Foreign exchange market in equilibrium – In the realm of global finance, the foreign exchange market, where currencies are traded, strives to achieve equilibrium—a state of balance where supply and demand align. This delicate balance is influenced by a myriad of factors, shaping the value of currencies and driving economic decisions.
Understanding the forces that govern foreign exchange market equilibrium is crucial for businesses, investors, and policymakers alike. It empowers them to navigate the complexities of currency markets and make informed decisions that can impact their financial outcomes.
Equilibrium in the Foreign Exchange Market
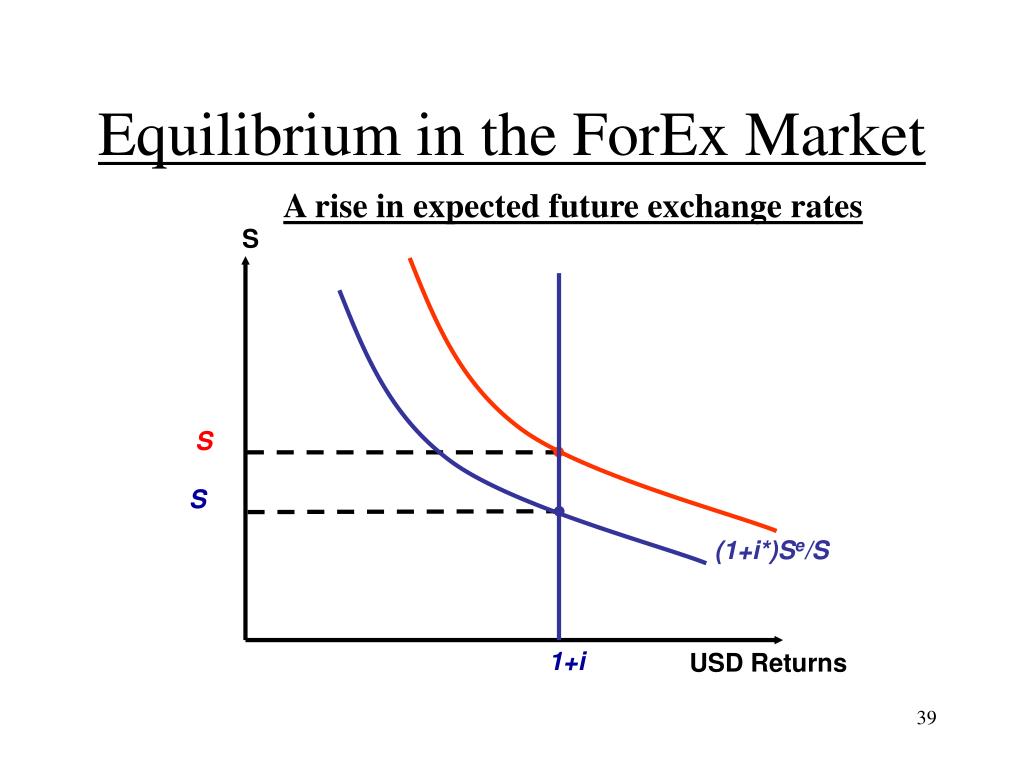
The foreign exchange market, where currencies are traded, is said to be in equilibrium when the supply of a currency is equal to the demand for that currency. At this point, there is no tendency for the exchange rate to change.
The equilibrium exchange rate is determined by a number of factors, including:
- Economic fundamentals: These include factors such as economic growth, inflation, and interest rates. Countries with strong economic fundamentals tend to have stronger currencies.
- Political stability: Political instability can lead to currency weakness, as investors are less likely to invest in countries that are perceived as risky.
- Speculation: Speculators can play a significant role in the foreign exchange market. If they believe that a currency is undervalued, they may buy it in the hope of selling it at a profit later.
Role of Supply and Demand, Foreign exchange market in equilibrium
The supply and demand for a currency is determined by a number of factors, including:
- Trade: When a country exports more goods and services than it imports, there is a greater demand for its currency.
- Investment: When investors buy assets in a country, there is a greater demand for its currency.
- Government intervention: Governments can intervene in the foreign exchange market to influence the exchange rate. For example, they may buy or sell their own currency to strengthen or weaken it.
When the supply and demand for a currency are equal, the exchange rate is said to be in equilibrium. At this point, there is no tendency for the exchange rate to change.
Factors Affecting Equilibrium
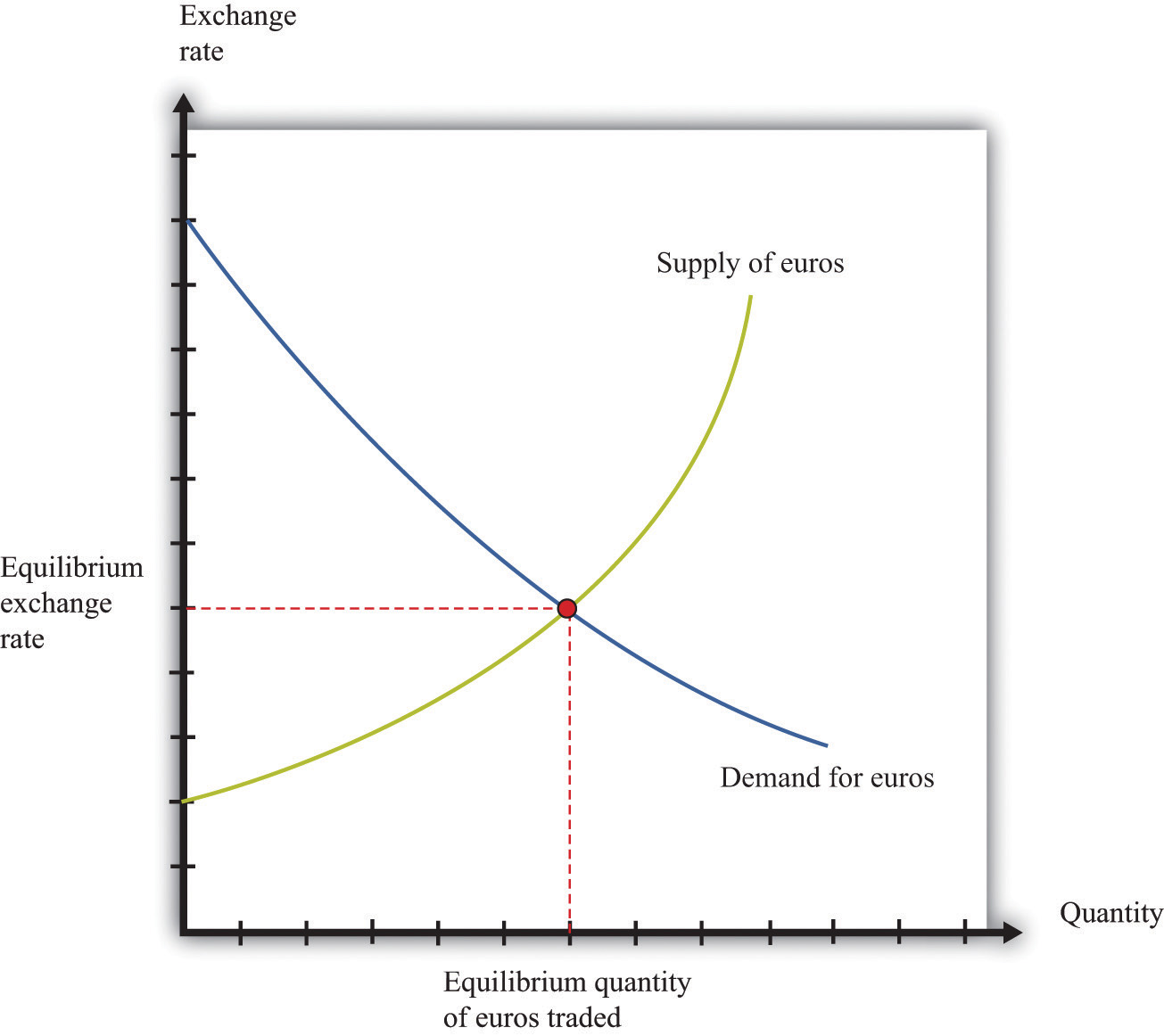
The equilibrium exchange rate is influenced by various macroeconomic factors that affect the demand and supply for currencies. These factors include interest rates, inflation, and economic growth.
Interest Rates
Interest rates have a significant impact on the foreign exchange market. Higher interest rates in one country compared to another can lead to increased demand for that country’s currency. This is because investors are attracted to countries with higher interest rates, as they can earn a higher return on their investments. Increased demand for a currency leads to its appreciation, while the currency of the country with lower interest rates depreciates.
In this topic, you find that market continental forex is very useful.
Inflation
Inflation, or the rate of price increases, also affects the equilibrium exchange rate. Higher inflation in one country can lead to a decrease in the demand for that country’s currency. This is because investors are concerned about the purchasing power of their investments being eroded by inflation. As a result, they may choose to invest in countries with lower inflation, leading to an appreciation of those currencies.
Economic Growth
Economic growth is another factor that can influence the equilibrium exchange rate. Strong economic growth in one country can lead to increased demand for that country’s currency. This is because investors are attracted to countries with strong economic growth, as they believe that their investments will be more profitable. Increased demand for a currency leads to its appreciation, while the currency of the country with weaker economic growth depreciates.
Disequilibrium and Adjustment: Foreign Exchange Market In Equilibrium
Disequilibrium occurs when the foreign exchange market is not in equilibrium. This can happen due to various factors, such as changes in economic conditions, political events, or speculative trading. When the market is out of equilibrium, the exchange rate is not at its equilibrium level, and there is a tendency for the market to move back towards equilibrium.
Browse the implementation of foreign exchange market definition pdf in real-world situations to understand its applications.
Several mechanisms help bring the foreign exchange market back to equilibrium. One mechanism is the movement of capital. When the exchange rate is below its equilibrium level, investors will buy the undervalued currency, expecting it to appreciate in value. This increased demand for the undervalued currency will push the exchange rate up towards its equilibrium level. Conversely, when the exchange rate is above its equilibrium level, investors will sell the overvalued currency, expecting it to depreciate in value. This increased supply of the overvalued currency will push the exchange rate down towards its equilibrium level.
Another mechanism that helps bring the foreign exchange market back to equilibrium is the intervention of central banks. Central banks can buy or sell currencies to influence the exchange rate. For example, if the exchange rate is below its equilibrium level, the central bank can buy the undervalued currency to increase its value. Conversely, if the exchange rate is above its equilibrium level, the central bank can sell the overvalued currency to decrease its value.
Obtain direct knowledge about the efficiency of speculation and arbitrage in foreign exchange market through case studies.
Central Bank Intervention
Central banks play a crucial role in maintaining equilibrium in the foreign exchange market. They can intervene in the market by buying or selling currencies to influence the exchange rate. This intervention can help to stabilize the exchange rate and prevent large fluctuations that could harm the economy.
However, central bank intervention can also have negative consequences. For example, if a central bank intervenes too heavily in the market, it can create distortions and reduce the efficiency of the foreign exchange market. Therefore, central banks must carefully consider the costs and benefits of intervention before taking action.
Examples of Equilibrium in the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market achieves equilibrium when the demand for a currency equals its supply. Several factors can contribute to establishing equilibrium, including economic growth, interest rates, inflation, and political stability. Here are some real-world examples of how the foreign exchange market has achieved equilibrium:
US Dollar and Euro
In 2017, the US dollar and euro reached equilibrium at an exchange rate of approximately 1.18. This equilibrium was primarily driven by strong economic growth in both the United States and the Eurozone, leading to increased demand for both currencies. Additionally, interest rates in both regions were relatively similar, reducing the incentive for investors to move their money from one currency to another.
Japanese Yen and Chinese Yuan
In 2019, the Japanese yen and Chinese yuan reached equilibrium at an exchange rate of approximately 110 yen per yuan. This equilibrium was largely influenced by the trade relationship between Japan and China. As China’s economy grew rapidly, demand for Japanese goods increased, leading to increased demand for the yen. At the same time, Japan’s aging population and declining birth rate contributed to a decrease in the supply of the yen, further supporting the equilibrium exchange rate.
British Pound and Swiss Franc
In 2021, the British pound and Swiss franc reached equilibrium at an exchange rate of approximately 1.25 pounds per franc. This equilibrium was primarily driven by the political stability and economic growth in both the United Kingdom and Switzerland. Additionally, the Swiss franc’s safe-haven status during periods of global uncertainty contributed to increased demand for the currency, further supporting the equilibrium exchange rate.
The following table summarizes these examples of equilibrium in the foreign exchange market:
| Currency Pair | Exchange Rate | Contributing Factors |
|—|—|—|
| US Dollar / Euro | 1.18 | Strong economic growth, similar interest rates |
| Japanese Yen / Chinese Yuan | 110 yen per yuan | Increased trade between Japan and China, Japan’s aging population |
| British Pound / Swiss Franc | 1.25 pounds per franc | Political stability, economic growth, Swiss franc’s safe-haven status |
Closure
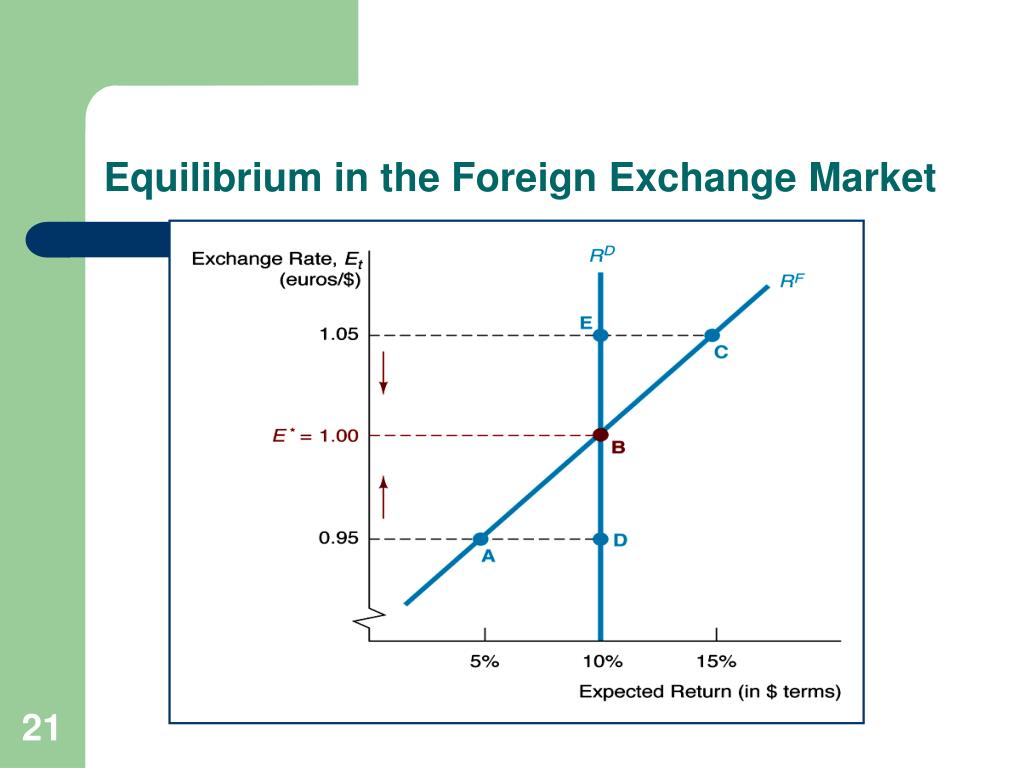
The foreign exchange market equilibrium is a dynamic concept, constantly adjusting to changing economic conditions. By understanding the factors that influence equilibrium, we gain insights into the intricate workings of the global financial system and its implications for our economic well-being.
