Forward exchange contract adalah a financial instrument that allows businesses and individuals to manage the risk associated with currency fluctuations. It is a binding agreement between two parties to exchange a specific amount of currency at a predetermined exchange rate on a future date. Forward exchange contracts play a vital role in international trade and investment, enabling businesses to protect their profits and mitigate potential losses due to exchange rate volatility.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of forward exchange contracts, exploring their key features, benefits, risks, and practical applications. We will also examine the regulatory considerations and technological advancements that have shaped the forward exchange contract market. By the end of this guide, you will have a thorough understanding of how forward exchange contracts can be used to effectively manage foreign exchange risk and enhance your global business operations.
Definition of Forward Exchange Contract

A forward exchange contract is an agreement between two parties to exchange currencies at a predetermined exchange rate on a future date. It is a binding contract that obligates both parties to fulfill the terms of the agreement.
Forward exchange contracts are used by businesses and individuals to manage the risk of currency fluctuations. They allow parties to lock in an exchange rate today for a transaction that will take place in the future. This can help to protect against unexpected changes in the exchange rate, which can impact the cost of goods or services purchased or sold internationally.
Purpose of Forward Exchange Contracts
Forward exchange contracts serve several important purposes, including:
- Hedging against currency risk: Forward exchange contracts allow businesses to hedge against the risk of currency fluctuations. By locking in an exchange rate today, businesses can protect themselves from the potential impact of adverse currency movements in the future.
- Locking in exchange rates: Forward exchange contracts allow businesses to lock in an exchange rate for a future transaction. This can be particularly beneficial when the exchange rate is expected to move in a favorable direction.
- Facilitating international trade: Forward exchange contracts facilitate international trade by providing a mechanism for businesses to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate.
How Forward Exchange Contracts Work
Forward exchange contracts are typically traded over-the-counter (OTC) between two parties. The contract specifies the following details:
- The amount of currency to be exchanged
- The exchange rate
- The settlement date
On the settlement date, the two parties exchange the currencies at the agreed-upon exchange rate. Forward exchange contracts are typically used for transactions that will take place within one year, but they can be used for longer periods.
Examples of Forward Exchange Contracts
Here are some examples of how forward exchange contracts are used in international trade:
- A U.S. company imports goods from China: The U.S. company can use a forward exchange contract to lock in an exchange rate for the Chinese yuan today. This will protect the company from the risk of the yuan appreciating against the U.S. dollar before the goods are delivered.
- A European company exports goods to the United States: The European company can use a forward exchange contract to lock in an exchange rate for the U.S. dollar today. This will protect the company from the risk of the dollar depreciating against the euro before the goods are delivered.
Key Features of Forward Exchange Contract
Forward exchange contracts are financial agreements that allow parties to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date. These contracts offer several key features that make them useful for managing foreign exchange risk.
Role of Buyer and Seller
- Buyer: The party that agrees to buy a specific amount of foreign currency at a fixed rate on a future date.
- Seller: The party that agrees to sell a specific amount of foreign currency at a fixed rate on a future date.
Terms and Conditions
Forward exchange contracts typically include the following terms and conditions:
- Contract Size: The amount of foreign currency to be exchanged.
- Contract Rate: The fixed exchange rate at which the currencies will be exchanged.
- Value Date: The future date on which the currencies will be exchanged.
- Settlement Currency: The currency in which the contract will be settled.
Benefits of Using Forward Exchange Contracts: Forward Exchange Contract Adalah
Forward exchange contracts offer several advantages to businesses and investors, making them a valuable tool for managing foreign exchange risk and enhancing international trade and investment.
Managing Foreign Exchange Risk, Forward exchange contract adalah
One of the primary benefits of forward exchange contracts is their ability to mitigate foreign exchange risk. By locking in an exchange rate in advance, businesses can protect themselves against adverse currency fluctuations that could erode their profits or increase their costs. This certainty allows businesses to plan and budget more effectively, reducing uncertainty and improving financial stability.
Get the entire information you require about foreign exchange market in currency on this page.
Enhancing International Trade and Investment
Forward exchange contracts also play a crucial role in facilitating international trade and investment. They enable businesses to enter into cross-border transactions with confidence, knowing that they have secured a favorable exchange rate for their future payments or receipts. This reduces the risk associated with currency fluctuations and encourages businesses to expand their operations globally. Additionally, forward exchange contracts provide a mechanism for investors to hedge against currency risk when investing in foreign markets, making international investments more attractive and accessible.
Risks Associated with Forward Exchange Contracts
Forward exchange contracts are not without risks. Understanding the potential risks associated with these contracts is crucial for businesses and individuals engaging in international transactions.
The primary risk associated with forward exchange contracts is the potential for currency fluctuations. If the exchange rate moves against the contracted rate, one party may face losses.
Find out further about the benefits of foreign exchange market why is it important that can provide significant benefits.
Currency Fluctuations and Contract Impact
Currency fluctuations can significantly impact the value of a forward exchange contract. If the exchange rate moves in favor of the party buying the foreign currency, they will benefit from the contract. However, if the exchange rate moves against them, they will incur losses.
For example, if a company enters into a forward contract to buy euros at a rate of 1 euro = 1.10 USD, and the actual exchange rate on the settlement date is 1 euro = 1.05 USD, the company will incur a loss.
Potential Losses and Mitigation Strategies
The potential losses from forward exchange contracts can be substantial, especially for large transactions. To mitigate these risks, businesses can employ various strategies:
- Hedging: Using other financial instruments, such as options or swaps, to offset potential losses from currency fluctuations.
- Diversification: Engaging in transactions with multiple currencies to reduce the impact of fluctuations in any single currency.
- Close Monitoring: Regularly monitoring currency market trends and adjusting strategies as needed.
Practical Applications of Forward Exchange Contracts
Forward exchange contracts play a crucial role in the global financial markets, enabling businesses and individuals to manage currency risk and facilitate international trade. Let’s explore some real-world applications:
Businesses Managing Currency Risk
Businesses engaged in international trade often face currency fluctuations that can impact their profitability. Forward exchange contracts allow them to lock in an exchange rate today for a future transaction, mitigating the risk of adverse currency movements.
Discover the crucial elements that make foreign exchange rate market meaning the top choice.
For instance, an American importer expecting to purchase goods from Europe in six months can enter into a forward contract to exchange dollars for euros at a predetermined rate. This ensures that the importer knows the exact cost of the goods, regardless of any changes in the euro-dollar exchange rate during the six-month period.
Forward Exchange Contracts in International Trade
Forward exchange contracts facilitate international trade by reducing the uncertainty associated with currency fluctuations. Exporters and importers can use forward contracts to secure a favorable exchange rate for their transactions, protecting themselves from potential losses due to adverse currency movements.
For example, a Japanese exporter selling goods to the United States can use a forward contract to sell the expected dollar proceeds at a fixed rate. This ensures that the exporter receives a predictable amount of yen, regardless of any fluctuations in the dollar-yen exchange rate.
Alternative Risk Management Strategies
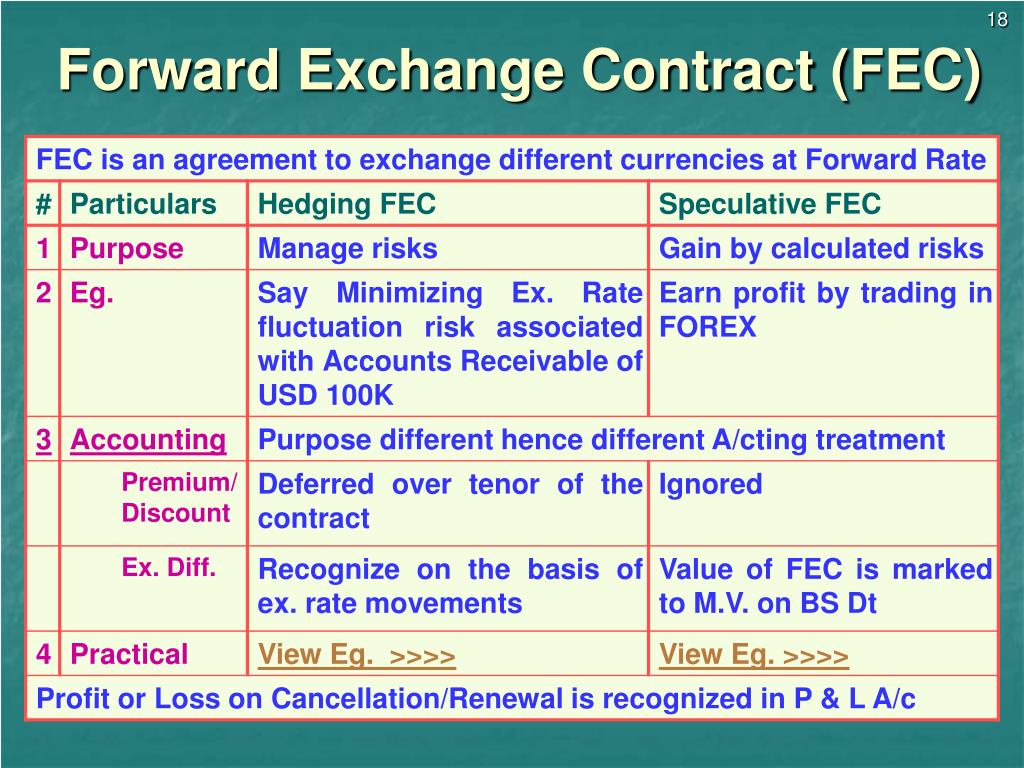
Forward exchange contracts are one of several risk management strategies available to businesses. Other strategies include:
- Hedging: Hedging involves using financial instruments to offset the risk of price fluctuations. This can be done through options, futures contracts, or swaps.
- Diversification: Diversification involves spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, or geographic regions to reduce overall risk.
- Natural hedging: Natural hedging occurs when a company’s revenues and expenses are denominated in different currencies, which can offset the impact of exchange rate fluctuations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Strategies
Each risk management strategy has its own advantages and disadvantages:
| Strategy | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Forward exchange contracts | – Lock in exchange rate – Reduce risk of currency fluctuations | – May not be available for all currencies – Can be expensive |
| Hedging | – Can be customized to specific risk – Can be used to offset risk of other investments | – Can be complex and expensive – May not be effective in all market conditions |
| Diversification | – Reduces overall risk – Can be implemented relatively easily | – May not be effective in all market conditions – Can reduce potential returns |
| Natural hedging | – Free and automatic – No need for additional transactions | – May not be available for all companies – May not fully offset exchange rate risk |
When to Use Forward Exchange Contracts
Forward exchange contracts are most appropriate when a company has a specific and predictable need for a foreign currency at a future date. They can be used to:
- Lock in a favorable exchange rate for a future transaction.
- Reduce the risk of exchange rate fluctuations on a specific transaction.
- Manage the overall currency exposure of a business.
Regulatory Considerations for Forward Exchange Contracts
Forward exchange contracts are subject to various regulatory considerations imposed by central banks and other regulatory bodies to ensure market stability and protect participants.
Central banks play a crucial role in regulating forward exchange contracts by setting guidelines and policies that govern their issuance, trading, and settlement. They may also intervene in the market to stabilize exchange rates or prevent excessive speculation.
Role of Central Banks and Other Regulatory Bodies
- Set guidelines for the issuance and trading of forward exchange contracts.
- Monitor and supervise the market to prevent excessive speculation and market manipulation.
- Intervene in the market to stabilize exchange rates or address imbalances.
Examples of Regulations
- Margin requirements: Regulators may impose margin requirements on forward exchange contracts to mitigate risk and prevent excessive leverage.
- Settlement procedures: Regulations may specify the settlement procedures for forward exchange contracts, including the timing and method of delivery.
- Reporting requirements: Regulators may require participants in the forward exchange market to report their positions and transactions to facilitate oversight and market surveillance.
Technological Advancements in Forward Exchange Contracts
The advent of technology has revolutionized the forward exchange contracts market. Electronic trading platforms have made it easier for participants to access the market and execute trades. Blockchain technology has also emerged as a potential game-changer in the industry.
Electronic Trading Platforms
Electronic trading platforms have transformed the forward exchange contracts market by providing a centralized marketplace where participants can trade anonymously and efficiently. These platforms offer a range of features, including real-time pricing, order matching, and risk management tools. They have also reduced transaction costs and increased market liquidity.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger system that has the potential to further revolutionize the forward exchange contracts market. Blockchain can be used to create secure and transparent records of transactions, which can reduce the risk of fraud and settlement disputes. It can also be used to automate the execution of forward exchange contracts, which can save time and costs.
Case Studies of Forward Exchange Contract Usage

Forward exchange contracts have been widely used by businesses to manage currency risk and enhance their financial performance. Here are some notable case studies that demonstrate the successful implementation of forward exchange contracts:
Case Study 1: Multinational Manufacturing Company
A multinational manufacturing company with operations in multiple countries faced significant currency fluctuations that threatened its profitability. To mitigate this risk, the company entered into forward exchange contracts to lock in exchange rates for future payments and receipts in foreign currencies. This strategy allowed the company to protect its margins and ensure stable cash flows, despite currency volatility.
Case Study 2: Import-Export Business
An import-export business regularly purchased goods from overseas suppliers. To avoid losses due to adverse exchange rate movements, the business used forward exchange contracts to secure favorable exchange rates for future payments. By doing so, the business could minimize the impact of currency fluctuations on its profitability and maintain competitive pricing.
Case Study 3: Tourism Operator
A tourism operator catering to international travelers faced challenges in managing currency risk associated with fluctuating exchange rates. To address this issue, the operator used forward exchange contracts to lock in exchange rates for future bookings and minimize the impact of currency volatility on its revenue. This strategy helped the operator maintain stable pricing and avoid potential losses due to unfavorable exchange rates.
Lessons Learned
These case studies highlight the following lessons learned regarding the use of forward exchange contracts:
- Forward exchange contracts can effectively mitigate currency risk and protect profitability.
- Businesses should carefully assess their currency exposure and determine the appropriate hedging strategies.
- Proper execution and monitoring of forward exchange contracts are crucial for successful risk management.
- Forward exchange contracts can provide peace of mind and allow businesses to focus on their core operations without being overly concerned about currency fluctuations.
Future Trends in Forward Exchange Contracts
The forward exchange contract market is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and shifting economic conditions. Several key trends are expected to shape the future of forward exchange contracts, impacting businesses and investors alike.
One emerging trend is the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in forward exchange contract trading. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make predictions, helping businesses and investors make more informed decisions.
Integration with Blockchain Technology
Another trend is the integration of forward exchange contracts with blockchain technology. Blockchain can provide a secure and transparent platform for executing and settling forward exchange contracts, reducing counterparty risk and increasing efficiency.
Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes are also expected to impact the forward exchange contract market. Governments worldwide are exploring new regulations to address concerns about market manipulation and systemic risk. These regulations may affect the way forward exchange contracts are traded and settled.
Opportunities and Challenges
These emerging trends present both opportunities and challenges for businesses and investors. The use of AI and ML can enhance decision-making and improve risk management. Blockchain technology can increase security and efficiency. However, regulatory changes may introduce new complexities and costs.
Final Thoughts
Forward exchange contracts are an indispensable tool for businesses and individuals seeking to mitigate the risks associated with currency fluctuations. By understanding the key features, benefits, and risks of forward exchange contracts, you can harness their power to protect your financial interests and make informed decisions in the global marketplace. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, forward exchange contracts will continue to play a pivotal role in facilitating international trade and investment.
