Definition of terms foreign exchange market – Embarking on a journey into the realm of global finance, we present the definitive definition of the foreign exchange market, commonly known as forex. This dynamic marketplace serves as the cornerstone of international trade, facilitating the exchange of currencies and shaping the global economic landscape.
The foreign exchange market is a decentralized, 24-hour trading hub where participants from around the world converge to buy, sell, and exchange currencies. From multinational corporations to central banks and individual investors, the forex market caters to a diverse range of players, each seeking to navigate the ever-fluctuating currency landscape.
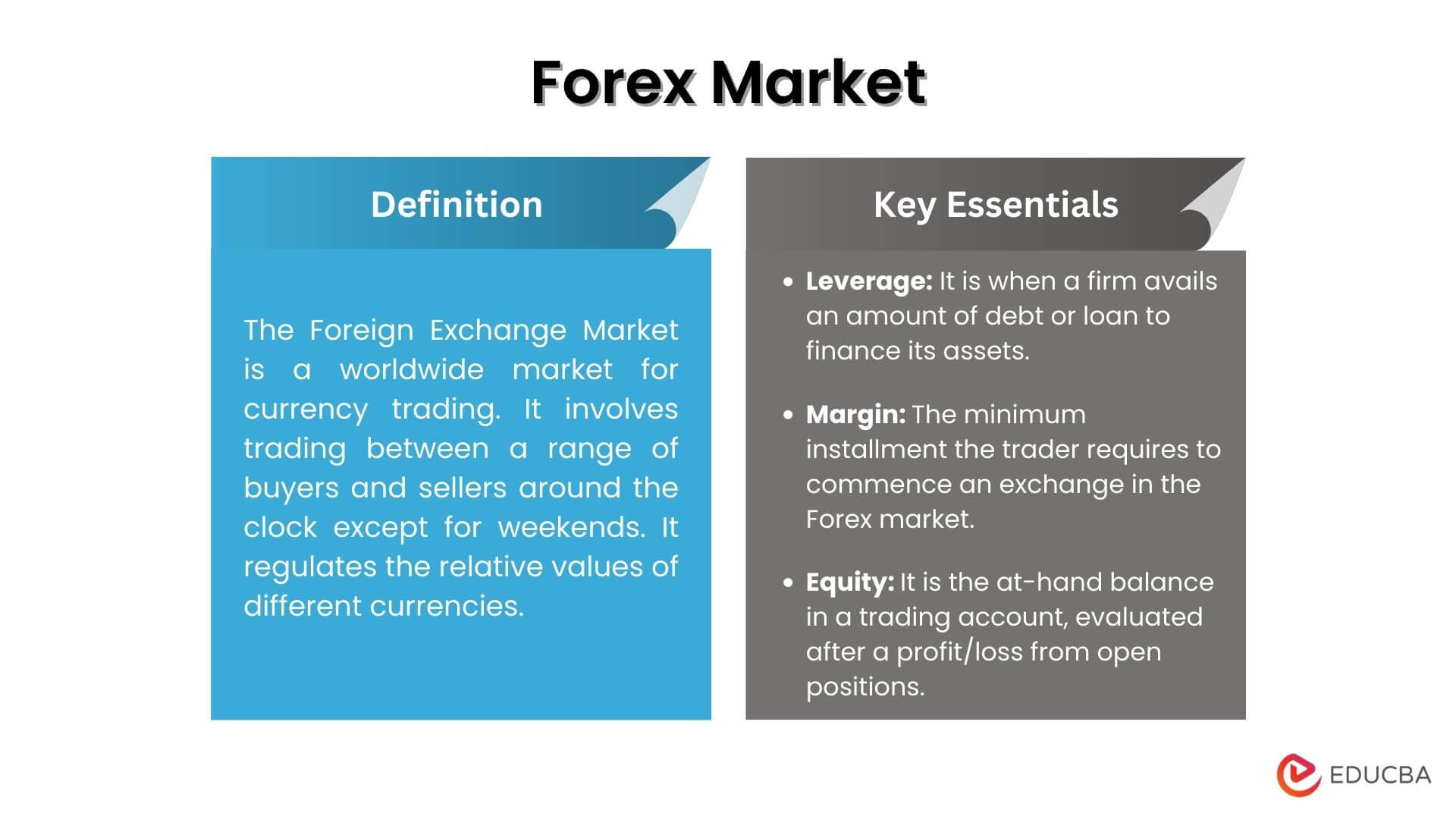
Definition of the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market, is a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with an estimated daily trading volume of over $6.6 trillion.
The forex market facilitates the exchange of currencies for various purposes, including international trade, investment, and tourism. It allows businesses, individuals, and governments to convert one currency into another at prevailing market rates.
Participants in the Forex Market
The forex market involves a wide range of participants, including:
- Commercial banks: They facilitate foreign exchange transactions for their customers, including businesses and individuals.
- Investment banks: They engage in large-scale currency trading and provide advisory services to clients.
- Central banks: They intervene in the forex market to influence exchange rates and manage monetary policy.
- Currency brokers: They act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, providing access to liquidity and competitive rates.
- Corporations: They engage in forex transactions to facilitate international trade and manage currency risk.
- Individuals: They participate in forex trading for speculative purposes or to hedge against currency fluctuations.
Types of Forex Transactions
The forex market involves different types of transactions, including:
- Spot transactions: These involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the current market rate.
- Forward transactions: These involve the exchange of currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date.
- Swap transactions: These involve the simultaneous purchase and sale of currencies with different maturities.
- Option transactions: These give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a specified price on a future date.
Key Features of the Foreign Exchange Market

The foreign exchange market (forex market) exhibits several distinctive characteristics that set it apart from other financial markets. These key features contribute to its unique nature and its significance in the global financial system.
Discover more by delving into foreign exchange market the meaning further.
Decentralized Nature
Unlike traditional exchanges like the stock market, the forex market is decentralized. It lacks a central location or authority that governs its operations. Instead, it operates through a network of banks, financial institutions, and brokers located around the world. This decentralized structure allows for greater accessibility and participation from various market participants.
24-Hour Trading Cycle
The forex market operates continuously 24 hours a day, five days a week. This uninterrupted trading cycle enables participants to execute transactions at any time, regardless of their location. The market opens on Sunday evening in Sydney, Australia, and closes on Friday evening in New York, USA. This extended trading period accommodates the global nature of the market and allows for seamless trading across different time zones.
Finish your research with information from who are foreign exchange market participants.
High Liquidity, Definition of terms foreign exchange market
The forex market is highly liquid, meaning there is a vast amount of currency available for trading at any given time. This liquidity is primarily driven by the participation of large financial institutions, banks, and central banks. The high liquidity ensures that orders can be executed quickly and efficiently, with minimal price slippage.
Risks and Rewards of Foreign Exchange Trading
Foreign exchange trading involves inherent risks and potential rewards. Understanding these factors is crucial before venturing into this market.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of foreign exchange market terminology.
Risks Involved
- Currency Volatility: Currency values can fluctuate rapidly, leading to losses if market movements are not accurately predicted.
- Leverage: Traders often use leverage to amplify their returns. However, this can also magnify losses if the market moves against them.
- Political and Economic Factors: Political events, economic news, and central bank policies can significantly impact currency values.
- Liquidity Risk: Some currency pairs may have low liquidity, making it difficult to enter or exit positions quickly.
- Counterparty Risk: There is always the risk that the counterparty to a trade may default on their obligations.
Potential Rewards
- High Returns: Currency markets offer the potential for substantial returns, especially with leverage.
- 24-Hour Trading: Forex markets operate around the clock, providing opportunities for trading at any time.
- Global Market: The foreign exchange market is the largest financial market in the world, with trillions of dollars traded daily.
- Diversification: Forex trading can help diversify a portfolio by reducing exposure to single currencies or markets.
Importance of Risk Management
Risk management is paramount in foreign exchange trading. It involves strategies such as setting stop-loss orders, using appropriate leverage, and diversifying positions. Effective risk management can minimize potential losses and protect capital.
Applications of the Foreign Exchange Market

The foreign exchange market plays a crucial role in facilitating global trade and financial activities. Its applications extend beyond currency exchange and encompass various financial and economic functions.
International Trade
The forex market enables international trade by facilitating the exchange of currencies for goods and services. When a company imports or exports products, it needs to convert its domestic currency into the currency of the country it is trading with. The forex market provides the platform for this exchange, ensuring smooth transactions and eliminating the need for barter systems.
Hedging Against Currency Fluctuations
Businesses and investors often engage in currency hedging to mitigate the risks associated with currency fluctuations. Hedging involves entering into financial contracts, such as forward contracts or options, that allow them to lock in a specific exchange rate for future transactions. This protects them from adverse currency movements that could impact their profitability or financial stability.
Speculation
The forex market also attracts speculators who seek to profit from currency price movements. Speculators buy and sell currencies based on their expectations of future exchange rate changes. They aim to profit from short-term fluctuations in currency values, often using leverage to amplify their returns.
End of Discussion: Definition Of Terms Foreign Exchange Market
In essence, the foreign exchange market is a microcosm of the global economy, reflecting the ebb and flow of international trade, political events, and economic indicators. Understanding the intricacies of this vast and complex marketplace empowers individuals and businesses alike to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and capitalize on opportunities.
