Discuss the demand and supply of foreign exchange market, delving into the intricate factors that drive the dynamics of this global marketplace. From international trade to central bank interventions, we explore the forces that shape the demand and supply of foreign currencies, ultimately determining the equilibrium exchange rate.
This comprehensive analysis unravels the complexities of the foreign exchange market, providing insights into its pivotal role in facilitating global trade and investment. Join us as we navigate the ever-evolving landscape of currency exchange, uncovering the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Demand for Foreign Exchange
Demand for foreign exchange arises from the need to settle international transactions and investments. It is influenced by various factors, including international trade, tourism, and foreign direct investment.
International Trade
International trade is a major driver of demand for foreign exchange. When a country imports goods or services from another country, it needs to pay for those imports in the currency of the exporting country. This creates a demand for the foreign currency.
- Example: If a U.S. company imports goods from China, it will need to purchase Chinese yuan to pay for the imports.
Supply of Foreign Exchange

The supply of foreign exchange refers to the amount of foreign currency that is available for purchase in the foreign exchange market. It is determined by various factors, including the economic conditions of a country, its trade policies, and the actions of central banks.
Factors Affecting the Supply of Foreign Exchange
- Exports: Countries that export goods and services earn foreign currency, which increases the supply of foreign exchange.
- Foreign direct investment (FDI): When foreign investors invest in a country, they bring in foreign currency, increasing the supply.
- Tourism: Tourists visiting a country spend foreign currency, adding to the supply of foreign exchange.
- Remittances: Individuals working abroad send money back to their home countries, which contributes to the supply of foreign exchange.
- Government borrowing: Governments may borrow foreign currency to finance their budgets, increasing the supply of foreign exchange.
Role of Central Banks
Central banks play a crucial role in influencing the supply of foreign exchange. They can:
- Intervene in the foreign exchange market: Central banks can buy or sell foreign currency to stabilize exchange rates or influence the supply of foreign exchange.
- Set interest rates: Interest rate changes can affect the attractiveness of a country’s currency and influence the supply of foreign exchange.
- Manage foreign exchange reserves: Central banks hold foreign exchange reserves to facilitate international transactions and stabilize exchange rates.
Examples of Businesses and Individuals Supplying Foreign Exchange
- Exporters: Companies that sell goods and services abroad earn foreign currency, which they can supply to the foreign exchange market.
- Multinational corporations: MNCs may have operations in multiple countries and need to convert currencies for their business transactions.
- Individuals: Individuals traveling abroad or sending remittances to their home countries supply foreign exchange to the market.
- Financial institutions: Banks and other financial institutions facilitate foreign exchange transactions and act as intermediaries in the foreign exchange market.
Equilibrium in the Foreign Exchange Market: Discuss The Demand And Supply Of Foreign Exchange Market
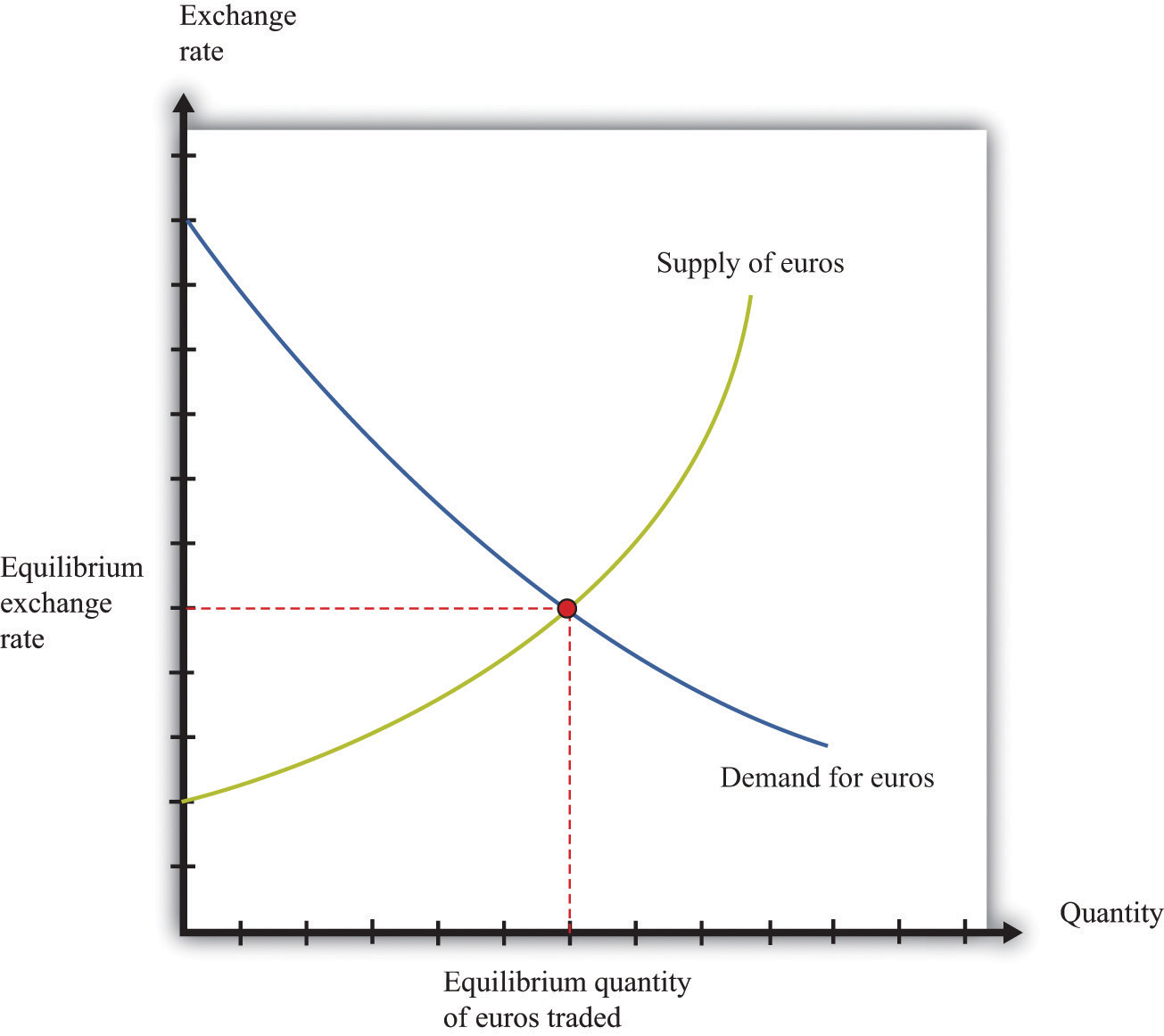
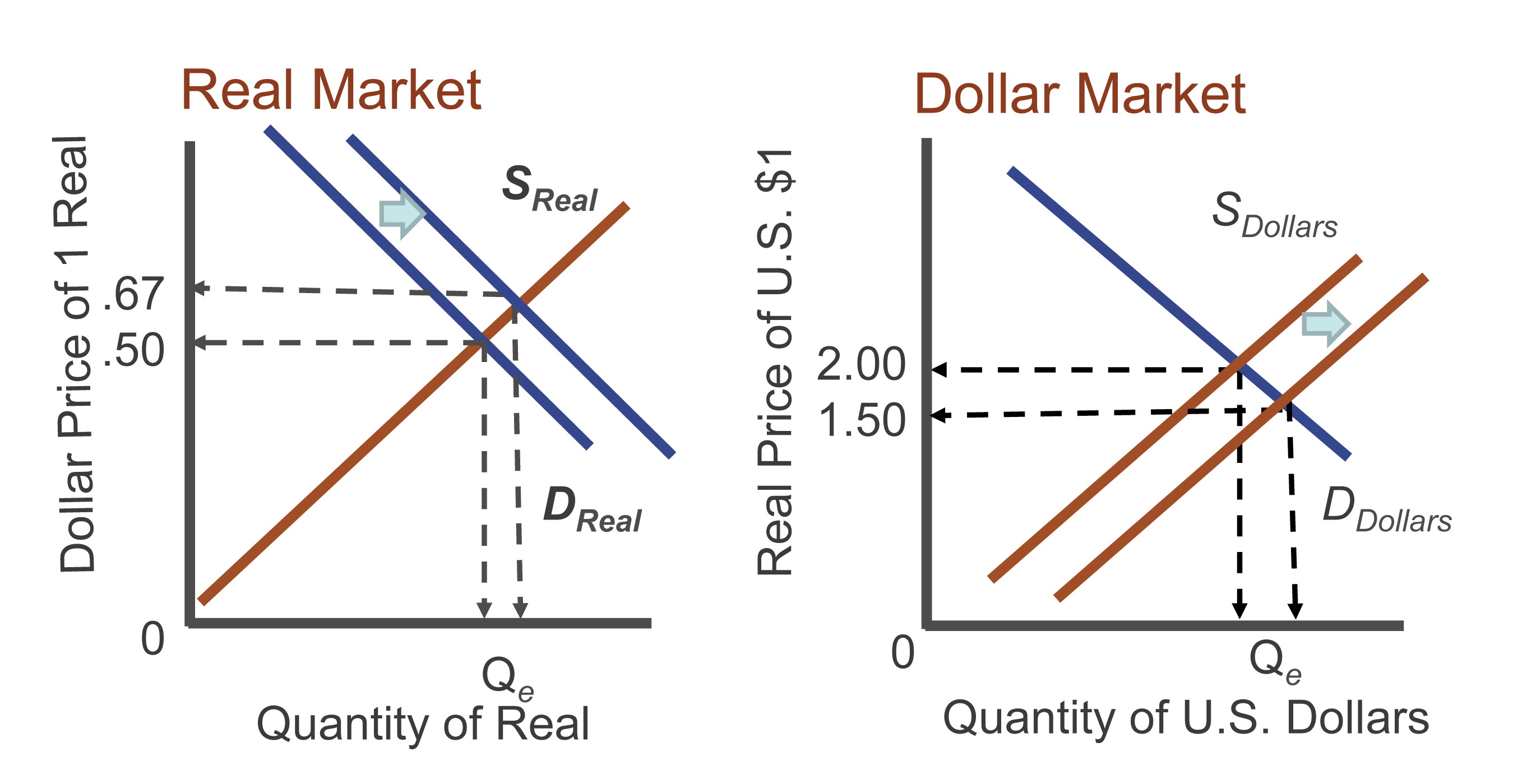
Equilibrium in the foreign exchange market occurs when the quantity of foreign exchange demanded equals the quantity supplied. At this point, the exchange rate is stable and there is no tendency for it to change.
The forces that determine the equilibrium exchange rate are the demand for and supply of foreign exchange. The demand for foreign exchange is determined by the demand for imports and the desire to hold foreign assets. The supply of foreign exchange is determined by the supply of exports and the desire to hold domestic assets.
Interaction of Demand and Supply
The interaction of demand and supply in the foreign exchange market is illustrated in the following diagram:
[Image of a graph showing the demand and supply of foreign exchange]
The equilibrium exchange rate is determined by the intersection of the demand and supply curves. At this point, the quantity of foreign exchange demanded equals the quantity supplied, and there is no tendency for the exchange rate to change.
Factors that can Shift the Equilibrium Exchange Rate
A number of factors can shift the equilibrium exchange rate. These include:
- Changes in the demand for imports or exports
- Changes in the desire to hold foreign or domestic assets
- Changes in government policies
- Changes in economic conditions
When any of these factors change, the equilibrium exchange rate will adjust to a new level that reflects the new conditions.
You also will receive the benefits of visiting foreign exchange market liquidity definition today.
Exchange Rate Regimes
Exchange rate regimes refer to the framework within which a country manages the value of its currency against other currencies. Different types of exchange rate regimes offer varying degrees of flexibility and stability, and each regime has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Check what professionals state about introduction about foreign exchange market and its benefits for the industry.
The choice of exchange rate regime depends on several factors, including the country’s economic conditions, its level of development, and its monetary and fiscal policies.
Fixed Exchange Rate Regime
Under a fixed exchange rate regime, the value of a country’s currency is pegged to another currency, a basket of currencies, or a standard like gold. This means that the central bank intervenes in the foreign exchange market to maintain the fixed exchange rate.
Advantages:
Remember to click definition of foreign exchange market in finance to understand more comprehensive aspects of the definition of foreign exchange market in finance topic.
- Price stability: Fixed exchange rates can help stabilize prices by reducing exchange rate volatility.
- Lower transaction costs: Fixed exchange rates reduce uncertainty and transaction costs for businesses and individuals engaged in international trade and investment.
- Credibility and confidence: A fixed exchange rate can enhance the credibility of a country’s monetary policy and boost investor confidence.
Disadvantages:
- Loss of monetary independence: Fixed exchange rates limit a country’s ability to pursue independent monetary policy, as the central bank must prioritize maintaining the fixed rate.
- Speculative attacks: Fixed exchange rates can make a currency vulnerable to speculative attacks, where investors bet against the currency’s ability to maintain its fixed value.
- Economic rigidity: Fixed exchange rates can limit a country’s ability to adjust to external shocks, such as changes in demand or supply.
Floating Exchange Rate Regime
Under a floating exchange rate regime, the value of a country’s currency is determined by the forces of supply and demand in the foreign exchange market. The central bank does not intervene to maintain a fixed rate.
Advantages:
- Monetary independence: Floating exchange rates allow a country to pursue independent monetary policy, as the central bank can adjust interest rates to manage inflation and economic growth.
- Shock absorption: Floating exchange rates can help a country absorb external shocks by allowing the currency to depreciate or appreciate.
- Flexibility: Floating exchange rates provide flexibility to adjust to changing economic conditions, such as changes in trade patterns or capital flows.
Disadvantages:
- Exchange rate volatility: Floating exchange rates can lead to increased volatility in the value of a currency, which can impact businesses and individuals.
- Uncertainty: Exchange rate volatility can create uncertainty for businesses and investors, making it difficult to plan for the future.
- Competitive devaluations: Floating exchange rates can lead to competitive devaluations, where countries intentionally devalue their currencies to gain an export advantage.
Managed Float
A managed float is a hybrid regime that combines elements of both fixed and floating exchange rate regimes. The central bank intervenes in the foreign exchange market to smooth out excessive exchange rate fluctuations but does not maintain a fixed rate.
Advantages:
- Balance of flexibility and stability: Managed floats offer a balance between the flexibility of floating exchange rates and the stability of fixed exchange rates.
- Shock absorption: Managed floats allow a country to absorb external shocks while maintaining some degree of exchange rate stability.
- Reduced volatility: Central bank intervention can help reduce exchange rate volatility and provide greater certainty for businesses and investors.
Disadvantages:
- Loss of monetary independence: Managed floats can limit a country’s ability to pursue independent monetary policy, as the central bank must consider the impact of its actions on the exchange rate.
- Potential for speculative attacks: Managed floats can still be vulnerable to speculative attacks if investors believe that the central bank cannot maintain the desired exchange rate.
- Complexity: Managed floats can be complex to implement and manage, requiring a high level of expertise and coordination among policymakers.
Foreign Exchange Market Intervention
Governments intervene in the foreign exchange market to influence the value of their currency and achieve specific economic objectives. These objectives can include managing inflation, promoting economic growth, and maintaining financial stability.
Types of Foreign Exchange Market Intervention
There are several different types of foreign exchange market intervention that governments can use, including:
- Buying or selling foreign currency: The central bank can buy or sell foreign currency in the market to directly influence the exchange rate.
- Changing interest rates: The central bank can raise or lower interest rates to make the domestic currency more or less attractive to foreign investors.
- Imposing capital controls: The government can restrict the flow of capital into or out of the country to limit the impact of foreign exchange market volatility.
Effectiveness of Foreign Exchange Market Intervention, Discuss the demand and supply of foreign exchange market
The effectiveness of foreign exchange market intervention is a subject of debate. Some economists argue that intervention can be effective in achieving short-term objectives, such as stabilizing the exchange rate or managing inflation. However, others argue that intervention is often ineffective and can have unintended consequences, such as creating market distortions or reducing market liquidity.
The Role of the Foreign Exchange Market in the Global Economy
The foreign exchange market plays a crucial role in the global economy by facilitating international trade and investment. It enables businesses and individuals to exchange currencies, allowing them to conduct transactions across borders.
Impact on Economic Growth and Development
The foreign exchange market supports economic growth and development by promoting trade and investment. It provides a mechanism for businesses to access foreign markets, enabling them to export goods and services globally. This leads to increased production, job creation, and overall economic prosperity.
Moreover, the foreign exchange market facilitates foreign direct investment (FDI). When businesses invest in other countries, they bring capital, technology, and expertise, contributing to economic growth in both the host and home countries.
Challenges and Opportunities in the 21st Century
The foreign exchange market faces several challenges in the 21st century, including:
- Increased volatility: Technological advancements and globalization have led to increased currency volatility, making it more difficult for businesses to manage foreign exchange risks.
- Regulatory changes: Governments are implementing stricter regulations to prevent financial instability, which can impact the functioning of the foreign exchange market.
- Cybersecurity threats: The rise of cyberattacks poses a significant threat to the security of the foreign exchange market.
Despite these challenges, the foreign exchange market also presents opportunities for growth and innovation:
- Technological advancements: New technologies, such as blockchain and artificial intelligence, can improve the efficiency and transparency of the foreign exchange market.
- Emerging markets: The growth of emerging markets is creating new opportunities for foreign exchange trading.
- Increased demand for foreign exchange services: The increasing globalization of trade and investment will continue to drive demand for foreign exchange services.
Summary
In conclusion, the foreign exchange market stands as a vibrant and dynamic arena where demand and supply converge to determine currency values. Understanding these forces empowers businesses, individuals, and policymakers to navigate the complexities of international trade and investment. As the global economy continues to evolve, the foreign exchange market will undoubtedly remain a critical factor in shaping economic growth and development.
