Capital flows in foreign exchange market – Capital flows in the foreign exchange market stand as the driving force behind the ebb and flow of currency values. This intricate interplay between economics, politics, and global finance shapes the very fabric of international trade and investment.
From the bustling streets of Tokyo to the boardrooms of London, capital flows exert a profound influence on exchange rates, economic growth, and the interconnectedness of global markets.
Definition of Capital Flows in Foreign Exchange Market
Capital flows in the foreign exchange market refer to the movement of financial capital across borders. These flows can be motivated by various factors, including economic growth prospects, interest rate differentials, and political stability.
Capital flows can take different forms, such as foreign direct investment (FDI), portfolio investment, and short-term capital flows.
Types of Capital Flows
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): FDI involves the establishment of a long-term presence in a foreign country through the acquisition of assets, such as factories, equipment, or real estate.
- Portfolio Investment: Portfolio investment refers to the purchase of foreign stocks, bonds, or other financial assets that do not confer ownership or control over the underlying company.
- Short-Term Capital Flows: Short-term capital flows are short-term investments that are typically motivated by interest rate differentials and currency fluctuations. These flows can be volatile and can lead to rapid changes in exchange rates.
Factors Influencing Capital Flows
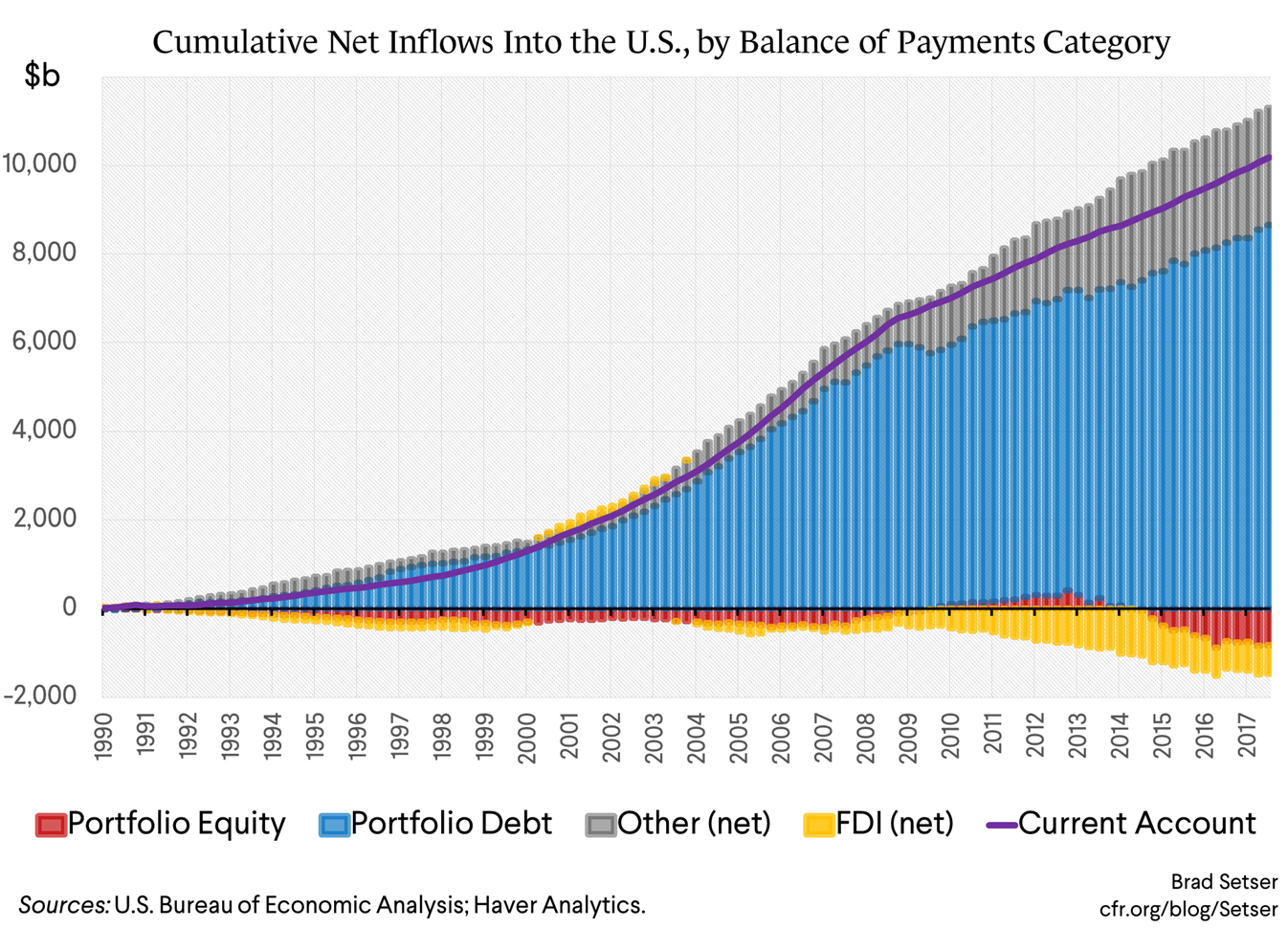
Capital flows in the foreign exchange market are influenced by a complex interplay of economic, political, and social factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for policymakers and investors alike.
In this topic, you find that exchange arbitrage is very useful.
Economic factors that affect capital flows include interest rates, inflation, and economic growth. Interest rate differentials between countries can attract or deter capital inflows, as investors seek higher returns. Inflationary pressures and economic growth prospects also influence capital flows, as investors seek stability and opportunities for growth.
Political and Social Factors
Political and social stability play a significant role in capital flows. Investors are more likely to invest in countries with stable political systems, strong institutions, and low levels of corruption. Social factors, such as cultural affinity and trade relationships, can also influence capital flows.
Role of Central Banks and Governments
Central banks and governments play a critical role in managing capital flows. Central banks use monetary policy tools, such as interest rate adjustments, to influence the attractiveness of their currency for investment. Governments implement fiscal policies, such as tax incentives or infrastructure investments, to attract foreign capital.
Impact of Capital Flows on Exchange Rates
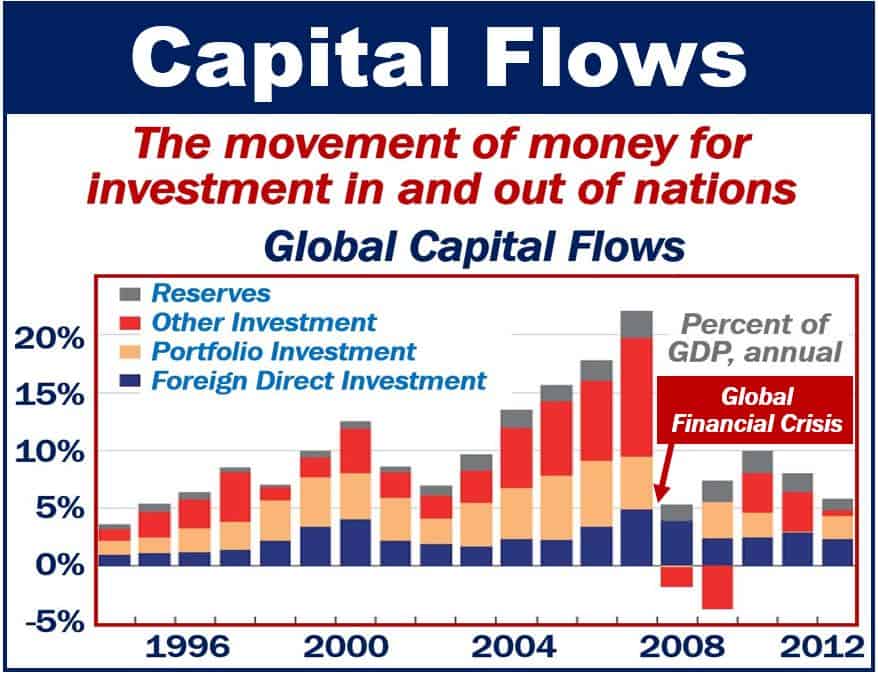
Capital flows significantly influence exchange rates by altering the demand and supply of currencies in the foreign exchange market. When there is a net inflow of capital into a country, the demand for its currency increases, leading to currency appreciation. Conversely, a net outflow of capital results in decreased demand for the currency, causing depreciation.
Finish your research with information from difference between money market and foreign exchange market pdf.
Capital Inflows
Capital inflows occur when foreign investors purchase domestic assets, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate. This increased demand for the domestic currency drives up its value, leading to appreciation. For example, if a large foreign investment fund decides to invest heavily in the US stock market, it will need to exchange its foreign currency for US dollars, increasing the demand for the dollar and causing it to appreciate against other currencies.
Capital Outflows
Capital outflows occur when domestic investors sell foreign assets or invest in foreign markets. This reduces the demand for the domestic currency, leading to depreciation. For example, if a large domestic company decides to invest in a foreign country, it will need to exchange its domestic currency for the foreign currency, increasing the supply of the domestic currency and causing it to depreciate against other currencies.
Obtain access to foreign exchange market project file to private resources that are additional.
Capital Controls and Their Effects: Capital Flows In Foreign Exchange Market
Capital controls are government regulations that restrict the flow of capital into and out of a country. They can be used to manage exchange rates, protect the domestic financial system, or influence the level of foreign investment.
There are different types of capital controls, including:
- Outflow controls: These controls restrict the movement of capital out of a country.
- Inflow controls: These controls restrict the movement of capital into a country.
- Exchange controls: These controls restrict the exchange of one currency for another.
Capital controls can have both benefits and drawbacks.
Potential Benefits
Potential benefits of capital controls include:
- Managing exchange rates: Capital controls can be used to stabilize exchange rates by preventing large inflows or outflows of capital.
- Protecting the domestic financial system: Capital controls can be used to protect the domestic financial system from external shocks, such as a sudden reversal of capital flows.
- Influencing the level of foreign investment: Capital controls can be used to influence the level of foreign investment in a country.
Potential Drawbacks, Capital flows in foreign exchange market
Potential drawbacks of capital controls include:
- Reduced economic growth: Capital controls can reduce economic growth by discouraging foreign investment and limiting access to foreign capital.
- Increased volatility: Capital controls can increase exchange rate volatility by making it more difficult for investors to adjust their positions.
- Black markets: Capital controls can lead to the development of black markets for foreign exchange, which can undermine the effectiveness of the controls.
The decision of whether or not to implement capital controls is a complex one that depends on a number of factors, including the country’s economic conditions, its political situation, and its relationship with the global financial system.
Capital Flows and Economic Development
Capital flows play a significant role in the economic development of countries. They can provide much-needed investment for developing countries, contributing to economic growth, infrastructure development, and job creation.
Potential Benefits of Capital Inflows
- Increased investment: Capital inflows can provide additional capital for businesses and governments to invest in productive activities, leading to economic growth.
- Improved infrastructure: Foreign investment can help finance the construction of roads, bridges, and other infrastructure projects, which can improve the business environment and attract further investment.
- Job creation: Capital inflows can create new jobs in industries that receive foreign investment.
- Access to new technologies: Foreign investment can bring new technologies and expertise to developing countries, helping to improve productivity and competitiveness.
- Currency appreciation: Capital inflows can lead to currency appreciation, making it cheaper for countries to import goods and services.
Potential Risks of Capital Inflows
- Exchange rate volatility: Sudden changes in capital flows can lead to exchange rate volatility, which can disrupt trade and investment.
- Inflation: Large capital inflows can lead to inflation if they are not managed properly.
- Financial instability: Excessive capital inflows can lead to financial instability, such as asset bubbles and financial crises.
- Dependence on foreign investment: Developing countries that rely heavily on capital inflows may become vulnerable to external shocks, such as changes in global financial markets.
- Debt accumulation: Foreign investment can lead to increased debt levels, which can become a burden on the country’s economy.
Final Wrap-Up

In conclusion, capital flows in the foreign exchange market are a multifaceted phenomenon that presents both opportunities and challenges for nations and investors alike. Understanding their dynamics is crucial for navigating the ever-changing landscape of global finance and fostering sustainable economic development.
