Ap macroeconomics the foreign exchange market worksheet – Embark on a journey through the captivating realm of the foreign exchange market with AP Macroeconomics: The Foreign Exchange Market Worksheet. Prepare to unravel the intricacies of currency exchange, explore the forces that shape exchange rates, and delve into the strategies for navigating this dynamic global marketplace.
The worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the foreign exchange market, encompassing its key players, transaction types, market dynamics, risks, and regulatory framework. Through engaging discussions and practical examples, you will gain a deep understanding of the forces that drive currency fluctuations and the strategies employed by market participants to manage risk.
Foreign Exchange Market Overview
The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market or currency market, is a global decentralized market where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of trillions of dollars.
The foreign exchange market plays a crucial role in international trade and finance. It allows businesses to import and export goods and services, and it facilitates cross-border investments and transactions.
You also will receive the benefits of visiting foreign exchange market project pdf today.
Major Currencies Traded
The most traded currencies in the foreign exchange market are:
- US dollar (USD)
- Euro (EUR)
- Japanese yen (JPY)
- British pound (GBP)
- Swiss franc (CHF)
Factors Influencing Exchange Rates
The exchange rate between two currencies is determined by a number of factors, including:
- Economic growth
- Interest rates
- Inflation
- Political stability
- Supply and demand
Key Players in the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market involves a wide range of participants, each playing a distinct role in shaping the market’s dynamics.
Central banks, commercial banks, and other financial institutions serve as the primary intermediaries in the market, facilitating currency exchange transactions for various purposes. Speculators and retail traders also contribute to the market’s activity, influencing exchange rates through their trading strategies.
Central Banks
- Responsible for managing monetary policy and regulating the financial system within their respective countries.
- Engage in foreign exchange interventions to influence exchange rates and maintain economic stability.
- Hold substantial foreign exchange reserves to support their currencies and intervene in the market when necessary.
Commercial Banks
- Provide foreign exchange services to businesses and individuals, facilitating international trade and payments.
- Act as market makers, quoting bid and ask prices for currencies and facilitating transactions.
- Manage foreign exchange risk for their clients and hold foreign exchange positions to meet customer demands.
Other Financial Institutions
- Investment banks, hedge funds, and pension funds engage in foreign exchange trading for various purposes, including investment, hedging, and speculation.
- Non-bank financial institutions, such as money transfer companies and currency exchanges, provide foreign exchange services to retail customers.
- Electronic trading platforms facilitate online currency trading, connecting buyers and sellers globally.
Speculators and Retail Traders
- Speculators attempt to profit from short-term fluctuations in exchange rates by buying and selling currencies.
- Retail traders engage in foreign exchange trading on a smaller scale, often using online platforms and leverage to enhance potential returns.
- The activities of speculators and retail traders can contribute to market volatility and liquidity.
Types of Foreign Exchange Transactions
Foreign exchange transactions encompass various types, each tailored to specific needs and purposes in the foreign exchange market. These transactions are broadly categorized into three primary types: spot transactions, forward transactions, and currency swaps.
Spot Transactions
Spot transactions involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the prevailing market rate. These transactions are typically settled within two business days, making them suitable for immediate currency needs.
Forward Transactions
Forward transactions, also known as foreign exchange forwards, are contracts that lock in an exchange rate for a future date. These transactions allow businesses and investors to hedge against currency fluctuations and secure future currency needs at a predetermined rate.
Explore the different advantages of foreign exchange market in simple words that can change the way you view this issue.
Currency Swaps
Currency swaps are agreements between two parties to exchange currencies at a specific rate on a predetermined date. These transactions are often used for long-term currency management and to mitigate foreign exchange risk.
Foreign Exchange Market Dynamics
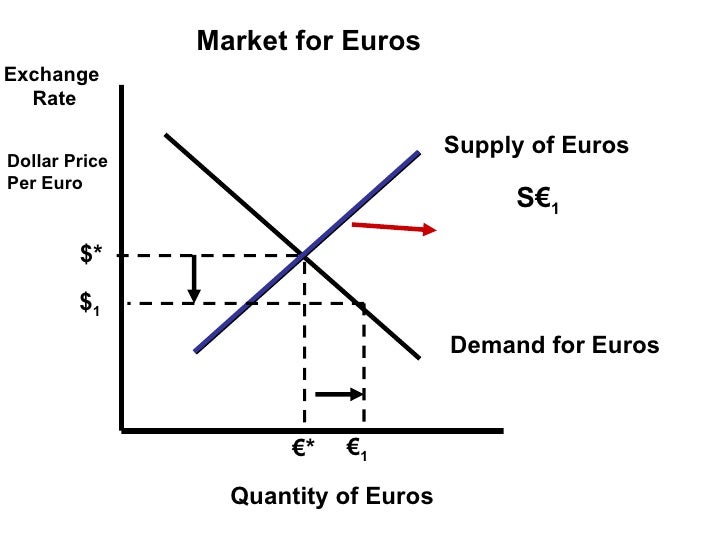
The foreign exchange market is a dynamic and ever-changing environment, influenced by a wide range of factors that affect the supply and demand for foreign currencies. These factors can be broadly categorized into economic data, political events, and market sentiment.
Economic Data
Economic data plays a crucial role in shaping currency exchange rates. Key economic indicators such as GDP growth, inflation, unemployment rates, and interest rates provide valuable insights into the health of a country’s economy. Strong economic data typically leads to an appreciation of the currency, while weak data can cause depreciation. For example, if the US economy is growing at a faster pace than the Eurozone, the demand for US dollars will increase, leading to an appreciation of the dollar against the euro.
Political Events
Political events can have a significant impact on the foreign exchange market. Changes in government policies, elections, and geopolitical tensions can create uncertainty and volatility in the market. For instance, the Brexit vote in 2016 led to a sharp depreciation of the British pound as investors reacted to the potential economic consequences of the UK’s exit from the European Union.
Market Sentiment
Market sentiment refers to the overall attitude of market participants towards a particular currency or asset. Positive sentiment, driven by factors such as optimism about economic growth or geopolitical stability, can lead to increased demand for a currency and its appreciation. Conversely, negative sentiment, fueled by concerns about economic downturns or political instability, can cause a currency to depreciate.
Historical events have played a significant role in shaping the foreign exchange market. The 2008 financial crisis, for example, led to a global recession and a sharp depreciation of many currencies against the US dollar, which was seen as a safe haven asset. The subsequent quantitative easing measures implemented by central banks around the world also had a significant impact on currency exchange rates.
Foreign Exchange Market Risks: Ap Macroeconomics The Foreign Exchange Market Worksheet

Engaging in foreign exchange trading exposes participants to various risks that can impact their financial positions. These risks can arise from factors such as currency fluctuations, interest rate changes, and political events.
It is crucial for market participants to understand and mitigate these risks effectively to preserve capital and achieve their investment objectives.
Currency Risk
Currency risk refers to the potential loss or gain resulting from changes in the exchange rates between two currencies. When the value of a currency appreciates (increases) against another, it can result in losses for those holding the depreciating currency and gains for those holding the appreciating currency.
Currency risk is particularly relevant for businesses that operate internationally and have exposure to multiple currencies. Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact their revenue, expenses, and overall profitability.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk arises when changes in interest rates affect the value of foreign exchange contracts. When interest rates rise in one country relative to another, it can make it more attractive to hold the currency of the country with higher interest rates. This can lead to an appreciation of the currency and potential losses for those holding the currency with lower interest rates.
Interest rate risk is a concern for investors who hold foreign bonds or other interest-bearing securities denominated in different currencies.
Political Risk
Political risk refers to the potential for political events or changes in government policies to adversely affect the value of a currency. Political instability, economic sanctions, or changes in foreign exchange regulations can all contribute to currency volatility and create risks for foreign exchange traders.
Political risk is particularly relevant for emerging markets and countries with unstable political environments. It can make it difficult to predict the future value of a currency and increase the likelihood of unexpected losses.
Learn about more about the process of foreign exchange market today news in the field.
Strategies for Mitigating Risks
There are various strategies that foreign exchange traders can employ to mitigate these risks. These include:
- Hedging: Using financial instruments, such as forward contracts or options, to offset potential losses from currency fluctuations.
- Diversification: Investing in a portfolio of currencies to reduce the impact of any single currency’s depreciation.
- Currency Forecasting: Using economic and political analysis to predict future currency movements and make informed trading decisions.
- Risk Management: Setting clear risk limits and implementing stop-loss orders to prevent excessive losses.
Foreign Exchange Market Regulation

The foreign exchange market operates within a regulatory framework established by central banks and other regulatory bodies to ensure its stability and integrity.
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, play a crucial role in regulating the foreign exchange market by setting interest rates, managing foreign exchange reserves, and intervening in the market to stabilize exchange rates.
Role of Central Banks
- Setting interest rates: Central banks adjust interest rates to influence the flow of funds in and out of a country, thereby affecting the demand for and supply of foreign currencies.
- Managing foreign exchange reserves: Central banks hold reserves of foreign currencies to intervene in the market when necessary to stabilize exchange rates.
- Intervention in the market: Central banks may buy or sell foreign currencies to influence exchange rates and prevent excessive volatility.
Other Regulatory Bodies, Ap macroeconomics the foreign exchange market worksheet
In addition to central banks, other regulatory bodies also play a role in overseeing the foreign exchange market:
- Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the United Kingdom
- Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) in the United States
- International Monetary Fund (IMF)
These bodies set regulations to ensure fair and transparent trading practices, prevent market manipulation, and protect investors.
Impact of Regulation on Market Participants
Regulation has a significant impact on market participants:
- Increased transparency: Regulations require market participants to disclose information about their transactions, which enhances transparency and reduces the risk of fraud.
- Reduced systemic risk: Regulation aims to minimize systemic risk by ensuring that market participants operate within sound financial practices and risk management frameworks.
- Increased compliance costs: Regulations impose compliance costs on market participants, which can impact their profitability.
Technology and the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market has undergone a significant transformation due to the advent of technology. Electronic trading platforms and algorithmic trading have revolutionized the way currencies are traded, making the market more accessible, efficient, and transparent.
Electronic Trading Platforms
- Electronic trading platforms, such as EBS and Bloomberg FXGO, have replaced traditional over-the-counter trading methods. These platforms provide a centralized marketplace where traders can execute trades electronically, reducing transaction costs and increasing liquidity.
- Electronic trading platforms offer real-time price quotes, allowing traders to make informed decisions and execute trades quickly.
- They also facilitate anonymity, as traders do not need to interact directly with each other, which can reduce potential conflicts of interest.
Algorithmic Trading
- Algorithmic trading involves using computer programs to execute trades based on pre-defined rules and algorithms. This automated approach allows traders to trade large volumes of currencies quickly and efficiently.
- Algorithmic trading can help traders capitalize on market inefficiencies and execute complex trading strategies.
- However, algorithmic trading can also increase market volatility and liquidity, as it can lead to rapid and large-scale buying or selling.
Blockchain and Other Emerging Technologies
- Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the foreign exchange market by providing a secure and transparent platform for currency trading.
- Blockchain can eliminate the need for intermediaries, reducing transaction costs and increasing settlement speed.
- Other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, are also being explored to improve the efficiency and accuracy of foreign exchange trading.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the AP Macroeconomics: The Foreign Exchange Market Worksheet serves as an invaluable resource for students seeking to master the intricacies of this global marketplace. By delving into the complexities of exchange rates, market dynamics, and risk management, you will emerge with a profound understanding of the factors that shape the foreign exchange market and the strategies necessary to navigate its ever-changing landscape.
