Define foreign exchange market with example – Delving into the world of foreign exchange markets, we embark on a journey to define this global financial hub. The foreign exchange market, often abbreviated as forex market, stands as a crucial component of the global economy, facilitating the exchange of currencies between nations, businesses, and individuals. Its significance lies in its role as a catalyst for international trade, investment, and tourism.
At the heart of the forex market lies a diverse cast of participants, each playing a pivotal role in shaping its dynamics. Major banks, financial institutions, multinational corporations, and individual traders converge in this arena, driven by a shared desire to capitalize on currency fluctuations.
Introduction
The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market, is a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion. The forex market plays a crucial role in facilitating international trade and investment, and it is used by a wide range of participants, including banks, corporations, hedge funds, and individual traders.
The primary purpose of the forex market is to facilitate the exchange of currencies between different countries. This is necessary because different countries use different currencies, and in order to conduct international trade or investment, it is necessary to convert one currency into another. The forex market provides a platform for this conversion to take place, and it allows participants to buy and sell currencies at market-determined prices.
Significance of the Forex Market
The forex market is significant for several reasons. First, it provides liquidity to the global financial system. This liquidity allows participants to easily buy and sell currencies, which facilitates international trade and investment. Second, the forex market helps to determine the value of currencies. The prices of currencies are determined by supply and demand, and the forex market provides a platform for supply and demand to interact. Third, the forex market is a source of investment for many participants. Some participants trade currencies in order to make a profit, while others use the forex market to hedge against currency risk.
Key Participants in the Forex Market
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Exchange-Rate-1b1df02db6a14eee998e1b76d5c9b82d.jpg)
The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market, is a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It involves the exchange of one currency for another at an agreed-upon exchange rate. Various participants play crucial roles in the forex market, each with unique motivations and strategies.
The major participants in the forex market include:
Central Banks
Central banks are government institutions responsible for managing a country’s monetary policy and financial system. They participate in the forex market to influence the value of their currency, manage inflation, and maintain economic stability. Central banks buy and sell currencies to intervene in the market and achieve their monetary policy goals.
Enhance your insight with the methods and methods of foreign exchange reserves.
Commercial Banks
Commercial banks are financial institutions that provide a range of banking services to individuals and businesses. They participate in the forex market to facilitate international trade and investment, manage foreign exchange risk for their clients, and generate profits from currency trading.
Investment Banks
Investment banks are financial institutions that provide a range of financial services to corporations and governments. They participate in the forex market to facilitate currency trading for their clients, engage in proprietary trading, and manage risk for their own portfolios.
You also can investigate more thoroughly about foreign exchange market in kannada to enhance your awareness in the field of foreign exchange market in kannada.
Hedge Funds, Define foreign exchange market with example
Hedge funds are investment funds that use advanced trading strategies to generate high returns for their investors. They participate in the forex market to speculate on currency movements and profit from currency fluctuations.
Retail Traders
Retail traders are individuals who trade currencies on a smaller scale. They participate in the forex market to speculate on currency movements and potentially profit from them.
Other Participants
Other participants in the forex market include corporations, governments, and institutional investors. Corporations may trade currencies to manage foreign exchange risk associated with their international operations. Governments may intervene in the forex market to influence the value of their currency for economic or political reasons. Institutional investors, such as pension funds and insurance companies, may invest in the forex market as part of their asset allocation strategies.
Forex Market Dynamics
The foreign exchange market is a highly dynamic environment, where currency exchange rates are constantly fluctuating. Several factors influence these fluctuations, including economic conditions, political events, and market sentiment.
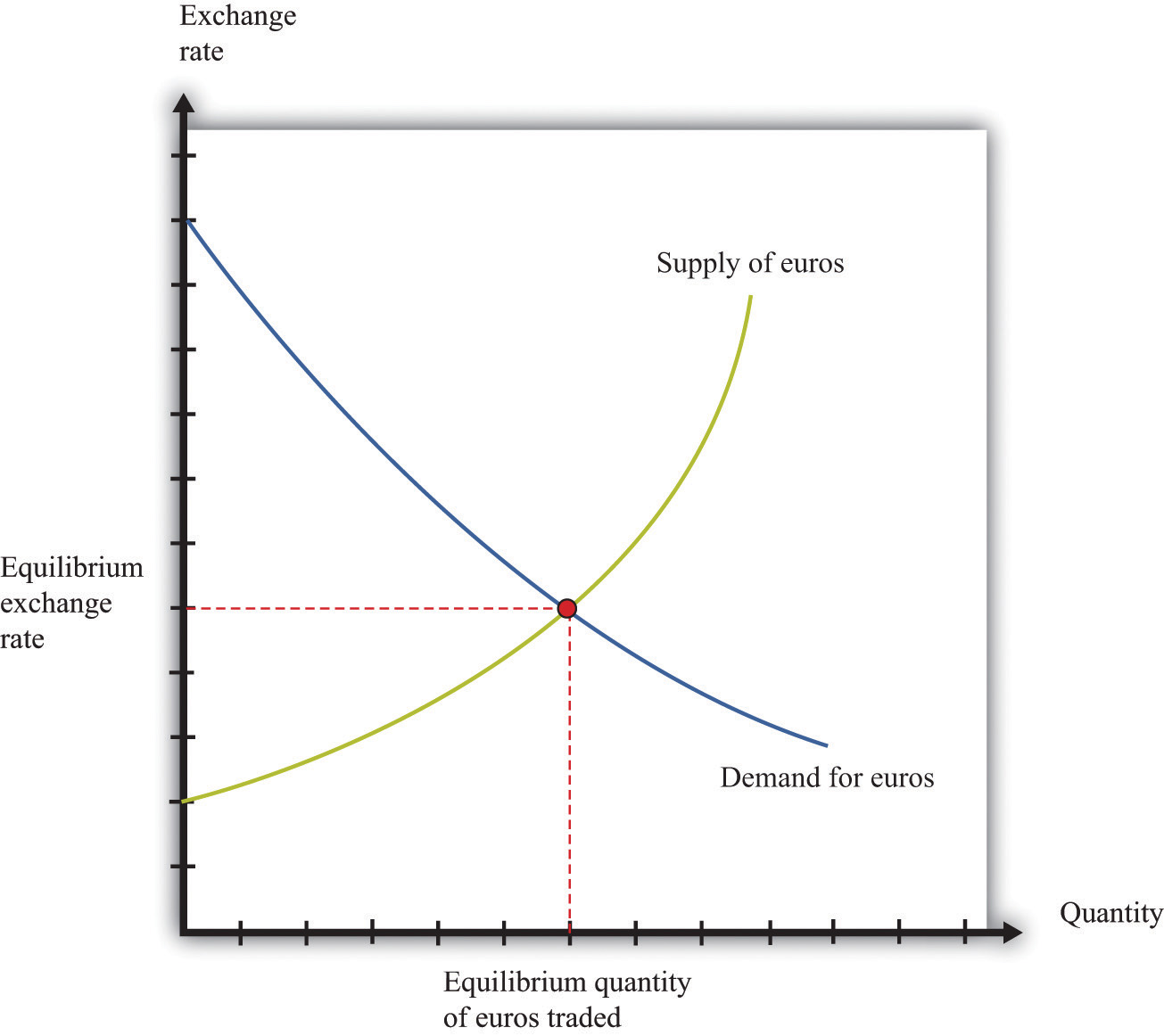
One of the most fundamental factors that affect currency exchange rates is supply and demand. When there is a high demand for a particular currency, its value will tend to increase. Conversely, when there is a low demand for a currency, its value will tend to decrease.
Factors Influencing Currency Exchange Rates
- Economic conditions: The economic health of a country can have a significant impact on the value of its currency. A strong economy with low unemployment and inflation will typically lead to a stronger currency, while a weak economy with high unemployment and inflation will typically lead to a weaker currency.
- Political events: Political events can also have a significant impact on currency exchange rates. For example, a change in government or a major political crisis can lead to a sharp decline in the value of a currency.
- Market sentiment: The market sentiment towards a particular currency can also affect its value. If investors are optimistic about a currency, they will be more likely to buy it, which will drive up its value. Conversely, if investors are pessimistic about a currency, they will be more likely to sell it, which will drive down its value.
How Supply and Demand Affect Currency Values
The supply and demand for a currency is determined by a number of factors, including:
- The interest rate differential between two countries: If one country has a higher interest rate than another, investors will be more likely to buy the currency of the country with the higher interest rate, which will drive up its value.
- The inflation rate differential between two countries: If one country has a higher inflation rate than another, investors will be more likely to sell the currency of the country with the higher inflation rate, which will drive down its value.
- The trade balance between two countries: If one country has a trade deficit with another country, it will need to buy more of the other country’s currency to pay for its imports, which will drive up the value of the other country’s currency.
Forex Market Structure
The forex market is a decentralized market, meaning there is no central exchange where all trades take place. Instead, trades are executed through a network of banks, brokers, and other financial institutions. This decentralized structure has a number of advantages and disadvantages.
One advantage of the decentralized structure of the forex market is that it makes it very difficult for any single entity to manipulate the market. This is because there is no central authority that can set prices or control the flow of orders. As a result, the forex market is one of the most transparent and efficient markets in the world.
However, the decentralized structure of the forex market also has some disadvantages. One disadvantage is that it can be difficult for new traders to enter the market. This is because there is no central exchange where traders can go to find liquidity. As a result, new traders may have to pay higher spreads and commissions than they would if they were trading on a centralized exchange.
Types of Forex Market Structures
There are two main types of forex market structures: the interbank market and the retail market.
The interbank market is the market where banks and other financial institutions trade with each other. This is the largest and most liquid part of the forex market, and it is where the majority of forex trades are executed.
The retail market is the market where individual traders trade with each other. This is a much smaller and less liquid market than the interbank market, and it is where most retail forex traders execute their trades.
Each of these market structures has its own advantages and disadvantages. The interbank market is more liquid and has lower spreads, but it is also more difficult for new traders to enter. The retail market is less liquid and has higher spreads, but it is easier for new traders to enter.
Forex Market Instruments
The forex market involves trading various financial instruments, each with its characteristics, risks, and rewards.
Currency Pairs
Currency pairs are the most traded instruments in the forex market. They represent the exchange rate between two currencies, such as EUR/USD (Euro versus US Dollar). Traders speculate on the price movements of currency pairs, aiming to profit from fluctuations in their relative values. The risks involved in currency pair trading include exchange rate volatility and geopolitical events.
Spot Forex
Spot forex refers to the immediate exchange of currency pairs at the current market rate. Traders buy and sell currencies simultaneously, with the settlement typically occurring within two business days. Spot forex trading is highly liquid and offers opportunities for short-term profit but also carries the risk of rapid price fluctuations.
Forward Contracts
Forward contracts are agreements to exchange currencies at a specified rate on a future date. They allow traders to lock in exchange rates for future transactions, mitigating the risk of unfavorable price movements. However, forward contracts are less flexible than spot forex and may involve fees or penalties for early termination.
Currency Options
Currency options give traders the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency pair at a specific price on a specified date. Traders use options to hedge against currency risk or speculate on price movements. The risks involved in currency options include the premium paid for the option and the potential for the option to expire worthless.
Currency Futures
Currency futures are standardized contracts that obligate traders to buy or sell a specific amount of currency at a set price on a future date. Futures contracts provide greater leverage than spot forex but also carry higher risks due to their binding nature.
Forex Market Trading Strategies: Define Foreign Exchange Market With Example
The forex market offers a diverse range of trading strategies to suit different risk appetites and investment objectives. Each strategy comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages, which traders must carefully consider before making any investment decisions.
When investigating detailed guidance, check out the foreign exchange market basics now.
Trend Trading
Trend trading involves identifying and trading in the direction of an established market trend. Traders using this strategy aim to capitalize on the momentum of a trend, buying assets when prices are rising and selling when prices are falling.
- Pros: Relatively straightforward to implement; can yield significant profits if the trend continues.
- Cons: Can lead to losses if the trend reverses; requires patience and discipline to stay in the trade.
Range Trading
Range trading focuses on identifying and trading within a specific price range. Traders using this strategy buy when prices reach the lower end of the range and sell when prices reach the upper end.
- Pros: Lower risk than trend trading; can provide consistent profits over time.
- Cons: Can be less profitable than trend trading; requires constant monitoring of price movements.
Carry Trading
Carry trading involves borrowing a currency with a low interest rate and investing it in a currency with a higher interest rate. The difference between the two interest rates, known as the carry, represents the potential profit for the trader.
- Pros: Can generate a steady stream of income; can benefit from favorable currency exchange rates.
- Cons: High risk if the currency with the higher interest rate depreciates; requires a large amount of capital.
Scalping
Scalping is a short-term trading strategy that involves taking small profits from frequent, small price movements. Traders using this strategy aim to make multiple trades throughout the day, each with a small profit target.
- Pros: Can be very profitable; requires minimal capital.
- Cons: High stress and requires constant attention; can be difficult to consistently make profits.
News Trading
News trading involves trading on the release of economic data or other news events that can impact currency prices. Traders using this strategy aim to anticipate the market’s reaction to the news and position themselves accordingly.
- Pros: Can generate large profits if the trade is timed correctly; can be exciting and fast-paced.
- Cons: High risk; requires a deep understanding of market dynamics and the ability to make quick decisions.
Forex Market Risks

Forex trading involves various risks that traders must be aware of and manage effectively. These risks include:
- Currency risk: Fluctuations in exchange rates can lead to losses if the trader’s predictions are incorrect.
- Leverage risk: Using leverage to increase trading positions can amplify both profits and losses.
- Liquidity risk: Some currency pairs may have low liquidity, making it difficult to enter or exit trades quickly.
- Political and economic risk: Political and economic events can impact currency values, potentially causing losses.
- Counterparty risk: The risk of a counterparty failing to fulfill its obligations in a trade.
Mitigating Forex Market Risks
To mitigate these risks, traders can employ various strategies:
- Proper risk management: Setting stop-loss orders, limiting leverage, and diversifying trades.
- Thorough research: Analyzing currency trends, economic indicators, and political events to make informed decisions.
- Choosing liquid currency pairs: Trading currency pairs with high liquidity reduces the risk of slippage and execution delays.
- Hedging strategies: Using financial instruments to offset the risk of currency fluctuations.
- Working with reputable brokers: Choosing brokers with strong financial standing and reliable trading platforms.
By understanding and managing these risks, traders can increase their chances of success in the forex market.
Examples of Foreign Exchange Market Transactions
The foreign exchange market facilitates various transactions involving the exchange of currencies. These transactions serve different purposes, including international trade, tourism, and investment.
Here are a few real-world examples of forex market transactions:
Importing Goods and Services
- When a company in the United States imports goods from China, it needs to purchase Chinese yuan (CNY) to pay the Chinese exporter. This transaction involves converting US dollars (USD) into CNY.
- Similarly, if a tourist from Japan visits Europe, they need to exchange Japanese yen (JPY) into euros (EUR) to cover their expenses during their trip.
International Investment
- A multinational corporation may need to convert its profits earned in one country into another currency to reinvest in a different country.
- A portfolio manager may purchase foreign bonds or stocks as part of a diversification strategy, requiring them to exchange their domestic currency into the currency of the foreign investment.
Hedging Against Currency Risk
- Companies with international operations may use forex transactions to hedge against currency fluctuations. For example, a US-based company with operations in Europe may purchase euro futures contracts to protect itself against potential losses due to a decline in the value of the euro.
- Importers and exporters can use forward contracts to lock in an exchange rate for future transactions, mitigating the risk of unfavorable currency movements.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, the foreign exchange market emerges as a complex and ever-evolving ecosystem, where currencies dance to the rhythm of global economic forces. Its participants, instruments, and strategies intertwine to create a vibrant and dynamic marketplace that shapes the financial landscape worldwide.
