Embarking on an exploration of who are the brokers of the foreign exchange market class 12, we delve into the dynamic world of currency exchange, where brokers play a pivotal role. This comprehensive guide unravels the significance of these market intermediaries, their diverse functions, and the regulatory landscape that governs their operations.
The foreign exchange market, a vast and ever-evolving arena, serves as a global marketplace for trading currencies. Within this intricate ecosystem, brokers emerge as essential facilitators, bridging the gap between buyers and sellers, ensuring seamless currency exchange transactions.
Introduction
The foreign exchange market, often known as Forex or FX, is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $5 trillion. It facilitates the exchange of currencies between countries, enabling international trade, investment, and tourism.
The market participants include central banks, commercial banks, investment banks, hedge funds, retail traders, and corporations. Central banks play a significant role in managing exchange rates and ensuring financial stability, while commercial banks facilitate currency exchange for businesses and individuals. Investment banks provide liquidity and execute trades for institutional clients, and hedge funds engage in speculative trading to generate profits. Retail traders, including individuals and small businesses, participate in the market to speculate on currency movements or hedge against currency risk. Corporations use the FX market to manage their international operations and minimize foreign exchange risk.
Brokers in the Foreign Exchange Market

Brokers play a crucial role in the foreign exchange market, acting as intermediaries between buyers and sellers of currencies. They provide a platform for traders to execute their orders and facilitate the smooth functioning of the market.
Browse the multiple elements of meaning of foreign exchange market pdf to gain a more broad understanding.
Types of Brokers
There are different types of brokers operating in the foreign exchange market, each catering to specific needs of traders. These include:
- Retail Brokers: These brokers cater to individual traders and offer a range of services, including trading platforms, market analysis, and customer support.
- Institutional Brokers: These brokers provide services to large financial institutions, such as banks, hedge funds, and asset managers. They offer tailored solutions and specialized services.
- Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs): These brokers use electronic systems to match buy and sell orders, providing anonymity and reducing spreads.
- Interbank Brokers: These brokers facilitate transactions between banks and other large financial institutions, offering deep liquidity and competitive pricing.
Functions of Foreign Exchange Brokers

Foreign exchange brokers play a crucial role in facilitating currency exchange transactions. They act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers of currencies, providing a platform for efficient and transparent execution of trades.
Check what professionals state about foreign exchange market in bangladesh and its benefits for the industry.
The primary functions of foreign exchange brokers include:
- Providing liquidity: Brokers maintain a pool of liquidity by matching buy and sell orders, ensuring that traders can execute their trades quickly and efficiently.
- Pricing: Brokers determine the bid and ask prices for currencies based on market conditions and their own analysis. This allows traders to compare prices and make informed decisions.
- Execution: Brokers execute trades on behalf of their clients, ensuring that orders are filled at the best possible prices and with minimal slippage.
- Clearing and settlement: Brokers handle the clearing and settlement of trades, ensuring that funds are transferred between buyers and sellers securely and efficiently.
- Customer support: Brokers provide customer support to traders, answering queries, providing market analysis, and assisting with trading strategies.
Examples of services offered by foreign exchange brokers include:
- Online trading platforms
- Mobile trading apps
- Research and analysis tools
- Educational resources
- Demo accounts for practice trading
Regulation of Foreign Exchange Brokers: Who Are The Brokers Of The Foreign Exchange Market Class 12
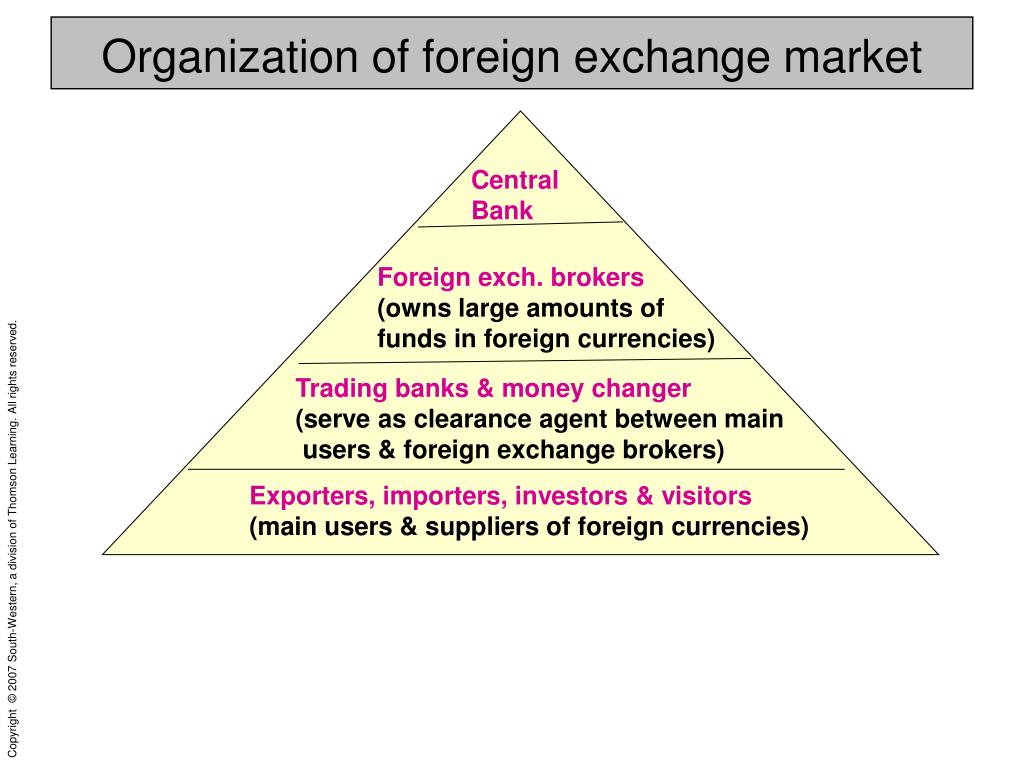
Foreign exchange brokers operate in a highly regulated environment to ensure market integrity and protect investors. Regulatory frameworks vary across jurisdictions, but they generally aim to prevent fraud, manipulation, and conflicts of interest.
Regulation is crucial for maintaining a fair and transparent market. It provides guidelines for brokers’ conduct, disclosure requirements, and risk management practices. It also establishes mechanisms for resolving disputes and enforcing compliance.
Check the largest foreign exchange market in the world is to inspect complete evaluations and testimonials from users.
Regulatory Bodies, Who are the brokers of the foreign exchange market class 12
Various regulatory bodies oversee foreign exchange brokers, including:
- Financial Conduct Authority (FCA): Regulates brokers in the United Kingdom.
- Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC): Regulates brokers in the United States.
- Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC): Regulates brokers in Australia.
- Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA): Regulates brokers in Switzerland.
Selecting a Foreign Exchange Broker
Choosing the right foreign exchange broker is crucial for successful forex trading. Consider the following key factors to make an informed decision:
Due Diligence and Research
Thoroughly research potential brokers to assess their credibility, reliability, and suitability for your trading needs. Verify their regulatory status, financial stability, and track record.
Reputation and Credibility
- Check online reviews and testimonials from reputable sources.
- Inquire about the broker’s history of customer complaints and resolutions.
- Verify the broker’s membership in industry associations and compliance with regulatory standards.
Financial Stability
- Examine the broker’s financial statements to assess their capital adequacy and solvency.
- Inquire about the broker’s risk management policies and insurance coverage.
Trading Conditions
- Compare spreads, commissions, and other trading fees offered by different brokers.
- Consider the available trading platforms and their features, such as execution speed and charting tools.
- Review the broker’s leverage options and margin requirements.
Customer Support
- Evaluate the broker’s customer support channels, including phone, email, and live chat.
- Inquire about the availability of educational resources and technical assistance.
Regulatory Compliance
- Ensure that the broker is regulated by a reputable financial authority, such as the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) or the National Futures Association (NFA).
- Verify the broker’s adherence to industry best practices and ethical guidelines.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, brokers of the foreign exchange market class 12 stand as indispensable figures, orchestrating the intricate dance of currency exchange. Their functions, ranging from order execution to risk management, are vital to the smooth functioning of this global marketplace. As we navigate the complexities of international trade and investment, understanding the role of these brokers becomes paramount.
