Foreign exchange market is an example of perfect competition – As Foreign Exchange Market Epitomizes Perfect Competition takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with casual formal language style into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
The foreign exchange market, a global marketplace for currency trading, stands as a prime example of perfect competition. This highly liquid and decentralized market exhibits characteristics that align closely with the theoretical construct of perfect competition, making it an ideal case study for economic analysis.
Definition of Perfect Competition
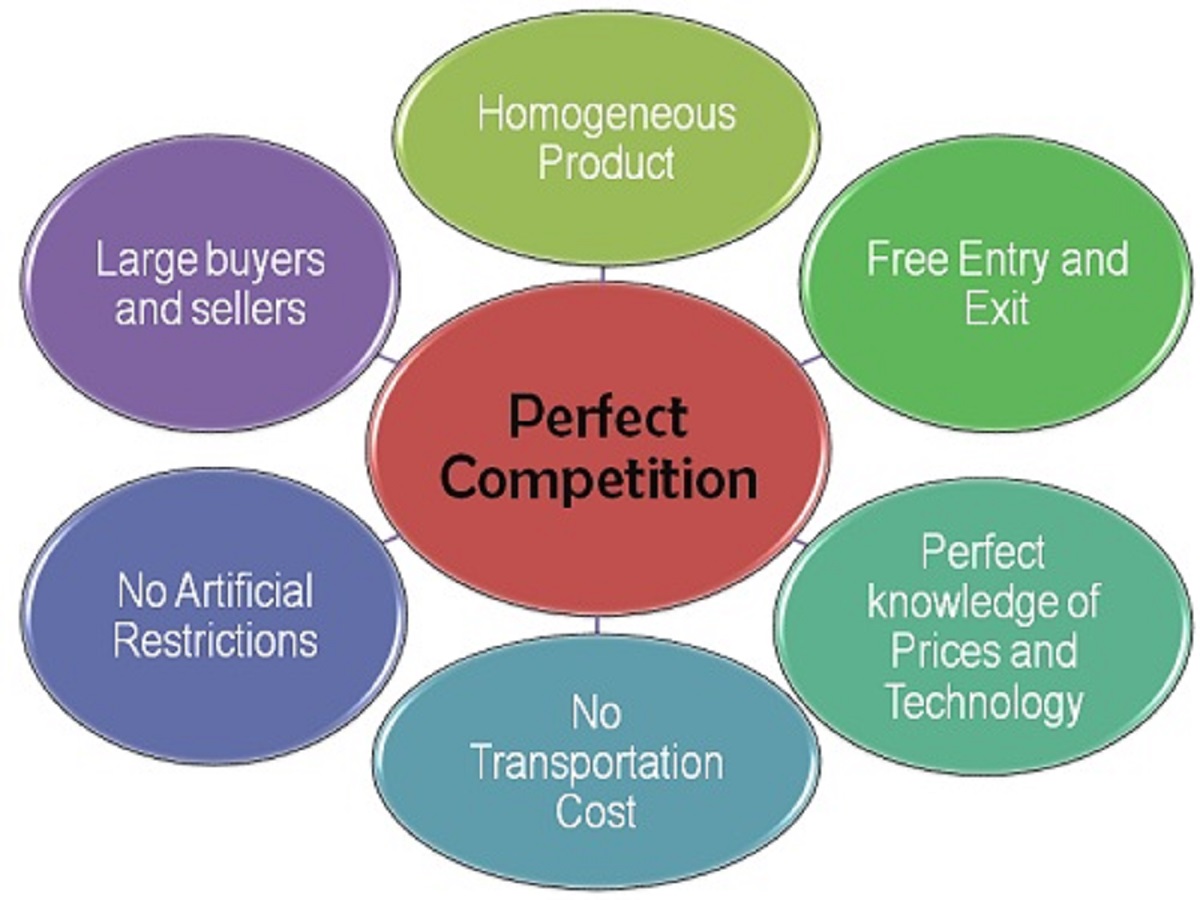
Perfect competition is a market structure in which there are many buyers and sellers, and each firm produces an identical product. This means that no single firm has any market power, and the price of the good is determined by the forces of supply and demand.
Characteristics of Perfect Competition
The characteristics of perfect competition are as follows:
- Many buyers and sellers: In a perfectly competitive market, there are so many buyers and sellers that no single firm can influence the market price.
- Identical products: The products sold by all firms in a perfectly competitive market are identical. This means that buyers are indifferent between the products of different firms.
- No barriers to entry or exit: Firms can freely enter or exit a perfectly competitive market. This means that there are no barriers to entry or exit, such as high start-up costs or government regulations.
- Perfect information: All buyers and sellers have perfect information about the market. This means that they know the prices of all the products in the market, as well as the costs of production.
Examples of Perfect Competition
Some examples of industries that exhibit perfect competition include:
- Agriculture: The market for agricultural products, such as corn, wheat, and soybeans, is a perfectly competitive market. There are many buyers and sellers, and the products are identical.
- Foreign exchange market: The market for foreign currencies is a perfectly competitive market. There are many buyers and sellers, and the products are identical.
- Stock market: The market for stocks is a perfectly competitive market. There are many buyers and sellers, and the products are identical.
Foreign Exchange Market Overview
The foreign exchange market (forex market or FX market) is a global decentralized market for the trading of currencies. It is the largest financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
The forex market is used by a wide range of participants, including banks, corporations, institutional investors, and retail traders. These participants use the forex market to exchange currencies for a variety of reasons, including:
Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market
- Banks: Banks are the largest participants in the forex market. They trade currencies on behalf of their customers, as well as for their own account.
- Corporations: Corporations use the forex market to exchange currencies for a variety of reasons, including:
- To pay for goods and services imported from other countries
- To receive payment for goods and services exported to other countries
- To hedge against currency fluctuations
- Institutional investors: Institutional investors, such as pension funds and hedge funds, use the forex market to invest in currencies. They may do this to diversify their portfolios or to speculate on currency movements.
- Retail traders: Retail traders are individuals who trade currencies for their own account. They may do this to speculate on currency movements or to make a profit from the difference in exchange rates.
Characteristics of the Foreign Exchange Market
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Perfect-Competition-2de51ba3fa8a40e9bdfdc7b98a195ce0.png)
The foreign exchange market, or forex market, is a global, decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion. The forex market is often compared to a perfect competition market due to its size, liquidity, and transparency.
When investigating detailed guidance, check out pasar valuta asing (foreign exchange market) adalah now.
A perfect competition market is a theoretical construct that describes a market in which there are many buyers and sellers, all of whom have perfect information about the market. In a perfect competition market, no single buyer or seller has the power to influence the price of the good or service being traded. The foreign exchange market meets many of the characteristics of a perfect competition market, including:
- Large number of buyers and sellers: The forex market is a global market with participants from all over the world. This large number of participants ensures that there is always someone willing to buy or sell a currency at any given time.
- Homogeneous product: All currencies are essentially the same product. They are all used to facilitate trade and investment. This homogeneity ensures that buyers and sellers are not concerned with the quality of the currency they are trading.
- Perfect information: The forex market is a very transparent market. All market participants have access to the same information about the prices of currencies. This transparency ensures that buyers and sellers can make informed decisions about their trades.
- No barriers to entry or exit: Anyone can participate in the forex market. There are no barriers to entry or exit, which ensures that the market is always competitive.
However, the foreign exchange market does not meet all of the characteristics of a perfect competition market. One of the most important characteristics of a perfect competition market is that no single buyer or seller has the power to influence the price of the good or service being traded. In the forex market, there are a few large banks that have a significant share of the market. These banks can sometimes influence the price of currencies, especially in times of high volatility.
Despite this, the foreign exchange market is a very competitive market. The large number of participants, the homogeneous product, and the perfect information ensure that buyers and sellers can always find a fair price for their currencies.
Browse the implementation of economics definition of foreign exchange market in real-world situations to understand its applications.
Implications of Perfect Competition in the Foreign Exchange Market
Perfect competition in the foreign exchange market leads to several significant implications that shape its efficiency and pricing dynamics.
Finish your research with information from foreign exchange market notes.
Efficiency of the Foreign Exchange Market
Perfect competition promotes efficiency in the foreign exchange market by ensuring:
- High Liquidity: A large number of participants and the ease of entry and exit create a deep and liquid market, facilitating smooth and efficient transactions.
- Transparency: The availability of real-time information and the absence of barriers to entry foster transparency, allowing market participants to make informed decisions.
- Low Transaction Costs: The presence of numerous competitors drives down transaction costs, benefiting both individuals and businesses engaged in foreign exchange transactions.
Pricing of Currencies
In a perfectly competitive foreign exchange market, the exchange rates between currencies are determined by the forces of supply and demand:
- Supply and Demand: The exchange rate of a currency is influenced by the relative supply and demand for that currency in the market. When demand for a currency increases, its value tends to rise, and vice versa.
- No Arbitrage: The absence of arbitrage opportunities ensures that the exchange rates across different markets are aligned, preventing any potential profit from buying and selling currencies in different markets.
- Market Equilibrium: The interaction of supply and demand ultimately leads to a market equilibrium, where the exchange rate settles at a level that balances the forces of supply and demand.
Exceptions to Perfect Competition in the Foreign Exchange Market
Perfect competition in the foreign exchange market is an ideal scenario where many buyers and sellers freely participate, leading to efficient price discovery and market equilibrium. However, there are certain factors that can hinder perfect competition in the forex market.
Market Concentration
A few large financial institutions, such as investment banks and hedge funds, control a significant share of the forex market. This market concentration can lead to reduced competition, giving these institutions the power to influence currency prices and affect market dynamics.
Information Asymmetry
In the forex market, participants have varying levels of access to information and expertise. Some institutions have advanced trading platforms and real-time data feeds, while others may have limited resources. This asymmetry can create an uneven playing field, potentially leading to unfair advantages for certain participants.
Government Intervention
Governments sometimes intervene in the forex market to influence currency exchange rates. This can be done through measures such as currency pegs, capital controls, or quantitative easing. Government intervention can distort market forces and hinder perfect competition.
Transaction Costs
Trading in the forex market involves transaction costs, such as bid-ask spreads and commissions. These costs can add up over time, especially for smaller participants. Transaction costs can create barriers to entry and reduce competition, particularly for retail traders.
Implications of Exceptions on Efficiency and Pricing, Foreign exchange market is an example of perfect competition
Exceptions to perfect competition in the foreign exchange market can have significant implications for market efficiency and currency pricing. Market concentration can lead to reduced liquidity and increased volatility, making it more difficult for participants to execute trades at fair prices. Information asymmetry can give certain participants an unfair advantage, potentially leading to price manipulation. Government intervention can distort market forces and create artificial price levels. Transaction costs can discourage participation and reduce competition, particularly for smaller traders.
Final Summary: Foreign Exchange Market Is An Example Of Perfect Competition
In conclusion, the foreign exchange market serves as a compelling example of perfect competition. Its vast size, numerous participants, and transparent pricing mechanisms contribute to its efficiency and resilience. While certain exceptions may arise, the market’s overall adherence to the principles of perfect competition underscores its significance as a benchmark for economic analysis.