Example of foreign exchange market in economics – In the realm of economics, the foreign exchange market stands as a global hub where currencies dance and interact, shaping international trade and investment. This intricate marketplace, often referred to as the Forex market, is a fascinating subject that warrants our attention.
The Forex market is not merely a theoretical concept; it has a profound impact on our daily lives, influencing the prices of imported goods, the value of our investments, and the stability of economies worldwide. Understanding the dynamics of this market is crucial for anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of global finance.
Definition of Foreign Exchange Market: Example Of Foreign Exchange Market In Economics
The foreign exchange market (forex market or FX market) is a global decentralized market for the trading of currencies. It is the largest financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
The forex market is open 24 hours a day, 5 days a week, and trades currencies in pairs. The most commonly traded currency pair is the EUR/USD, followed by the USD/JPY, GBP/USD, and USD/CHF.
Types of Foreign Exchange Markets, Example of foreign exchange market in economics
There are two main types of foreign exchange markets:
- Spot market: In the spot market, currencies are traded for immediate delivery.
- Forward market: In the forward market, currencies are traded for delivery at a future date.
Role of Foreign Exchange Market in International Trade
The foreign exchange market plays a vital role in international trade. It allows businesses to exchange currencies so that they can buy and sell goods and services from other countries.
Without the foreign exchange market, international trade would be much more difficult and expensive.
Participants in Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is a global marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
The major participants in the foreign exchange market are:
- Banks
- Corporations
- Central banks
- Investment funds
- Retail traders
Banks are the largest participants in the foreign exchange market. They act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers of currencies, and they also trade currencies for their own account. Banks play a vital role in the foreign exchange market by providing liquidity and facilitating the smooth flow of transactions.
Corporations are another major participant in the foreign exchange market. They buy and sell currencies to facilitate their international trade and investment activities. For example, a US company that imports goods from China will need to buy Chinese yuan to pay for those goods.
Central banks are government agencies that are responsible for managing the monetary policy of their respective countries. Central banks intervene in the foreign exchange market to influence the value of their currencies. For example, the Bank of Japan has been selling Japanese yen to weaken the yen and make Japanese exports more competitive.
Investment funds are pools of money that are invested in various financial assets, including currencies. Investment funds buy and sell currencies to generate profits for their investors.
Retail traders are individuals who trade currencies for their own account. Retail traders typically trade small amounts of currency and use leverage to increase their potential profits.
The different participants in the foreign exchange market have different roles and motivations. Banks are primarily motivated by profit, while corporations are motivated by the need to facilitate their international business activities. Central banks are motivated by the need to manage their currencies and achieve their monetary policy goals. Investment funds are motivated by the desire to generate profits for their investors. Retail traders are motivated by the desire to make money.
The presence of these different participants in the foreign exchange market creates a diverse and competitive marketplace. This diversity helps to ensure that the foreign exchange market is liquid and efficient.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Rates
Foreign exchange rates are influenced by a multitude of factors that can be broadly categorized into economic fundamentals, political events, and market sentiment. These factors interact in complex ways to determine the value of currencies relative to each other.
Economic fundamentals, such as economic growth, inflation, and interest rates, play a significant role in shaping foreign exchange rates. A country with strong economic growth, low inflation, and high interest rates is likely to attract foreign investment, leading to an appreciation of its currency. Conversely, a country with weak economic growth, high inflation, and low interest rates may experience a depreciation of its currency.
Political Events
Political events can also have a significant impact on foreign exchange rates. For example, a political crisis or instability in a country can lead to a loss of confidence in its currency, causing it to depreciate. Conversely, a peaceful transition of power or the implementation of sound economic policies can boost confidence in a currency, leading to its appreciation.
Market Sentiment
Market sentiment, or the prevailing mood of market participants, can also influence foreign exchange rates. If investors are optimistic about the future of a particular currency, they may buy it, leading to its appreciation. Conversely, if investors are pessimistic, they may sell the currency, leading to its depreciation.
Central Bank Interventions
Central banks can intervene in the foreign exchange market to influence the value of their currencies. They can do this by buying or selling their currencies in the market, or by adjusting interest rates. Central bank interventions can be effective in stabilizing foreign exchange rates, but they can also be controversial, as they can be seen as an attempt to manipulate the market.
Foreign Exchange Market Instruments
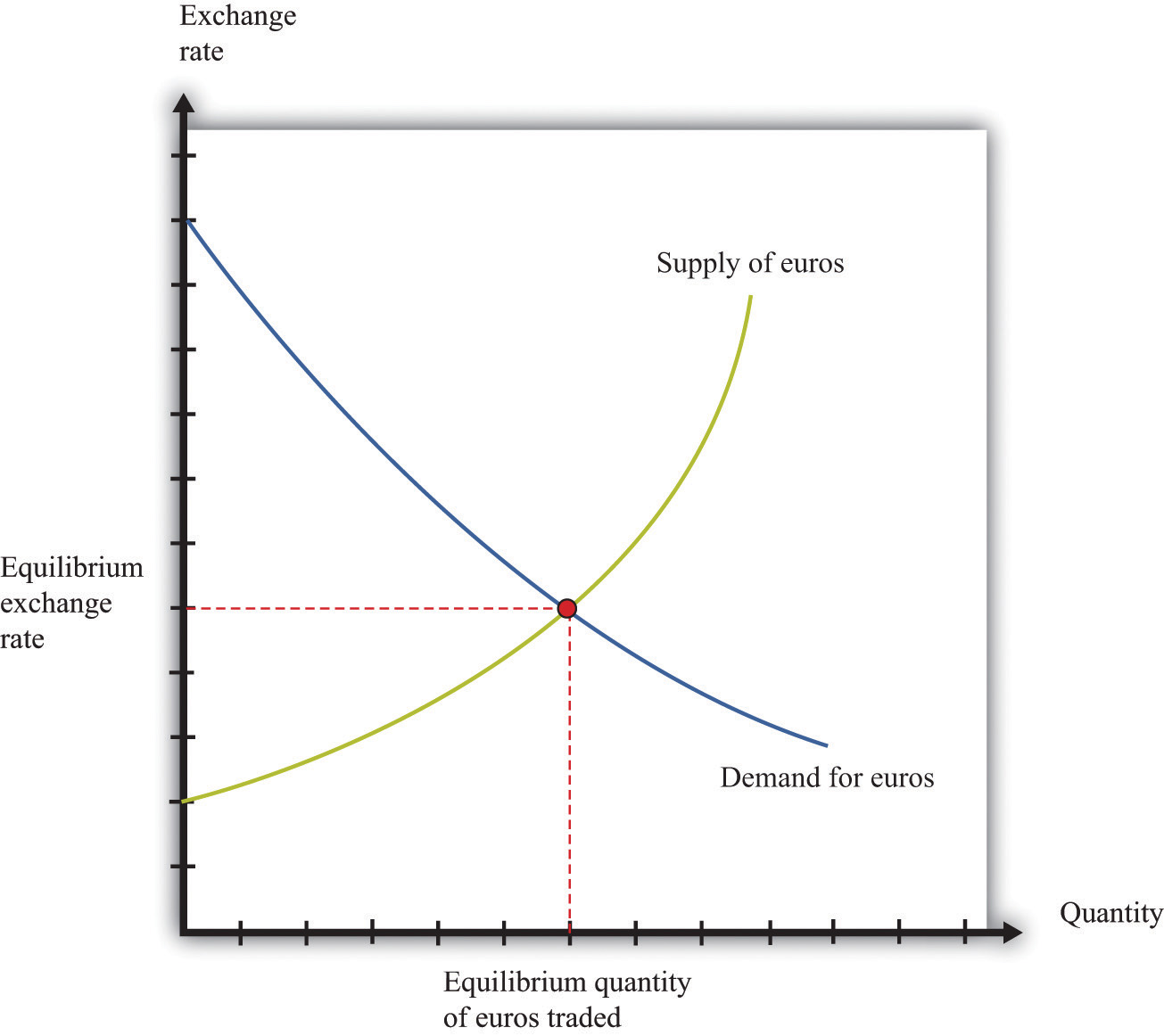
The foreign exchange market offers various instruments that facilitate trading and risk management. These instruments include spot contracts, forward contracts, and currency swaps, each with distinct features and applications.
Spot Contracts
Spot contracts involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the current market rate. They are typically settled within two business days and are used for short-term transactions, such as settling trade invoices or covering immediate foreign exchange needs.
Forward Contracts
Forward contracts are agreements to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date. They are used to lock in exchange rates for future transactions, reducing the risk of exchange rate fluctuations. Forward contracts are customized to meet the specific requirements of the parties involved.
Currency Swaps
Currency swaps are agreements between two parties to exchange a specific amount of currency at an agreed-upon exchange rate on a specified date. The parties also agree to reverse the transaction at a later date, usually with a different exchange rate. Currency swaps are commonly used for long-term risk management and hedging against exchange rate fluctuations.
Role of Derivatives in Foreign Exchange Risk Management
Derivatives play a crucial role in managing foreign exchange risk. They allow companies and investors to hedge against potential losses due to adverse exchange rate movements. Common foreign exchange derivatives include currency options and currency futures, which provide flexibility and customization in risk management strategies.
Foreign Exchange Market Regulations
The foreign exchange market is subject to regulations to ensure its stability, transparency, and fairness. These regulations vary across countries and are enforced by regulatory bodies such as central banks and financial authorities.
Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in overseeing the foreign exchange market, setting guidelines, and enforcing compliance. Their objectives include:
- Maintaining market stability and preventing excessive volatility
- Protecting investors and market participants from fraud and abuse
- Ensuring fair and orderly trading practices
Regulations impact foreign exchange market participants in various ways, including:
- Compliance requirements: Participants must adhere to regulations, such as reporting and record-keeping requirements.
- Risk management: Regulations help participants manage risks by setting capital requirements and other prudential measures.
- Market access: Regulations can restrict or grant access to the foreign exchange market for certain participants.
Examples of Foreign Exchange Market Transactions
The foreign exchange market facilitates the exchange of currencies between individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide. These transactions serve various purposes, including international trade, investments, and tourism.
Obtain recommendations related to foreign exchange market leader that can assist you today.
The process of buying and selling foreign currencies involves two parties: the buyer and the seller. The buyer wants to acquire a foreign currency, while the seller wants to dispose of it. The transaction occurs at an agreed-upon exchange rate, which represents the value of one currency relative to another.
When investigating detailed guidance, check out foreign exchange market components now.
Types of Foreign Exchange Transactions
- Spot Transactions: In spot transactions, the exchange of currencies occurs immediately, usually within two business days. These transactions are typically used for immediate payment obligations, such as settling international trade invoices or making travel arrangements.
- Forward Transactions: Forward transactions involve the buying or selling of foreign currencies at a predetermined exchange rate for a future date. These transactions are used to hedge against currency fluctuations and lock in exchange rates for future payments or receipts.
- Swap Transactions: Swap transactions involve the simultaneous buying and selling of currencies with different value dates. These transactions are often used for managing currency risk and optimizing cash flow.
Foreign Exchange Market for International Payments and Investments
The foreign exchange market plays a crucial role in facilitating international payments and investments. Businesses engaged in international trade use the foreign exchange market to convert their currencies into the currencies of their trading partners. Similarly, investors seeking to diversify their portfolios may use the foreign exchange market to invest in foreign stocks, bonds, or real estate.
Remember to click types of foreign exchange market class 12 to understand more comprehensive aspects of the types of foreign exchange market class 12 topic.
Foreign Exchange Market Data and Analysis

The foreign exchange market generates a vast amount of data that traders and analysts use to make informed decisions. This data includes historical prices, current quotes, order book information, and economic indicators.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is a method of forecasting future price movements based on historical data. Technical analysts use charts and indicators to identify trends, patterns, and support and resistance levels.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis is a method of forecasting future price movements based on economic data. Fundamental analysts consider factors such as interest rates, inflation, economic growth, and political stability.
Forecasting
Forecasting is an essential part of foreign exchange market decision-making. Traders and analysts use a variety of techniques to forecast future price movements, including technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and sentiment analysis.
Foreign Exchange Market Technology
Technology plays a pivotal role in the foreign exchange market, revolutionizing its operations and enhancing its efficiency.
The advent of electronic trading platforms has transformed the market by enabling traders to execute transactions seamlessly from remote locations. These platforms provide real-time access to market data, facilitate order matching, and offer a range of trading tools and functionalities.
Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading, also known as algo trading, involves the use of computer programs to automate trading decisions based on predefined criteria. These algorithms analyze market data, identify trading opportunities, and execute trades in real time, often at a speed that is beyond human capabilities.
Impact of Technology
Technology has significantly improved the efficiency and liquidity of the foreign exchange market. Electronic trading platforms have reduced transaction costs, increased market transparency, and facilitated faster execution of trades. Algorithmic trading has further enhanced liquidity by providing continuous market access and enabling traders to respond to market movements more quickly.
Closure
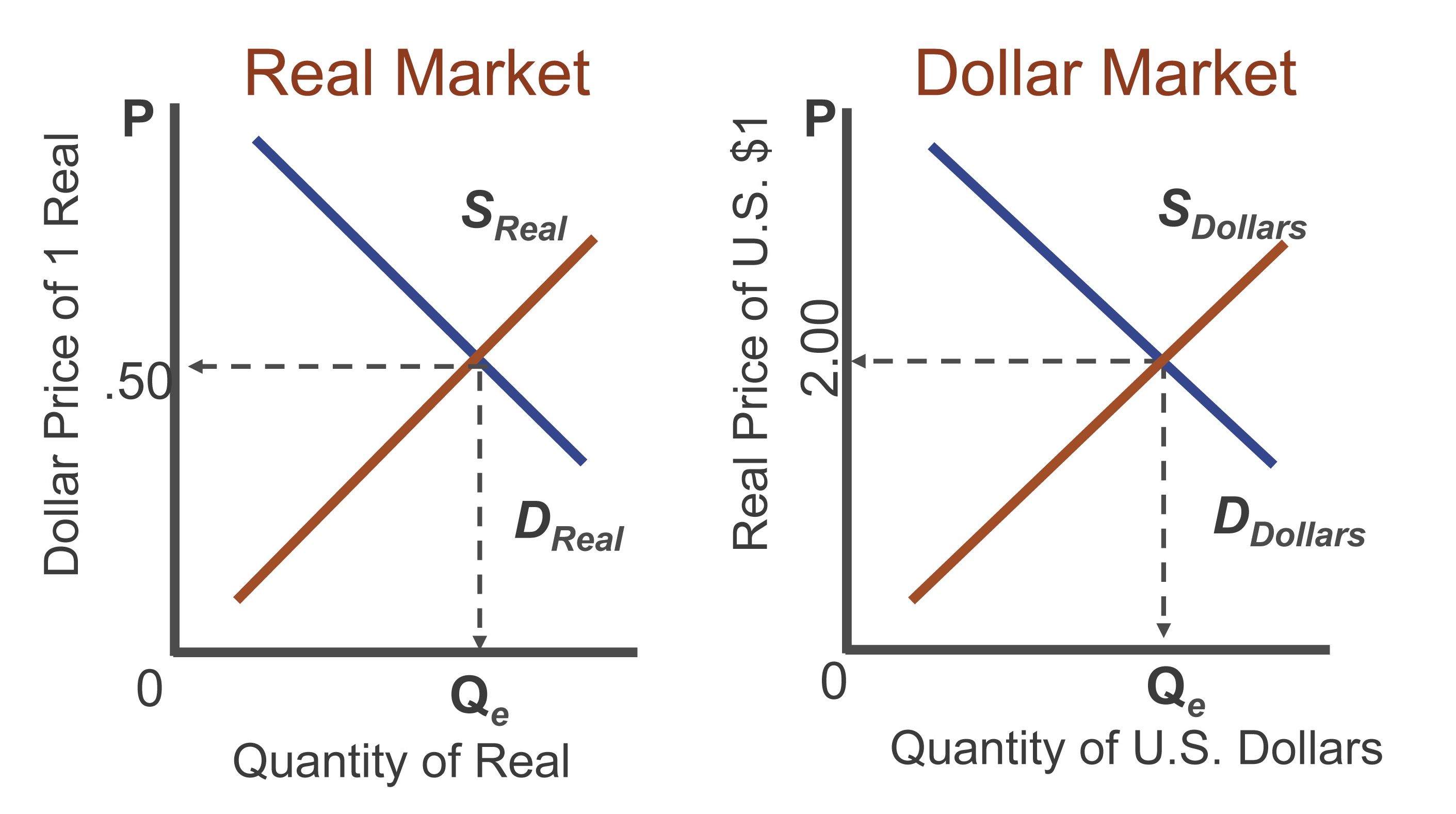
As we conclude our exploration of the foreign exchange market in economics, it is evident that this dynamic and ever-evolving realm plays a pivotal role in shaping the global economy. By comprehending the factors that influence exchange rates, the various participants involved, and the instruments used to manage currency risk, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of this fascinating marketplace.
Whether you are an investor, a business owner, or simply a curious observer, the foreign exchange market offers a wealth of knowledge and opportunities. By staying informed about the latest trends and developments, you can make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of international finance with greater confidence.
