts and patterns can help traders identify potential trading opportunities.
– Fundamental analysis: Analyzing economic data, news, and political events can provide insights into currency movements and help traders make informed decisions.
– Leverage: Using leverage can amplify potential returns, but it also increases the risk of losses. Traders should use leverage judiciously and within their risk tolerance.
Closing Summary
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Exchange-Rate-1b1df02db6a14eee998e1b76d5c9b82d.jpg)
In summary, the foreign exchange market is a complex and dynamic global marketplace where currencies are traded. It’s influenced by a multitude of economic and political factors, and it plays a crucial role in facilitating international trade and investment. Understanding the foreign exchange market definition in business is essential for businesses and individuals who engage in cross-border transactions or investments.
