Demand and supply of foreign exchange market is a fascinating subject that plays a pivotal role in international trade and investment. This intricate dance between demand and supply determines the equilibrium exchange rate, influencing global economic activities and shaping the financial landscape. Embark on this journey as we delve into the factors that drive demand and supply in the foreign exchange market, exploring its impact on businesses and individuals alike.
Economic conditions, interest rates, and political stability exert a significant influence on the demand for foreign currencies. Trade flows, foreign investment, and central bank intervention, on the other hand, shape the supply side of the equation. Understanding these determinants is crucial for navigating the complexities of the foreign exchange market.
Determinants of Foreign Exchange Demand
The demand for foreign currencies is influenced by a multitude of factors, ranging from economic conditions to political stability. Understanding these determinants is crucial for businesses, investors, and policymakers who engage in international transactions.
Economic Conditions
Economic growth, inflation, and unemployment rates play a significant role in determining the demand for foreign currencies. Strong economic growth in a country typically leads to an increase in demand for its currency as foreign investors seek opportunities in the expanding market.
Inflation, on the other hand, can erode the value of a currency, making it less desirable for foreign investors. Similarly, high unemployment rates can indicate economic weakness, reducing the attractiveness of a country’s currency.
Discover how foreign exchange market meaning and concept has transformed methods in RELATED FIELD.
Interest Rates
Interest rates are another key factor influencing foreign exchange demand. Higher interest rates in a country make its currency more attractive to foreign investors, as they can earn higher returns on their investments.
This increased demand for the currency leads to its appreciation against other currencies. Conversely, lower interest rates can make a currency less desirable, leading to depreciation.
Political Stability
Political stability and uncertainty can also impact foreign exchange demand. Investors tend to favor currencies from countries with stable political environments and strong institutions.
Political instability, such as civil unrest or government changes, can create uncertainty and make investors hesitant to invest in a country’s currency. This can lead to a decrease in demand for the currency and its depreciation.
Determinants of Foreign Exchange Supply
The supply of foreign currencies in the foreign exchange market is influenced by a range of factors, including trade flows, foreign investment, and central bank intervention. Understanding these determinants is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of the foreign exchange market.
Trade Flows
Trade flows play a significant role in determining the supply of foreign currencies. When a country exports goods and services to another country, it receives foreign currency in exchange. This increases the supply of foreign currency in the domestic market.
Conversely, when a country imports goods and services, it pays for them using its own currency. This reduces the supply of domestic currency in the foreign exchange market and increases the supply of foreign currency.
Foreign Investment
Foreign investment also affects the supply of foreign currencies. When foreign investors purchase assets in a country, they bring foreign currency into the country. This increases the supply of foreign currency in the domestic market.
Similarly, when domestic investors purchase assets abroad, they send domestic currency out of the country. This reduces the supply of domestic currency in the foreign exchange market and increases the supply of foreign currency.
Central Bank Intervention
Central banks can intervene in the foreign exchange market to influence the supply of foreign currencies. For example, if a central bank wants to increase the supply of domestic currency, it can sell foreign currencies from its reserves. This action increases the supply of domestic currency in the market and reduces the supply of foreign currency.
Conversely, if a central bank wants to reduce the supply of domestic currency, it can buy foreign currencies from the market. This action reduces the supply of domestic currency in the market and increases the supply of foreign currency.
Equilibrium in the Foreign Exchange Market

Equilibrium in the foreign exchange market occurs when the quantity of a currency demanded equals the quantity supplied at a particular exchange rate. At this point, there is no excess demand or supply, and the market is said to be in balance.
The Equilibrium Exchange Rate
The equilibrium exchange rate is the price of one currency in terms of another currency at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. It is determined by the interaction of demand and supply forces in the foreign exchange market.
Floating Exchange Rate System
In a floating exchange rate system, the exchange rate is determined by the forces of demand and supply in the foreign exchange market. The central bank does not intervene to fix the exchange rate at a particular level.
In a floating exchange rate system, the equilibrium exchange rate will adjust to changes in demand and supply. For example, if demand for a currency increases, the equilibrium exchange rate will appreciate. Conversely, if supply for a currency increases, the equilibrium exchange rate will depreciate.
Learn about more about the process of foreign exchange market define in the field.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Market Equilibrium
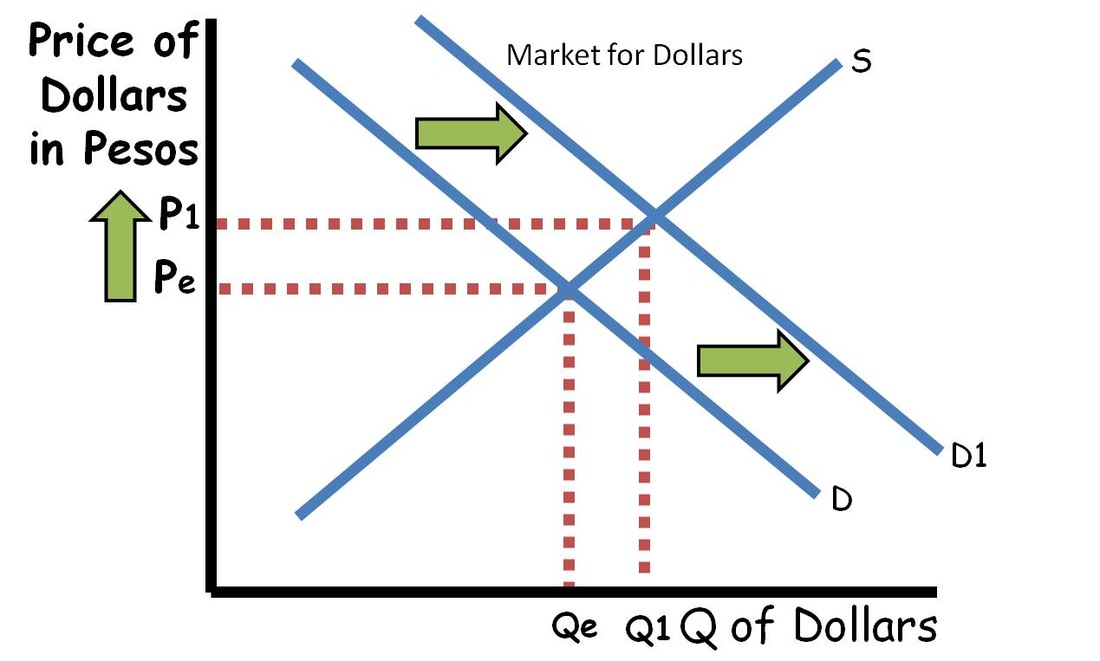
The equilibrium in the foreign exchange market is constantly being influenced by various factors. Speculation, market sentiment, macroeconomic policies, and other external factors play a crucial role in determining the exchange rates and the stability of the market.
Role of Speculation and Market Sentiment, Demand and supply of foreign exchange market
Speculation and market sentiment can significantly impact exchange rates. When market participants anticipate a future change in the value of a currency, they may buy or sell it in large volumes, creating temporary imbalances in supply and demand. This speculative activity can lead to sharp fluctuations in exchange rates, often overshooting the underlying fundamentals.
Market sentiment also plays a role. If investors are optimistic about a particular currency, they may be more likely to buy it, driving up its value. Conversely, negative sentiment can lead to a sell-off, depreciating the currency’s value.
Impact of Macroeconomic Policies
Macroeconomic policies implemented by governments can also affect foreign exchange market equilibrium. Monetary policies, such as changes in interest rates, can influence the attractiveness of a currency for investment. Higher interest rates can make a currency more attractive to foreign investors, leading to an appreciation in its value.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of foreign exchange market how does it work.
Fiscal policies, such as government spending and taxation, can also impact exchange rates. Expansionary fiscal policies that increase government spending or reduce taxes can lead to higher inflation and a depreciation of the currency. Conversely, contractionary fiscal policies can have the opposite effect.
Examples of Market Instability
The combined effects of speculation, market sentiment, and macroeconomic policies can sometimes lead to instability in the foreign exchange market. For instance, the 2008 financial crisis led to a sharp depreciation of the US dollar against other major currencies due to a combination of factors, including speculation, loss of confidence in the US economy, and expansionary monetary policies by the Federal Reserve.
Similarly, the recent COVID-19 pandemic has caused significant volatility in currency markets, as investors have sought safe havens and reacted to the economic uncertainty caused by the crisis.
Market Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is a vast and complex ecosystem, with a diverse range of participants who play varying roles in determining demand and supply. Understanding the behavior and motivations of these participants is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of the market.
Banks
Banks are the primary intermediaries in the foreign exchange market, facilitating the majority of transactions. They act as market makers, providing liquidity and setting bid-ask spreads for currencies. Banks also engage in proprietary trading, taking positions in the market to capitalize on exchange rate fluctuations.
Corporations
Corporations are major participants in the foreign exchange market due to their global operations. They require foreign currencies to pay for imports, make investments, and conduct international business. Corporations’ demand for foreign currencies can be substantial and can significantly influence exchange rates.
Individual Investors
Individual investors, including retail traders and hedge funds, participate in the foreign exchange market for various reasons. Some seek to profit from short-term exchange rate fluctuations through speculative trading, while others use foreign exchange as a hedge against currency risk in their investment portfolios.
Importance of the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is a crucial component of the global financial system, facilitating international trade and investment. It allows businesses and individuals to exchange currencies and engage in cross-border transactions.
Role in Facilitating International Trade
The foreign exchange market enables the exchange of currencies, allowing businesses to purchase goods and services from other countries and receive payment in their home currency. This exchange facilitates international trade and promotes economic growth.
Providing Liquidity and Reducing Risk
The foreign exchange market provides liquidity, ensuring there is sufficient supply and demand for currencies. This liquidity reduces the risk of exchange rate fluctuations and allows businesses to hedge against currency risk by entering into forward contracts.
Benefits to Businesses and Individuals
The foreign exchange market benefits businesses by reducing transaction costs, expanding market reach, and diversifying investments. Individuals can also benefit from the foreign exchange market by exchanging currencies for travel, remittances, or investments.
Closing Summary: Demand And Supply Of Foreign Exchange Market
In the ever-evolving foreign exchange market, speculation and market sentiment can introduce an element of unpredictability. Macroeconomic policies, such as monetary and fiscal policies, also play a role in shaping equilibrium. By recognizing the interplay of these factors, we gain a deeper appreciation for the dynamic nature of the foreign exchange market and its profound impact on the global economy.
