The foreign exchange market course hero is an indispensable resource for anyone looking to delve into the world of currency trading. This comprehensive guide provides a thorough overview of the foreign exchange market, its key players, and the factors that influence currency rates. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or just starting out, this course will equip you with the knowledge and skills you need to navigate the complex world of foreign exchange.
This course covers a wide range of topics, including the history of the foreign exchange market, the different types of foreign exchange transactions, and the risks associated with foreign exchange trading. You’ll also learn about the regulatory framework for the foreign exchange market and how to manage and mitigate risks.
Introduction to the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market, often known as the forex market, is a global marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $5 trillion. The forex market is open 24 hours a day, five days a week, and it operates in all major financial centers around the world.
The forex market plays a vital role in global trade and finance. It allows businesses and individuals to exchange currencies so that they can conduct international transactions. The forex market also helps to determine the exchange rates between different currencies, which can have a significant impact on the prices of goods and services.
History of the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market has a long and complex history. The earliest known currency exchange took place in ancient Mesopotamia in the 3rd millennium BC. In the Middle Ages, the forex market was used by merchants to facilitate trade between different regions of Europe. The modern forex market began to develop in the 19th century, with the rise of international trade and investment. The market has continued to grow and evolve in the 20th and 21st centuries, and it is now the largest financial market in the world.
Importance of the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is important for a number of reasons. First, it allows businesses and individuals to exchange currencies so that they can conduct international transactions. Second, the forex market helps to determine the exchange rates between different currencies, which can have a significant impact on the prices of goods and services. Third, the forex market provides a way for investors to hedge against currency risk. Finally, the forex market is a source of liquidity for banks and other financial institutions.
You also can investigate more thoroughly about foreign exchange market mcq questions and answers to enhance your awareness in the field of foreign exchange market mcq questions and answers.
Major Players in the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is a global marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion. The major players in the foreign exchange market are banks, institutional investors, corporations, and retail traders.
Banks are the largest players in the foreign exchange market. They provide liquidity to the market and facilitate the trading of currencies between their clients. Institutional investors, such as hedge funds and pension funds, are also major players in the foreign exchange market. They use the foreign exchange market to hedge their portfolios against currency risk and to speculate on currency movements.
Corporations are another major player in the foreign exchange market. They use the foreign exchange market to manage their currency risk and to facilitate their international trade. Retail traders are also active in the foreign exchange market, but they account for a relatively small share of the overall trading volume.
Roles and Responsibilities
The roles and responsibilities of the major players in the foreign exchange market vary. Banks provide liquidity to the market and facilitate the trading of currencies between their clients. Institutional investors use the foreign exchange market to hedge their portfolios against currency risk and to speculate on currency movements. Corporations use the foreign exchange market to manage their currency risk and to facilitate their international trade. Retail traders use the foreign exchange market to speculate on currency movements.
Interactions
The major players in the foreign exchange market interact with each other in a variety of ways. Banks provide liquidity to the market and facilitate the trading of currencies between their clients. Institutional investors use the foreign exchange market to hedge their portfolios against currency risk and to speculate on currency movements. Corporations use the foreign exchange market to manage their currency risk and to facilitate their international trade. Retail traders use the foreign exchange market to speculate on currency movements.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Rates
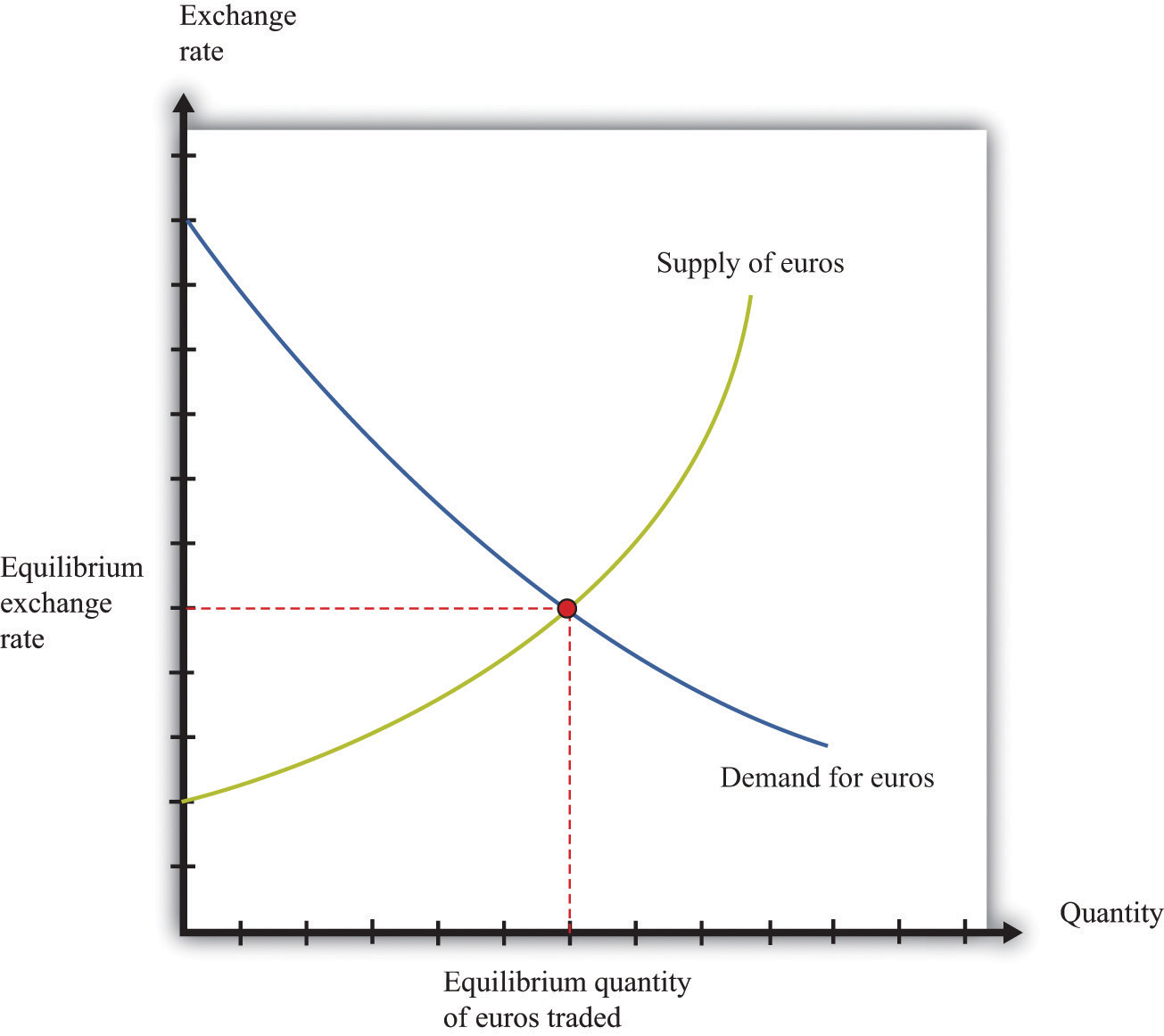
The foreign exchange market is a dynamic and complex system, and the value of currencies is constantly fluctuating. A variety of factors can affect foreign exchange rates, including economic, political, and psychological factors. Understanding these factors is essential for anyone who wants to trade in the foreign exchange market.
Economic Factors
Economic factors are some of the most important factors that affect foreign exchange rates. These factors include:
- Interest rates: Interest rates are the rates at which banks lend money to each other and to businesses and consumers. When interest rates are high in a country, it makes the country’s currency more attractive to investors, which can lead to an appreciation of the currency.
- Inflation: Inflation is the rate at which prices for goods and services are rising. When inflation is high in a country, it can lead to a depreciation of the country’s currency.
- Economic growth: Economic growth is the rate at which a country’s economy is growing. When economic growth is strong in a country, it can lead to an appreciation of the country’s currency.
- Trade balance: The trade balance is the difference between a country’s exports and imports. When a country has a trade surplus (exports > imports), it can lead to an appreciation of the country’s currency.
Political Factors, The foreign exchange market course hero
Political factors can also affect foreign exchange rates. These factors include:
- Political stability: Political stability is essential for a healthy economy. When a country is politically unstable, it can lead to a depreciation of the country’s currency.
- Government policies: Government policies can also affect foreign exchange rates. For example, if a government implements policies that are seen as being harmful to the economy, it can lead to a depreciation of the country’s currency.
- Wars and other conflicts: Wars and other conflicts can also affect foreign exchange rates. For example, if a country is involved in a war, it can lead to a depreciation of the country’s currency.
Types of Foreign Exchange Transactions

Foreign exchange transactions involve the conversion of one currency into another. These transactions occur for various purposes, including international trade, investment, and tourism. Different types of foreign exchange transactions cater to specific needs and are executed through various mechanisms.
The most common types of foreign exchange transactions include spot transactions, forward transactions, swaps, and options.
In this topic, you find that foreign exchange market definition economics is very useful.
Spot Transactions
Spot transactions are the most straightforward type of foreign exchange transaction. They involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the prevailing market rate. Spot transactions are typically settled within two business days.
For example, a company that imports goods from Japan may need to purchase Japanese yen to pay for the goods. The company can execute a spot transaction to convert its US dollars into Japanese yen at the current market rate.
Forward Transactions
Forward transactions are contracts to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date. They are used to hedge against currency fluctuations and lock in exchange rates for future transactions.
For example, a company that expects to receive payment in euros in three months can enter into a forward contract to sell euros at a fixed rate. This ensures that the company will receive a predetermined amount of US dollars, regardless of any fluctuations in the euro-dollar exchange rate.
Swaps
Swaps are agreements to exchange currencies and interest payments on a specified schedule. They are used to manage currency risk and optimize interest rate exposure.
For example, a company that has borrowed in US dollars and expects to receive income in euros can enter into a currency swap. Under the swap, the company will pay fixed interest payments in US dollars and receive floating interest payments in euros. This allows the company to hedge against currency fluctuations and interest rate risk.
Options
Options give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a specified price on or before a certain date. They are used to speculate on currency movements or hedge against currency risk.
Understand how the union of foreign exchange market short note can improve efficiency and productivity.
For example, a company that is concerned about a potential decline in the value of the euro can purchase a call option on the euro. This gives the company the right to buy euros at a fixed price on or before a certain date. If the euro declines in value, the company can exercise the option to buy euros at a favorable rate.
Foreign Exchange Market Risks
The foreign exchange market is a global marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion. However, the foreign exchange market is also a complex and volatile market, and there are a number of risks associated with trading in it.
The most common risks associated with foreign exchange trading include:
- Currency risk: This is the risk that the value of a currency will change against another currency. This can happen for a number of reasons, such as changes in economic conditions, political events, or natural disasters.
- Interest rate risk: This is the risk that interest rates will change, which can affect the value of currencies. For example, if interest rates in one country rise, it can make the currency of that country more attractive to investors, which can lead to an increase in its value.
- Liquidity risk: This is the risk that there will not be enough buyers or sellers for a particular currency, which can make it difficult to trade in it. This can happen during periods of market volatility, such as during a financial crisis.
- Operational risk: This is the risk of errors or fraud in the foreign exchange market. This can happen due to human error, computer glitches, or other factors.
These risks can be managed and mitigated in a number of ways, such as:
- Hedging: Hedging is a strategy that involves using financial instruments to offset the risk of currency fluctuations. For example, a company that imports goods from another country can use a forward contract to lock in the exchange rate at which it will buy the goods, which protects it from the risk of the currency appreciating.
- Diversification: Diversification is a strategy that involves investing in a variety of different currencies. This can help to reduce the risk of losses if one currency depreciates.
- Risk management: Risk management is a process that involves identifying, assessing, and managing risks. This can help to reduce the likelihood of losses and to protect against the financial impact of risks that do occur.
The foreign exchange market is a complex and volatile market, but it can also be a profitable market for those who are aware of the risks and who take steps to manage them.
Examples of Foreign Exchange Market Risks
There have been a number of examples of foreign exchange market risks that have impacted traders in the past. One example is the 2015 Swiss franc crisis. The Swiss National Bank (SNB) unexpectedly removed the peg between the Swiss franc and the euro, which caused the Swiss franc to appreciate by over 20% against the euro in a matter of minutes. This caused significant losses for traders who were short the Swiss franc.
Another example is the 2016 Brexit vote. The vote to leave the European Union caused the British pound to depreciate by over 10% against the US dollar. This caused losses for traders who were long the British pound.
These are just two examples of the many risks that can be associated with trading in the foreign exchange market. It is important to be aware of these risks and to take steps to manage them before trading in this market.
Foreign Exchange Market Regulation

The foreign exchange market is a vast and complex global marketplace where currencies are traded. Due to its size and impact on the global economy, it is essential to have a regulatory framework to ensure its stability and integrity.
Regulations for the foreign exchange market vary across jurisdictions, but they generally aim to:
- Prevent market manipulation and insider trading
- Ensure transparency and fair competition
- Protect investors and consumers
- Maintain financial stability
Some key examples of foreign exchange market regulations include:
- Capital adequacy requirements: These regulations set minimum capital requirements for banks and other financial institutions that participate in the foreign exchange market. This helps to ensure that these institutions have sufficient financial resources to withstand losses and maintain their solvency.
- Risk management guidelines: These guidelines provide guidance to financial institutions on how to manage their foreign exchange risk. This includes setting limits on their exposure to foreign currencies and requiring them to have robust risk management systems in place.
- Anti-money laundering and counter-terrorism financing regulations: These regulations require financial institutions to implement measures to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing. This includes conducting customer due diligence and monitoring transactions for suspicious activity.
Foreign exchange market regulations have had a significant impact on the market. They have helped to reduce market volatility, increase transparency, and protect investors and consumers. As the foreign exchange market continues to evolve, it is likely that regulations will continue to adapt to meet the changing needs of the market.
Closure: The Foreign Exchange Market Course Hero
The foreign exchange market is a vast and complex global marketplace where currencies are traded. Understanding how this market works is essential for anyone who wants to succeed in international business or finance. The foreign exchange market course hero provides a comprehensive overview of the foreign exchange market, its key players, and the factors that influence currency rates. This course is an essential resource for anyone who wants to learn more about the foreign exchange market and how to trade currencies.
