The foreign exchange market converts the currency of one country into that of another country – The foreign exchange market, where the currency of one country is converted into that of another, plays a pivotal role in international trade and investment. It’s a dynamic arena where different currencies are traded, and exchange rates fluctuate based on various factors.
This global marketplace connects banks, financial institutions, and individual traders, each with their unique roles and responsibilities. Their activities influence the market’s behavior, creating opportunities and risks for participants.
The Basics of Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market (forex market) is a global decentralized market where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $5 trillion. The forex market is used by businesses, governments, and individuals to exchange currencies for a variety of purposes, including international trade, investment, and speculation.
The forex market is open 24 hours a day, 5 days a week, and currencies are traded in pairs. For example, the EUR/USD currency pair represents the exchange rate between the euro and the US dollar. The first currency in the pair (EUR) is the base currency, and the second currency (USD) is the quote currency. The exchange rate between the two currencies is the number of quote currency units that are required to buy one unit of the base currency.
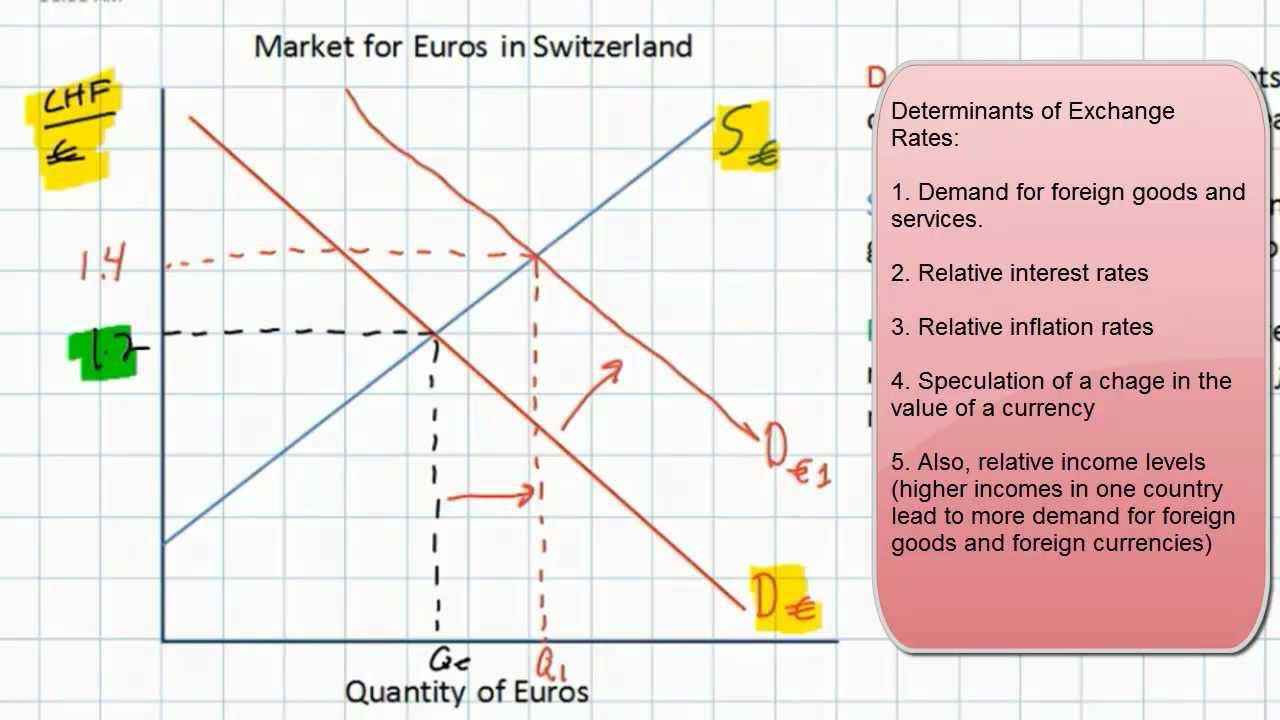
The forex market is influenced by a variety of factors, including economic conditions, political events, and central bank policies. These factors can cause currency exchange rates to fluctuate, which can have a significant impact on businesses and individuals who trade in foreign currencies.
Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is a vast and complex ecosystem involving a diverse range of participants. Each player has its unique role and responsibilities, contributing to the overall dynamics and liquidity of the market.
Discover more by delving into describe the meaning of foreign exchange market further.
Banks and Financial Institutions
- Banks and financial institutions are the cornerstone of the forex market, facilitating the majority of transactions.
- They act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, providing liquidity and pricing information.
- Major banks, such as Citigroup, JP Morgan Chase, and HSBC, are the primary market makers, setting the bid-ask spreads and providing quotes to other participants.
- Financial institutions, including hedge funds, investment banks, and asset managers, use the forex market to manage risk, speculate on currency movements, and facilitate international trade.
Central Banks
- Central banks play a crucial role in the forex market by implementing monetary policies that influence currency values.
- They intervene in the market to stabilize exchange rates, manage inflation, and support economic growth.
- The actions of central banks, such as interest rate adjustments and quantitative easing, can have significant impacts on currency movements and market sentiment.
Corporations
- Corporations participate in the forex market to facilitate international trade and manage currency risk.
- They buy and sell currencies to pay for imports, receive payments for exports, and hedge against potential losses due to currency fluctuations.
- Multinational corporations with operations in multiple countries have a significant presence in the forex market.
Individual Traders
- Individual traders, also known as retail traders, participate in the forex market to speculate on currency movements and potentially profit from exchange rate fluctuations.
- They typically trade through online platforms and use various strategies, such as technical analysis and fundamental analysis, to make trading decisions.
- While individual traders account for a smaller share of the forex market compared to institutional participants, they can contribute to market volatility and liquidity.
Forex Market Trading

The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market, is a global marketplace where currencies are traded. Forex market trading involves the buying and selling of currencies, with the aim of profiting from fluctuations in their exchange rates.
Discover how what are foreign exchange market example has transformed methods in RELATED FIELD.
There are three main types of forex market trading:
Spot Trading
Spot trading is the most common type of forex market trading. It involves the immediate buying and selling of currencies at the current market price. Spot trades are typically settled within two business days.
Forward Trading
Forward trading involves the buying and selling of currencies at a predetermined price, for delivery at a future date. Forward contracts are used to hedge against currency risk, or to speculate on future currency movements.
Options Trading, The foreign exchange market converts the currency of one country into that of another country
Options trading involves the buying and selling of options contracts. An options contract gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a certain amount of currency at a specified price on or before a certain date. Options trading can be used to speculate on future currency movements, or to hedge against currency risk.
Forex market trading can be a profitable venture, but it also carries significant risks. It is important to understand the different types of forex market trading, and the risks and rewards associated with each, before entering the market.
You also will receive the benefits of visiting foreign exchange market components today.
The Impact of the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange (forex) market has a profound impact on international trade and investment, as well as on businesses and economies worldwide. Exchange rate fluctuations can significantly affect the profitability of businesses engaged in cross-border transactions, influence investment decisions, and impact the overall economic growth of countries.
Impact on International Trade and Investment
- Exports and Imports: Exchange rate fluctuations can affect the competitiveness of exports and imports. A weaker currency makes exports cheaper and imports more expensive, potentially boosting exports and curbing imports.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Exchange rate movements can influence the flow of FDI. A stronger currency can make it more attractive for foreign investors to invest in a country, while a weaker currency can discourage FDI.
Impact on Businesses
- Revenue and Expenses: Businesses with international operations are exposed to exchange rate risk. Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact their revenue and expenses, as well as their overall profitability.
- Hedging Strategies: Businesses often use hedging strategies to mitigate exchange rate risk. These strategies involve using financial instruments, such as forward contracts or currency options, to lock in future exchange rates.
Role of Central Banks
Central banks play a crucial role in managing exchange rates. They use various monetary policy tools, such as interest rate adjustments and foreign exchange interventions, to influence the value of their currencies. By doing so, central banks aim to stabilize exchange rates, reduce volatility, and support economic growth.
The Future of the Foreign Exchange Market

The foreign exchange market is constantly evolving, and several potential developments and trends could shape its future. Technology is one of the most important factors driving change in the forex market. The development of new trading platforms and tools has made it easier for individuals and businesses to trade currencies. Globalization is another factor that is expected to continue to impact the forex market. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the demand for foreign currencies is likely to grow.
Impact of Technology
Technology has already had a significant impact on the foreign exchange market. The development of electronic trading platforms has made it possible for traders to execute orders quickly and efficiently. In addition, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is becoming increasingly common in the forex market. These technologies can be used to analyze market data and identify trading opportunities.
Impact of Globalization
Globalization is another factor that is expected to continue to impact the forex market. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the demand for foreign currencies is likely to grow. This is because businesses and individuals need to exchange currencies to conduct international trade and investment.
Challenges and Opportunities
The future of the foreign exchange market is likely to be shaped by a number of challenges and opportunities. One challenge is the increasing volatility of the market. This volatility can make it difficult for traders to make profits. Another challenge is the rise of protectionism. If countries begin to impose tariffs and other trade barriers, this could reduce the demand for foreign currencies.
Despite these challenges, there are also a number of opportunities for the forex market in the years to come. One opportunity is the growth of the global economy. As the global economy grows, the demand for foreign currencies is likely to increase. Another opportunity is the development of new technologies. These technologies could make it easier for traders to access the market and execute orders.
Final Thoughts: The Foreign Exchange Market Converts The Currency Of One Country Into That Of Another Country
The future of the foreign exchange market holds exciting possibilities and challenges. Technological advancements and globalization continue to shape its landscape. Central banks remain influential in managing exchange rates, while new developments, such as cryptocurrencies, may impact the market’s dynamics. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the foreign exchange market will continue to play a vital role in facilitating global trade and investment.
