Discover the multifaceted world of foreign exchange market examples, where currencies dance and global economies intertwine. From international trade to travel and investments, delve into real-world scenarios that illustrate the practical significance of forex transactions.
This comprehensive guide explores the various types of forex transactions, including spot, forward, and swap, shedding light on their purpose and mechanics. Learn about the methods used to trade currencies, from brokers to online platforms, and gain insights into selecting the most suitable trading method based on individual needs.
Overview of the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market, also known as forex or FX, is a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
The forex market plays a crucial role in facilitating international trade and investment. It allows businesses and individuals to exchange currencies for various purposes, such as importing and exporting goods, making foreign investments, and traveling abroad.
Understand how the union of what is concept of foreign exchange market can improve efficiency and productivity.
History of the Forex Market
The origins of the forex market can be traced back to ancient times when traders would exchange currencies to facilitate trade. However, the modern forex market as we know it today developed in the early 20th century with the advent of electronic trading and the establishment of major financial centers like London and New York.
Key Participants in the Forex Market
The forex market involves a wide range of participants, including:
- Banks: Commercial and investment banks are the primary dealers in the forex market, facilitating currency transactions for their clients.
- Corporations: Multinational corporations use the forex market to exchange currencies for cross-border transactions and investments.
- Investment funds: Hedge funds and other investment funds trade currencies as part of their investment strategies.
- Retail traders: Individual traders participate in the forex market through online brokers, speculating on currency movements.
- Central banks: Central banks intervene in the forex market to influence their currencies’ values and manage monetary policy.
Factors Influencing Foreign Exchange Rates
Foreign exchange rates are constantly fluctuating, influenced by a complex interplay of economic, political, and market forces. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses and individuals engaged in international transactions.
One of the primary drivers of currency exchange rates is the underlying economic health of a country. A strong economy with low inflation, high growth, and stable political conditions typically attracts foreign investment and increases demand for its currency, leading to currency appreciation.
Role of Supply and Demand
The foreign exchange market operates on the principles of supply and demand. When demand for a currency exceeds its supply, its value rises, and vice versa. This dynamic is influenced by factors such as international trade, foreign investment, and tourism.
Impact of Interest Rate Differentials
Interest rates play a significant role in currency exchange rates. Higher interest rates in a country make its currency more attractive to foreign investors seeking higher returns. This increased demand leads to currency appreciation. Conversely, lower interest rates can lead to currency depreciation.
Types of Foreign Exchange Transactions
The foreign exchange market facilitates a wide range of transactions, each tailored to specific needs and risk profiles. These transactions can be categorized into three main types: spot, forward, and swap transactions.
Spot transactions involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the prevailing market rate. Forward transactions, on the other hand, allow for the exchange of currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date, hedging against potential fluctuations in exchange rates.
Swap Transactions, Foreign exchange market examples
Swap transactions combine elements of both spot and forward transactions. They involve the simultaneous exchange of currencies at the spot rate and a reverse exchange at a predetermined forward rate. Swap transactions are often used to hedge against currency risk or to speculate on future exchange rate movements.
For example, a company expecting to receive a payment in euros in the future may enter into a forward contract to sell those euros at a fixed rate, ensuring a certain level of revenue regardless of future exchange rate fluctuations.
You also will receive the benefits of visiting foreign exchange market definition en francais today.
Methods of Trading in the Foreign Exchange Market

The foreign exchange market offers various methods for trading currencies, each with unique advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these methods and selecting the one that aligns with your needs is crucial for successful trading.
Through Brokers
Currency brokers act as intermediaries between traders and the interbank market, facilitating currency transactions. They provide access to competitive rates, real-time quotes, and market analysis. Advantages include:
– Access to interbank rates
– Personalization and tailored advice
– Lower transaction costs for high-volume traders
Disadvantages:
– Brokerage fees can add up
– Limited access to some currency pairs
– Potential for conflict of interest
Through Banks
Banks are traditional providers of foreign exchange services. They offer a range of products, including spot transactions, forward contracts, and currency options. Advantages include:
– Established and trusted institutions
– Wide range of services
– Physical branches for personal interaction
Disadvantages:
– Less competitive rates compared to brokers
– Slower execution times
– Limited access to advanced trading tools
Through Online Platforms
Online platforms, also known as retail forex brokers, provide a convenient and accessible way to trade currencies. They offer user-friendly interfaces, low minimum deposits, and various trading tools. Advantages include:
– Convenience and accessibility
– Low transaction costs
– Access to educational resources and market analysis
Disadvantages:
– Potential for scams and unregulated brokers
– Limited access to interbank rates
– Customer support may be limited
Selecting the Appropriate Trading Method
The choice of trading method depends on your individual needs, trading style, and experience. Consider the following factors:
– Volume: High-volume traders may benefit from brokers’ lower transaction costs.
– Access to Interbank Rates: Brokers and online platforms offer access to interbank rates, providing more competitive pricing.
– Customer Support: Banks and brokers offer personalized support, while online platforms may have limited availability.
– Trading Tools and Analysis: Online platforms often provide advanced trading tools and market analysis, which can be beneficial for experienced traders.
– Security and Regulation: Ensure the broker or platform you choose is reputable and regulated by a recognized authority.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select the trading method that best meets your requirements and helps you achieve your financial goals in the foreign exchange market.
Strategies for Foreign Exchange Trading: Foreign Exchange Market Examples
The foreign exchange market offers a wide range of trading strategies, each with its own risks and rewards. Choosing the right strategy depends on factors such as the trader’s risk tolerance, time horizon, and capital availability.
Trend Following
Trend following involves identifying the prevailing trend in the market and trading in line with that trend. Traders using this strategy aim to capture long-term price movements by buying or selling currencies that are trending higher or lower, respectively.
Risks: Trend following can be risky if the trend reverses unexpectedly or if the trader misidentifies the trend.
Obtain recommendations related to foreign exchange market nigeria that can assist you today.
Rewards: Trend following can be rewarding if the trend continues for an extended period.
Scalping
Scalping involves making numerous small profits over a short period of time by taking advantage of small price fluctuations. Scalpers typically hold positions for a few minutes or seconds, and they rely on high volume and tight spreads to generate profits.
Risks: Scalping can be risky due to the high frequency of trading and the small profit margins involved.
Rewards: Scalping can be rewarding for traders who are able to identify and execute trades quickly and accurately.
Arbitrage
Arbitrage involves taking advantage of price differences between different markets or currencies. Arbitrageurs buy a currency in one market and simultaneously sell it in another market where it is priced higher.
Risks: Arbitrage can be risky if the price difference between the two markets narrows or if there are unexpected delays in executing the trades.
Rewards: Arbitrage can be rewarding if the price difference between the two markets is large enough to cover the transaction costs.
Examples of Foreign Exchange Market Transactions
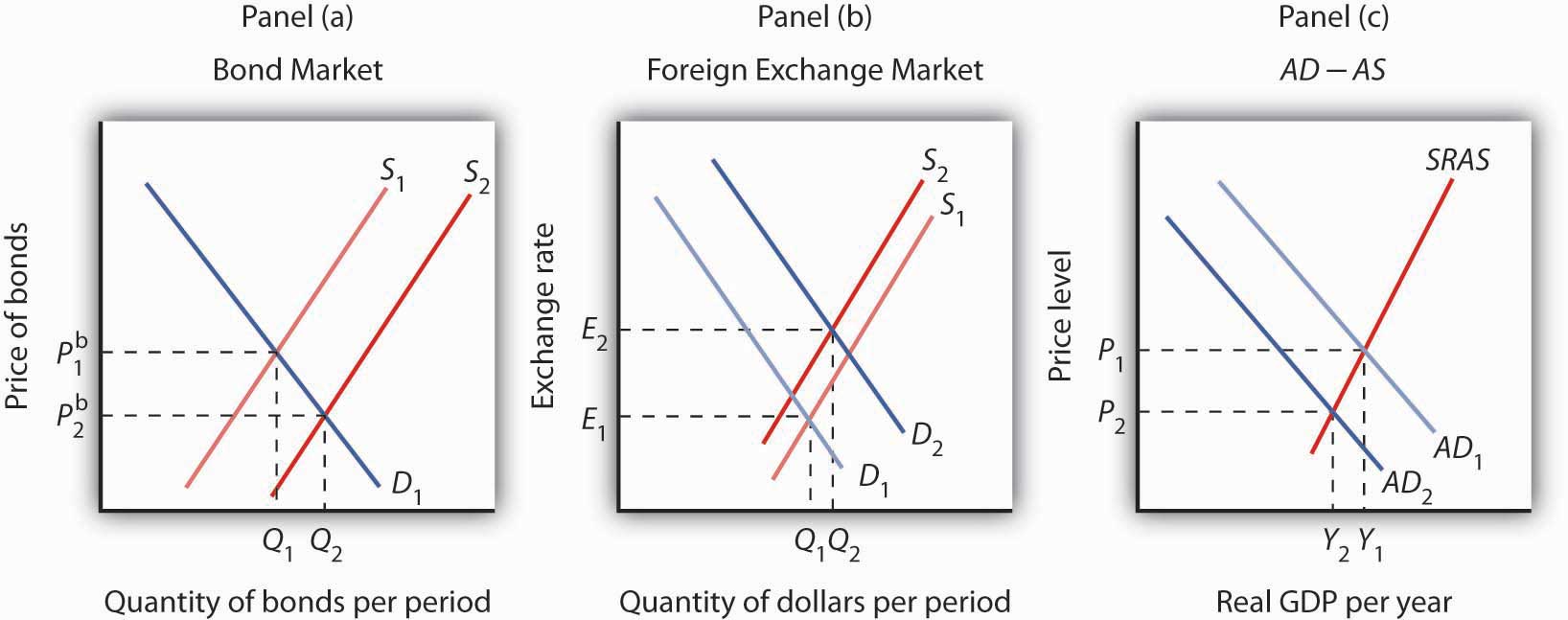
The foreign exchange market serves as a global marketplace for the exchange of currencies, facilitating international trade, travel, and investments. Businesses and individuals alike engage in forex transactions for a variety of purposes, from settling international payments to managing risk.
Here are some real-world examples of how forex transactions are used in different scenarios:
International Trade
- Transaction Type: Import Payment
- Currency Pair: USD/EUR
- Amount: 100,000 USD
- Purpose: A U.S. company purchases goods from a European supplier and needs to pay in Euros.
- Transaction Type: Export Receipt
- Currency Pair: EUR/USD
- Amount: 80,000 EUR
- Purpose: A European company sells goods to a U.S. customer and receives payment in U.S. Dollars.
Travel
- Transaction Type: Currency Exchange
- Currency Pair: GBP/USD
- Amount: 500 GBP
- Purpose: A British tourist exchanges Pounds into U.S. Dollars before traveling to the United States.
Investments
- Transaction Type: Stock Purchase
- Currency Pair: USD/JPY
- Amount: 100,000 USD
- Purpose: An American investor purchases shares of a Japanese company, requiring them to exchange U.S. Dollars for Japanese Yen.
- Transaction Type: Bond Issuance
- Currency Pair: EUR/USD
- Amount: 500 million EUR
- Purpose: A European government issues bonds denominated in U.S. Dollars, attracting investors seeking exposure to the U.S. currency.
Outcome Summary

Through engaging examples and expert analysis, this guide empowers individuals and businesses to navigate the complexities of the foreign exchange market. By understanding the factors influencing exchange rates, trading strategies, and practical applications, readers gain a competitive edge in managing currency risks and optimizing financial outcomes.
