Bis the foreign exchange market – BIS: Delving into the Labyrinth of the Foreign Exchange Market. A comprehensive guide to understanding the intricacies of the world’s largest financial market, where currencies dance and economies intertwine. Immerse yourself in the dynamics, instruments, and regulations that shape this ever-evolving landscape.
The foreign exchange market, a colossal arena where currencies are traded, serves as the lifeblood of international commerce. Its sheer size, with an estimated daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion, underscores its significance in facilitating global trade and investment. This market, a melting pot of participants ranging from central banks to retail traders, plays a pivotal role in determining exchange rates, influencing economic growth, and shaping geopolitical dynamics.
Market Overview
The foreign exchange (forex) market is a global decentralized market for the trading of currencies. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
The forex market is open 24 hours a day, five days a week, and is traded electronically over-the-counter (OTC). This means that there is no central exchange where currencies are traded, and instead, transactions are conducted directly between two parties.
Major Currencies Traded
The most heavily traded currencies in the forex market are the US dollar (USD), the euro (EUR), the Japanese yen (JPY), the British pound (GBP), and the Swiss franc (CHF). These currencies are known as the “majors” and account for over 80% of all forex trading.
Browse the multiple elements of foreign exchange market of india to gain a more broad understanding.
The relative importance of each currency is determined by a number of factors, including the size of the country’s economy, the stability of its political system, and the interest rates set by its central bank.
Market Participants

The foreign exchange market is a global decentralized market where currencies are traded. It involves a wide range of participants with diverse roles and motivations.
Participants in the foreign exchange market can be broadly classified into the following categories:
Commercial Participants
- Importers and exporters: Businesses that engage in international trade need to convert their domestic currency into foreign currencies to pay for goods and services imported from abroad, and convert foreign currencies into their domestic currency to receive payment for goods and services exported.
- Multinational corporations: Companies with operations in multiple countries need to manage their foreign exchange exposure and make payments in different currencies.
Financial Institutions
- Banks: Commercial banks play a crucial role in facilitating foreign exchange transactions for their clients. They provide services such as currency exchange, international payments, and hedging products.
- Investment banks: These institutions engage in foreign exchange trading for their own account, as well as for their clients. They provide liquidity to the market and offer a range of financial products related to foreign exchange.
- Forex brokers: Brokers act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers of foreign currencies. They provide access to the foreign exchange market and offer various trading platforms and services.
Central Banks
- Central banks: Central banks are responsible for managing the monetary policy of their respective countries. They intervene in the foreign exchange market to influence the value of their currencies and achieve macroeconomic objectives such as price stability and economic growth.
Other Participants
- Hedge funds: Hedge funds use foreign exchange trading as part of their investment strategies to generate profits.
- Retail traders: Individual traders participate in the foreign exchange market through online platforms and brokers.
Each type of participant has specific motivations and objectives in the foreign exchange market. Commercial participants aim to minimize transaction costs and manage their foreign exchange exposure. Financial institutions seek to profit from trading and providing services. Central banks focus on managing their currencies and achieving macroeconomic goals. Other participants participate for investment purposes or speculation.
Market Dynamics
The foreign exchange market is a dynamic and ever-changing environment, with exchange rates constantly fluctuating due to a multitude of factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for traders and investors seeking to navigate the market successfully.
The primary determinant of exchange rates is the interplay of supply and demand for currencies. When demand for a currency exceeds its supply, its value appreciates, while a decrease in demand or an increase in supply leads to depreciation.
Economic Data, Bis the foreign exchange market
Economic data plays a significant role in shaping exchange rates. Positive economic indicators, such as strong GDP growth, low unemployment, and rising inflation, typically strengthen a currency, as they signal a healthy and growing economy. Conversely, negative economic data, such as weak GDP growth, high unemployment, and falling inflation, can lead to currency depreciation.
Political Events
Political events can also have a significant impact on exchange rates. Political instability, elections, changes in government policies, and international conflicts can all affect the perceived risk associated with a country and its currency. Increased risk can lead to currency depreciation, while reduced risk can lead to appreciation.
Market Sentiment
Market sentiment, or the overall attitude of traders and investors towards a currency, can also influence exchange rates. Positive sentiment, such as optimism about a country’s economic prospects or political stability, can lead to currency appreciation. Negative sentiment, such as pessimism about the economy or concerns about political instability, can lead to depreciation.
Enhance your insight with the methods and methods of foreign exchange market data.
Trading Instruments and Techniques
Foreign exchange trading involves a diverse range of instruments and techniques. Understanding these aspects is crucial for navigating the complexities of the market.
Types of Foreign Exchange Trading Instruments
- Spot Transactions: Immediate exchange of currencies at the prevailing market rate.
- Forward Contracts: Agreements to exchange currencies at a specified future date and rate.
- Currency Swaps: Exchange of principal and interest payments in different currencies.
- Options: Contracts that provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a predetermined price and date.
- Futures: Standardized contracts to buy or sell a currency at a specific price and date in the future.
Mechanics of Foreign Exchange Trading
Foreign exchange trading occurs through electronic platforms that connect banks, brokers, and other market participants. Traders place orders to buy or sell currencies, and these orders are matched by counterparties with opposite interests. The exchange rates are determined by supply and demand in the market.
Trading Strategies and Risk Management Techniques
Traders employ various strategies to capitalize on market movements. These include:
- Trend Following: Identifying and trading in the direction of prevailing trends.
- Counter-Trend Trading: Attempting to profit from short-term reversals in market direction.
- Carry Trading: Borrowing in one currency with low interest rates and investing in another currency with higher rates.
- Scalping: Taking small profits on numerous trades throughout the day.
Risk management is essential in foreign exchange trading. Common techniques include:
- Stop-Loss Orders: Automatic orders to close a trade if the price moves against the trader’s position.
- Take-Profit Orders: Automatic orders to close a trade when a specific profit target is reached.
- Position Sizing: Managing the size of trades relative to the trader’s account balance.
- Hedging: Using one instrument to offset the risk of another.
Market Regulation and Oversight
The foreign exchange market, due to its global reach and substantial financial flows, requires robust regulation and oversight to ensure market stability, protect participants, and prevent financial irregularities. Various regulatory bodies, including central banks, play crucial roles in establishing and enforcing regulations that govern the market’s operations.
Discover more by delving into shifters of foreign exchange market ap macro further.
Central banks, as monetary authorities, hold significant responsibilities in regulating the foreign exchange market. They implement monetary policies that influence currency values and oversee foreign exchange reserves to maintain exchange rate stability. Central banks also collaborate internationally to coordinate policies and address cross-border financial issues.
Role of Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies play a vital role in ensuring market integrity and participant compliance. They establish rules and regulations governing market conduct, transparency, and risk management practices. Regulatory bodies also monitor market activities, investigate potential misconduct, and enforce penalties for violations. Their presence helps maintain market order, protects investors, and fosters fair and ethical trading practices.
Technology and Innovation

Technology has revolutionized the foreign exchange market, making it more efficient, transparent, and accessible. Electronic trading platforms have replaced traditional over-the-counter (OTC) trading, allowing traders to execute orders instantly and anonymously. Algorithmic trading, where computer programs execute trades based on pre-defined rules, has also become prevalent, enabling traders to automate their trading strategies.
Electronic Trading Platforms
Electronic trading platforms provide a centralized marketplace where traders can connect with each other and execute orders. These platforms offer real-time pricing, liquidity, and anonymity, making it easier for traders to find the best prices and execute their trades efficiently. Examples of popular electronic trading platforms include EBS, Reuters Dealing, and Bloomberg FXGO.
Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading involves using computer programs to execute trades based on pre-defined rules and strategies. These algorithms can analyze market data, identify trading opportunities, and execute trades automatically. Algorithmic trading allows traders to automate their trading strategies, reduce execution times, and improve overall performance.
Latest Trends and Innovations
The foreign exchange market is constantly evolving, with new technologies and innovations emerging all the time. Some of the latest trends include the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to analyze market data and identify trading opportunities. Blockchain technology is also being explored for its potential to enhance security and transparency in the foreign exchange market.
Market Outlook and Future Trends: Bis The Foreign Exchange Market
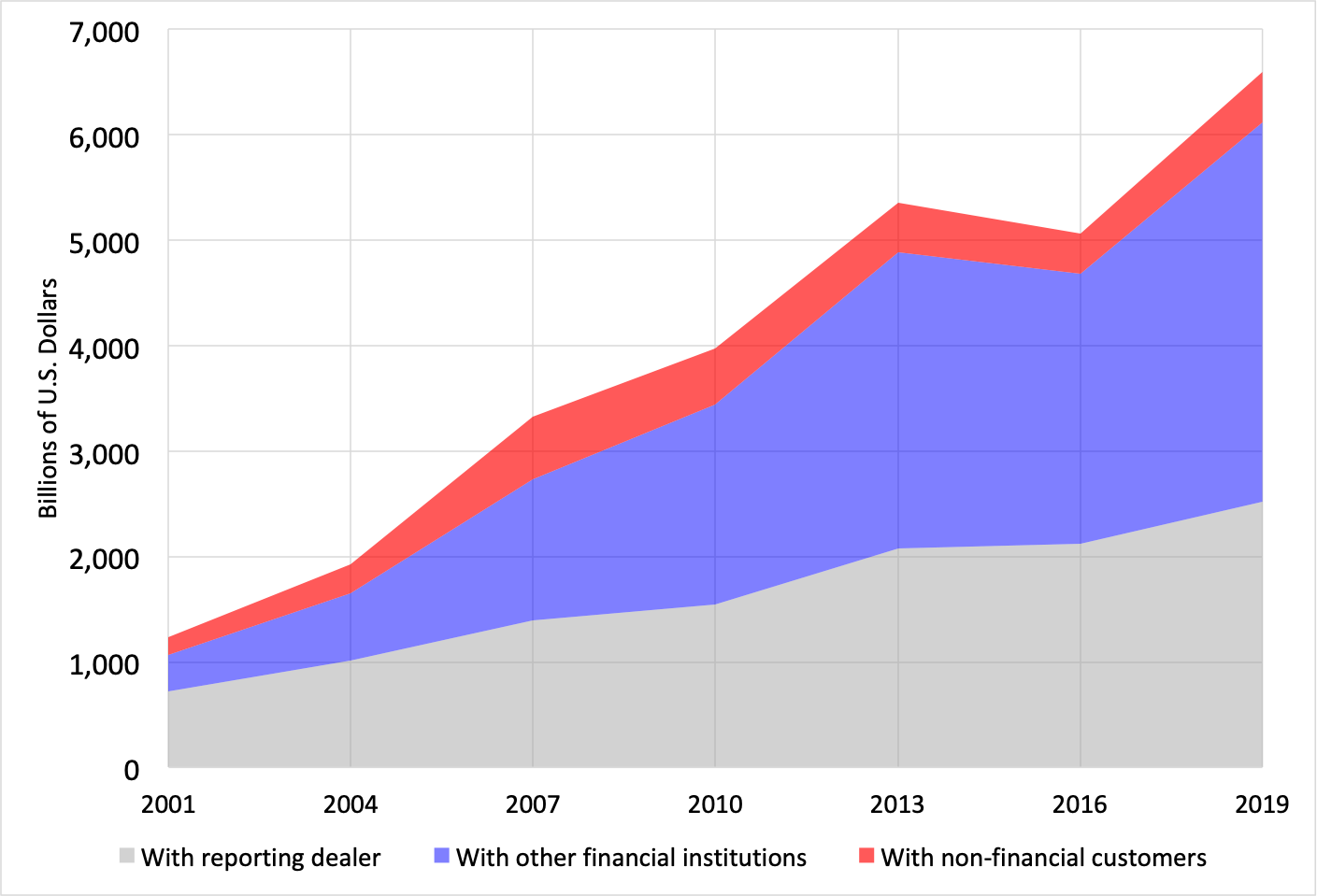
The foreign exchange market is constantly evolving, and its future outlook is shaped by a complex interplay of economic, political, and technological factors. Despite the challenges, the market is expected to continue to grow in the coming years, driven by increasing global trade and investment.
One of the key growth areas for the foreign exchange market is the increasing use of electronic trading platforms. These platforms have made it easier and more efficient for traders to access the market, and they have also reduced the cost of trading. As a result, electronic trading is expected to continue to grow in popularity in the coming years.
Another key trend in the foreign exchange market is the increasing use of mobile trading apps. These apps allow traders to access the market from anywhere in the world, and they have made it easier for retail investors to participate in the market. As a result, mobile trading is expected to continue to grow in popularity in the coming years.
Challenges and Opportunities
The foreign exchange market is not without its challenges. One of the biggest challenges is the volatility of the market. Currency prices can fluctuate rapidly, and this can make it difficult for traders to make a profit. However, volatility also creates opportunities for traders to make a profit, and it is one of the reasons why the market is so popular.
Another challenge facing the foreign exchange market is the increasing regulation of the market. Regulators are concerned about the potential for fraud and abuse in the market, and they are taking steps to increase oversight of the market. This regulation is expected to continue in the coming years, and it could have a significant impact on the market.
Last Point
As we navigate the complexities of the foreign exchange market, it becomes evident that its impact extends far beyond the realm of finance. Exchange rate fluctuations can ripple through economies, affecting inflation, trade balances, and overall economic stability. Understanding the intricacies of this market empowers us to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and harness its potential for growth and prosperity.
