Currency distribution of global foreign exchange market turnover – Currency distribution in the global foreign exchange market is a multifaceted subject that offers a unique perspective on the world’s financial landscape. This intricate network, where currencies are traded and exchanged, plays a pivotal role in international commerce and economic stability.
The distribution of currencies in the forex market is influenced by a myriad of factors, ranging from economic fundamentals to geopolitical events. Understanding these factors is crucial for investors, businesses, and policymakers alike, as it provides insights into market trends and potential opportunities.
Currency Distribution in Global Foreign Exchange Market Turnover
The global foreign exchange market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily turnover of over $5 trillion. The distribution of currencies traded in the forex market reflects the relative economic strength and importance of different countries.
Get the entire information you require about foreign exchange market meaning simple on this page.
Major Currencies
The most traded currencies in the forex market are the US dollar (USD), the euro (EUR), the Japanese yen (JPY), the British pound (GBP), and the Swiss franc (CHF). These currencies account for over 80% of all forex transactions.
Factors Influencing Currency Distribution
Several factors influence the distribution of currencies in the forex market, including:
- Economic size and strength: Countries with larger economies and stronger currencies tend to have a greater share of forex trading.
- Trade flows: The currencies of countries that engage in significant international trade tend to be more heavily traded in the forex market.
- Interest rates: Currencies with higher interest rates tend to attract more investment, which can increase their demand in the forex market.
- Political stability: Currencies of countries with stable political environments tend to be more attractive to investors, which can increase their demand in the forex market.
Major Currencies in the Global Foreign Exchange Market
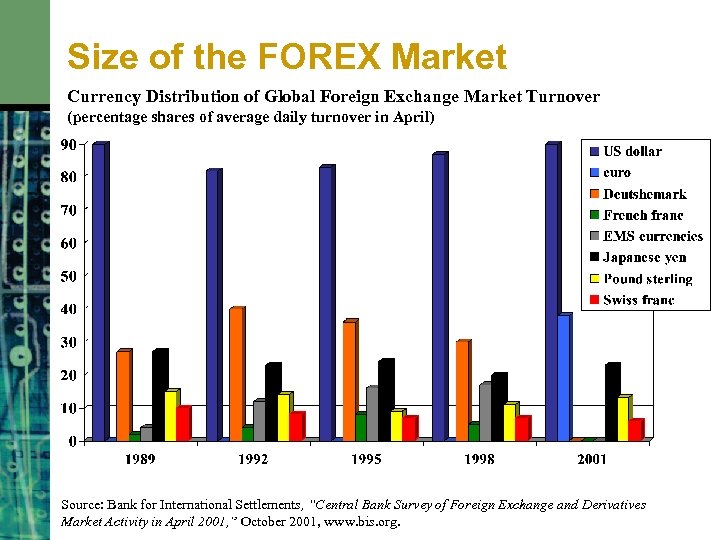
The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market, is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, where currencies are traded 24 hours a day, five days a week. The value of the global foreign exchange market turnover is estimated to be around $5.3 trillion per day, with the top currencies accounting for the majority of trades.
The dominance of certain currencies in the forex market can be attributed to a number of factors, including economic strength, political stability, and the level of international trade. The following are the top currencies traded in the forex market:
- US dollar (USD)
- Euro (EUR)
- Japanese yen (JPY)
- British pound sterling (GBP)
- Swiss franc (CHF)
- Canadian dollar (CAD)
- Australian dollar (AUD)
Economic Strength
The economic strength of a country is a major factor in determining the dominance of its currency in the forex market. A strong economy attracts foreign investment, which in turn increases the demand for the country’s currency. The US dollar, for example, is the most traded currency in the world due to the strength of the US economy.
Political Stability
Political stability is another important factor that affects the dominance of a currency in the forex market. Currencies from countries with stable political environments are generally more attractive to investors, as they are less likely to experience sudden changes in value. The Swiss franc, for example, is often considered a safe haven currency due to Switzerland’s long history of political stability.
Level of International Trade
The level of international trade a country engages in also affects the dominance of its currency in the forex market. Currencies from countries that are major exporters or importers are more likely to be traded frequently, as businesses need to exchange currencies to settle their transactions. The euro, for example, is the second most traded currency in the world due to the high level of international trade within the Eurozone.
Impact of Economic and Political Factors
The dominance of currencies in the forex market can also be impacted by economic and political factors. For example, a country’s interest rate policy can affect the value of its currency. A country with a high interest rate will attract foreign investment, which can lead to an appreciation of its currency. Similarly, political events, such as elections or wars, can also affect the value of a currency.
Regional Distribution of Currency Trading: Currency Distribution Of Global Foreign Exchange Market Turnover
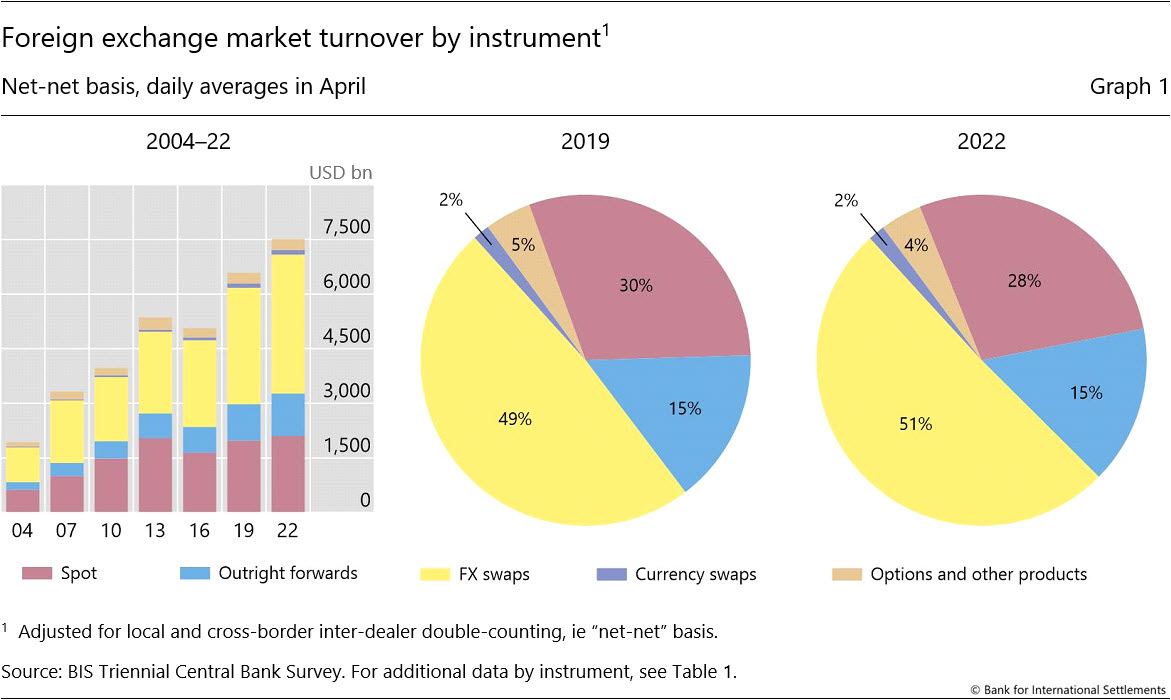
The regional distribution of currency trading in the global foreign exchange market varies significantly, influenced by economic factors, political stability, and geographical proximity.
Europe dominates the global foreign exchange market, accounting for over 35% of all trades. The region’s financial hubs, such as London and Frankfurt, are major centers for currency trading due to their well-established infrastructure, regulatory frameworks, and skilled workforce.
Check black book project on foreign exchange market to inspect complete evaluations and testimonials from users.
North America, Currency distribution of global foreign exchange market turnover
North America, primarily the United States, accounts for around 20% of global currency trading. The region’s large economy, liquid financial markets, and technological advancements contribute to its significant share in the foreign exchange market.
Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region, including Japan, China, and Singapore, has experienced rapid growth in currency trading in recent years. Its share has increased to over 25%, driven by the region’s economic expansion, increased trade volumes, and growing financial markets.
Investigate the pros of accepting foreign exchange market moneycontrol in your business strategies.
Other Regions
Other regions, including the Middle East, Latin America, and Africa, collectively account for a smaller portion of global currency trading. However, these regions are gaining importance due to their growing economies and increasing participation in international trade.
Trends and Developments in Currency Distribution
The global foreign exchange market is constantly evolving, with currency distribution shifting in response to various factors. Emerging currencies are gaining prominence, technological advancements are transforming trading patterns, and economic conditions are influencing currency preferences. These trends and developments are shaping the distribution of currencies in the forex market.
One significant trend is the rise of emerging currencies, such as the Chinese yuan (CNY) and the Indian rupee (INR). As emerging economies grow and their economies become more integrated with the global financial system, their currencies gain importance in the forex market. This is reflected in the increasing share of these currencies in global forex trading.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have also had a profound impact on currency distribution. Electronic trading platforms and algorithmic trading have made it easier for traders to access and trade currencies, leading to a more diverse distribution of currencies in the forex market. Additionally, mobile trading apps have made it possible for retail traders to participate in the forex market, further broadening the range of currencies traded.
Market Structure and Implications for Currency Distribution
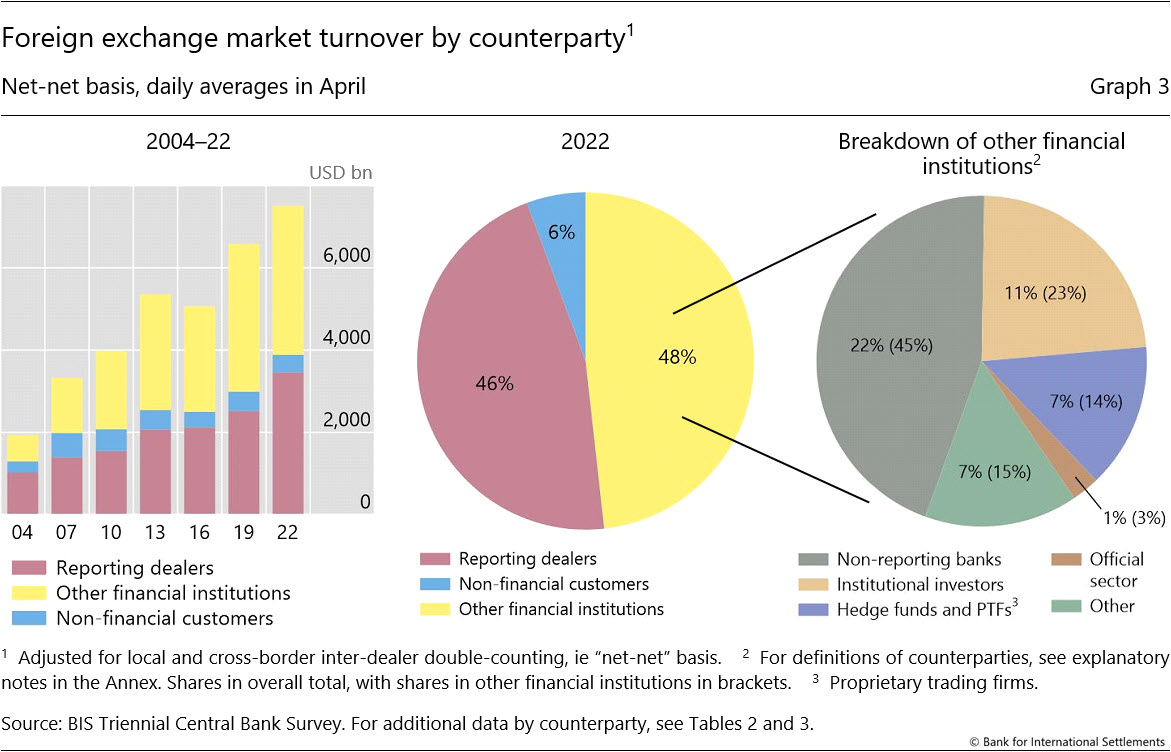
The global foreign exchange market is a decentralized, over-the-counter market where currencies are traded. The market is characterized by a vast network of participants, including banks, financial institutions, corporations, and individual traders. This complex structure has a significant impact on the distribution of currencies in the forex market.
Role of Market Participants
Market participants play a crucial role in shaping currency distribution. Banks, the primary dealers in the forex market, act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers. They provide liquidity to the market and facilitate the execution of trades. Financial institutions, such as hedge funds and investment banks, engage in currency trading for speculative purposes or to manage risk. Corporations use the forex market to facilitate international trade and manage currency risk. Individual traders participate in the market to profit from currency fluctuations.
Implications for Currency Distribution
The market structure has several implications for the distribution of currencies in the forex market:
- Concentration: The forex market is dominated by a few major currencies, such as the US dollar, euro, Japanese yen, and British pound. These currencies account for a significant portion of global forex trading volume due to their economic importance and widespread use in international trade and investment.
- Interdependence: The value of one currency is often influenced by the value of other currencies. For example, a rise in the value of the US dollar may lead to a decline in the value of the euro. This interdependence creates complex relationships between currencies and affects their distribution in the forex market.
- Liquidity: The liquidity of a currency refers to the ease with which it can be bought or sold. Major currencies are typically more liquid than minor currencies, as they are more widely traded and have a larger pool of buyers and sellers. Higher liquidity attracts more participants to the market, further reinforcing the concentration of trading in major currencies.
- Regulation: The forex market is regulated by various authorities worldwide. Regulations can impact the distribution of currencies by imposing restrictions on certain types of trading or requiring market participants to meet specific requirements. For example, some countries may have capital controls that limit the amount of foreign currency that can be traded.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, the currency distribution in the global foreign exchange market is a dynamic and ever-evolving landscape. Economic, political, and technological forces continue to shape the distribution of currencies, creating both challenges and opportunities for participants in this vast and interconnected market.
By staying abreast of these developments and understanding the underlying factors that drive currency distribution, individuals and institutions can make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of the global forex market.
