Foreign exchange market in economics meaning refers to the global marketplace where currencies are traded. It’s a dynamic and interconnected system that plays a crucial role in international trade, investment, and economic stability.
The foreign exchange market operates 24 hours a day, 5 days a week, and involves a wide range of participants, including central banks, commercial banks, corporations, and individual investors.
Definition of the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market (forex market or FX market) is a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $6.6 trillion.
The foreign exchange market serves several purposes:
- Facilitate international trade: Businesses and individuals need to exchange currencies to conduct international trade.
- Manage risk: Companies and investors use the foreign exchange market to hedge against currency fluctuations.
- Speculation: Traders speculate on currency movements to make a profit.
Currencies Traded in the Foreign Exchange Market
The most traded currencies in the foreign exchange market are:
- US dollar (USD)
- Euro (EUR)
- Japanese yen (JPY)
- British pound (GBP)
- Swiss franc (CHF)
Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Exchange-Rate-1b1df02db6a14eee998e1b76d5c9b82d.jpg)
The foreign exchange market is a vast and complex ecosystem involving a diverse range of participants, each playing a distinct role and driven by unique motivations.
Obtain a comprehensive document about the application of foreign exchange market hedging that is effective.
Central Banks
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve or the European Central Bank, are key players in the foreign exchange market. They intervene to influence exchange rates for various reasons, including managing inflation, maintaining economic stability, and supporting international trade.
Commercial Banks
Commercial banks facilitate foreign exchange transactions for their clients, including individuals, businesses, and other financial institutions. They provide services such as currency exchange, international wire transfers, and hedging instruments to manage currency risk.
Corporations
Multinational corporations engage in foreign exchange transactions to conduct international business, pay suppliers, and invest in foreign markets. Their activities can significantly impact exchange rates, especially when dealing with large currency volumes.
Obtain a comprehensive document about the application of foreign exchange market graph ap econ that is effective.
Individual Investors
Individual investors participate in the foreign exchange market primarily for speculative purposes, seeking to profit from currency fluctuations. They use various strategies, such as spot trading or currency options, to capitalize on exchange rate movements.
Impact of Market Participants
The actions and decisions of these participants collectively shape foreign exchange rates. Central bank interventions, commercial bank transactions, corporate demand, and speculative trading all contribute to the supply and demand dynamics that determine currency values.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Rates

The foreign exchange market is a dynamic and complex system, and the value of currencies is constantly fluctuating. Several factors can influence these fluctuations, including economic fundamentals, supply and demand, and market sentiment.
Economic fundamentals are the underlying economic conditions of a country that can affect the value of its currency. These fundamentals include economic growth, inflation, interest rates, and political stability. A country with a strong economy, low inflation, and high interest rates is likely to have a strong currency, while a country with a weak economy, high inflation, and low interest rates is likely to have a weak currency.
Supply and Demand
The supply and demand for a currency also play a role in determining its value. When the demand for a currency is high, its value will increase, and when the demand is low, its value will decrease. The demand for a currency is influenced by several factors, including international trade, investment, and speculation.
Economic News and Events
Economic news and events can also impact foreign exchange rates. For example, a positive economic report can lead to an increase in the value of a currency, while a negative economic report can lead to a decrease in value. Political events, such as elections or changes in government, can also affect foreign exchange rates.
Foreign Exchange Market Intervention
Foreign exchange market intervention refers to the actions taken by central banks or governments to influence the exchange rate of their currency against other currencies. This intervention involves buying or selling foreign currencies in the foreign exchange market to achieve desired exchange rate objectives.
Reasons for Foreign Exchange Market Intervention
Central banks intervene in the foreign exchange market for various reasons, including:
- Maintaining exchange rate stability: To prevent excessive fluctuations in the exchange rate, which can harm economic growth and stability.
- Correcting misalignments: To address situations where the exchange rate is deemed to be significantly overvalued or undervalued.
- Managing inflation: To influence the price of imported goods and services by affecting the exchange rate.
- Supporting domestic industries: To protect domestic industries from foreign competition or to promote exports.
Effectiveness of Foreign Exchange Market Intervention
The effectiveness of foreign exchange market intervention depends on several factors, such as:
- Size of the intervention: The amount of foreign currency bought or sold can impact the effectiveness of the intervention.
- Market conditions: The level of liquidity and volatility in the foreign exchange market can influence the effectiveness of intervention.
- Policy credibility: The market’s belief in the central bank’s commitment to the intervention can affect its effectiveness.
- Other economic factors: Broader economic conditions, such as interest rate differentials and economic growth, can influence the impact of intervention.
While foreign exchange market intervention can be effective in the short term, it may not be sustainable in the long run. It can lead to a loss of foreign exchange reserves, reduced market confidence, and potential distortions in the foreign exchange market.
Impact of the Foreign Exchange Market on the Economy: Foreign Exchange Market In Economics Meaning
The foreign exchange market plays a pivotal role in the global economy, influencing international trade, the competitiveness of domestic firms, and inflation. Understanding these impacts is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals involved in international transactions.
Impact on International Trade
Foreign exchange rate fluctuations can significantly affect the volume and direction of international trade. When the value of a country’s currency appreciates, its exports become more expensive in foreign markets, leading to a decrease in exports. Conversely, a depreciation in the currency value makes exports cheaper and boosts exports.
Similarly, imports are affected by foreign exchange rates. A currency appreciation makes imports cheaper, leading to an increase in imports. Conversely, a depreciation makes imports more expensive and reduces imports.
Impact on Competitiveness of Domestic Firms
Foreign exchange rates influence the competitiveness of domestic firms in the global market. A currency appreciation makes domestic goods and services more expensive for foreign buyers, reducing their competitiveness. This can lead to a loss of market share for domestic firms.
On the other hand, a currency depreciation makes domestic goods and services cheaper for foreign buyers, enhancing their competitiveness. This can result in increased exports and market share for domestic firms.
Further details about questionnaire on foreign exchange market is accessible to provide you additional insights.
Impact on Inflation, Foreign exchange market in economics meaning
Foreign exchange rates can affect inflation through the cost of imported goods and services. A currency depreciation makes imports more expensive, which can lead to an increase in inflation. Conversely, a currency appreciation makes imports cheaper, which can help to reduce inflation.
Additionally, foreign exchange rate fluctuations can influence the prices of domestic goods and services that compete with imports. A currency depreciation can make domestic goods and services relatively cheaper, leading to lower inflation. Conversely, a currency appreciation can make domestic goods and services relatively more expensive, contributing to higher inflation.
Risk Management in the Foreign Exchange Market
Risk management is a critical aspect of foreign exchange trading, as it helps market participants mitigate potential losses and protect their profits. There are several risks associated with foreign exchange trading, including exchange rate volatility, liquidity risk, and counterparty risk.
To manage these risks, market participants employ various strategies, such as diversification, hedging, and stop-loss orders. Hedging is a particularly important risk management technique that involves entering into offsetting positions in different markets to reduce the impact of adverse price movements.
Diversification
- Involves spreading investments across different currencies to reduce the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on any single currency.
- Helps mitigate risk by ensuring that losses in one currency may be offset by gains in another.
Hedging
- Involves entering into a contract to buy or sell a specific amount of currency at a predetermined exchange rate in the future.
- Protects against exchange rate fluctuations and is commonly used by businesses that engage in international trade or have foreign currency exposure.
Stop-Loss Orders
- Orders placed with a broker to automatically sell or buy a currency when it reaches a specified price level.
- Helps limit potential losses by exiting a trade when the market moves against the trader’s position.
Outcome Summary
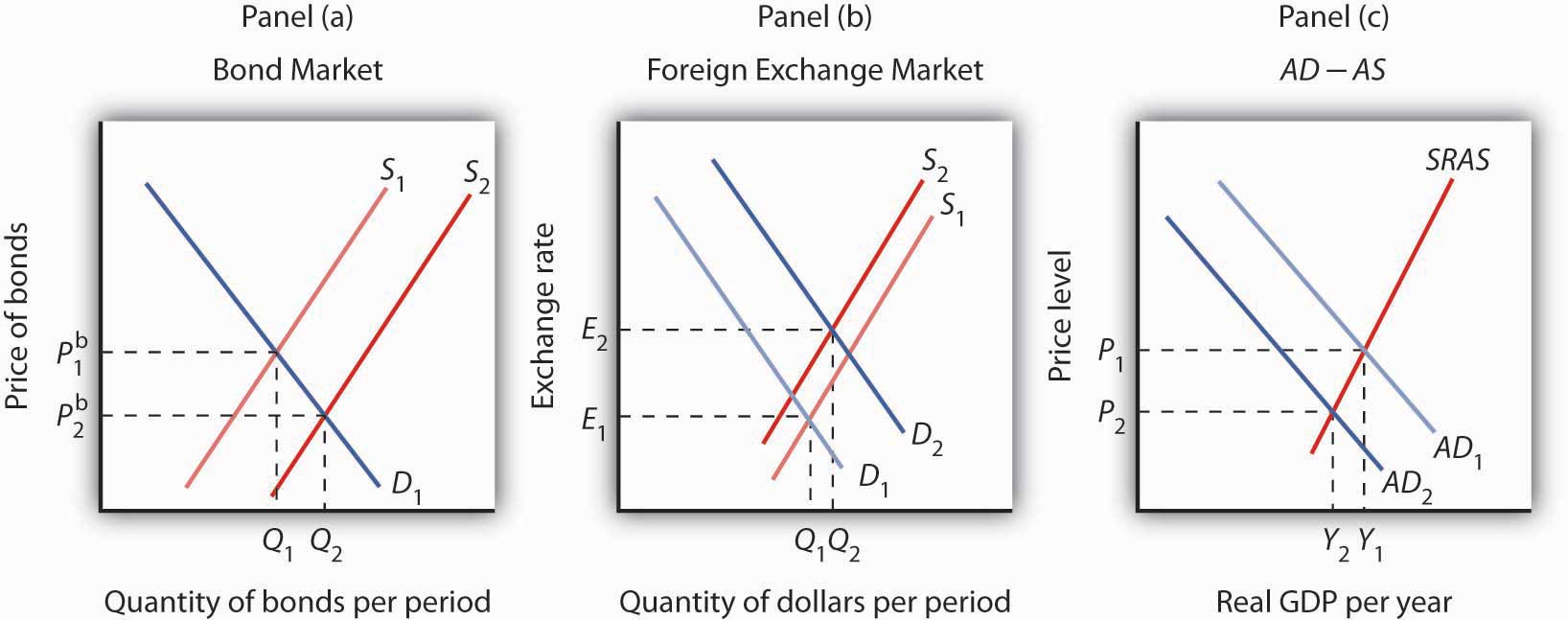
In summary, the foreign exchange market is a complex and ever-evolving ecosystem that has a profound impact on the global economy. Its participants, influenced by a multitude of factors, engage in currency trading to facilitate international transactions, manage risk, and seek profit opportunities.
