Easy definition of foreign exchange market sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with casual formal language style and brimming with originality from the outset.
The foreign exchange market, also known as forex, is a global marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion. Forex trading involves the buying and selling of currencies in order to make a profit.
Introduction
The foreign exchange market, commonly known as the forex market, is a global decentralized market where currencies are traded. It’s the largest financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume exceeding $6.6 trillion.
In the forex market, currencies are traded in pairs, such as EUR/USD (euro against the US dollar) or GBP/JPY (British pound against the Japanese yen). The exchange rate between two currencies represents the value of one currency relative to the other. For example, if the EUR/USD exchange rate is 1.15, it means that one euro is worth 1.15 US dollars.
Key Terms
- Currency Pair: A pair of currencies traded against each other, such as EUR/USD or GBP/JPY.
- Exchange Rate: The value of one currency relative to another, expressed as the number of units of one currency required to purchase one unit of another.
- Bid-Ask Spread: The difference between the bid price (the price at which a trader is willing to buy a currency) and the ask price (the price at which a trader is willing to sell a currency).
Participants in the Forex Market
The foreign exchange (forex) market is a vast and complex global marketplace where currencies are traded. Various participants play different roles and have unique motivations in this market, shaping its dynamics and driving currency exchange rates.
The major participants in the forex market include:
Banks, Easy definition of foreign exchange market
- Banks are the largest players in the forex market, facilitating currency exchange for their clients and conducting proprietary trading.
- They provide liquidity to the market by quoting bid and ask prices for various currency pairs.
- Banks also offer hedging services to protect clients from currency fluctuations.
Brokers
- Brokers act as intermediaries between traders and the interbank market.
- They provide traders with access to trading platforms and execute orders on their behalf.
- Brokers may also offer educational resources and analysis tools to support traders.
Institutional Investors
- Institutional investors, such as hedge funds, mutual funds, and pension funds, trade currencies for investment purposes.
- They often use sophisticated trading strategies and have a significant impact on market movements.
- Institutional investors may hold large positions in specific currencies or engage in carry trades to generate returns.
Retail Traders
- Retail traders are individuals who trade currencies on a smaller scale.
- They may trade for speculative purposes or to hedge against currency risks.
- Retail traders typically use online platforms and have varying levels of experience and expertise.
Factors Affecting Exchange Rates: Easy Definition Of Foreign Exchange Market

Exchange rates are constantly fluctuating, influenced by a complex interplay of economic and political factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses, investors, and anyone involved in international transactions.
Economic factors, such as interest rates, inflation, and economic growth, play a significant role in determining currency values. For instance, a country with higher interest rates tends to attract foreign investment, increasing demand for its currency and leading to an appreciation in its value.
Interest Rates
Interest rates set by central banks influence the flow of capital across borders. Higher interest rates make a country’s bonds and other financial instruments more attractive to foreign investors, leading to increased demand for the currency and an appreciation in its value.
Inflation
Inflation, or the rate at which prices rise, can impact exchange rates. High inflation erodes the purchasing power of a currency, making it less valuable compared to currencies with lower inflation rates.
Economic Growth
Strong economic growth indicates a healthy economy, attracting foreign investment and boosting demand for a country’s currency. Conversely, weak economic growth can lead to a depreciation in currency value.
Political Factors
Political stability and government policies also influence exchange rates. Political instability or uncertainty can lead to investors fleeing a country, causing its currency to depreciate. Conversely, sound economic policies and a stable political environment can boost investor confidence and strengthen a currency’s value.
Government Policies
Government policies, such as fiscal and monetary policies, can impact exchange rates. For example, expansionary fiscal policies that increase government spending can lead to inflation and a depreciation in currency value.
Political Events
Political events, such as elections, wars, or changes in government, can create uncertainty and volatility in exchange rates. Unexpected events can cause sudden shifts in currency values.
Check foreign exchange market definition english to inspect complete evaluations and testimonials from users.
Types of Forex Transactions
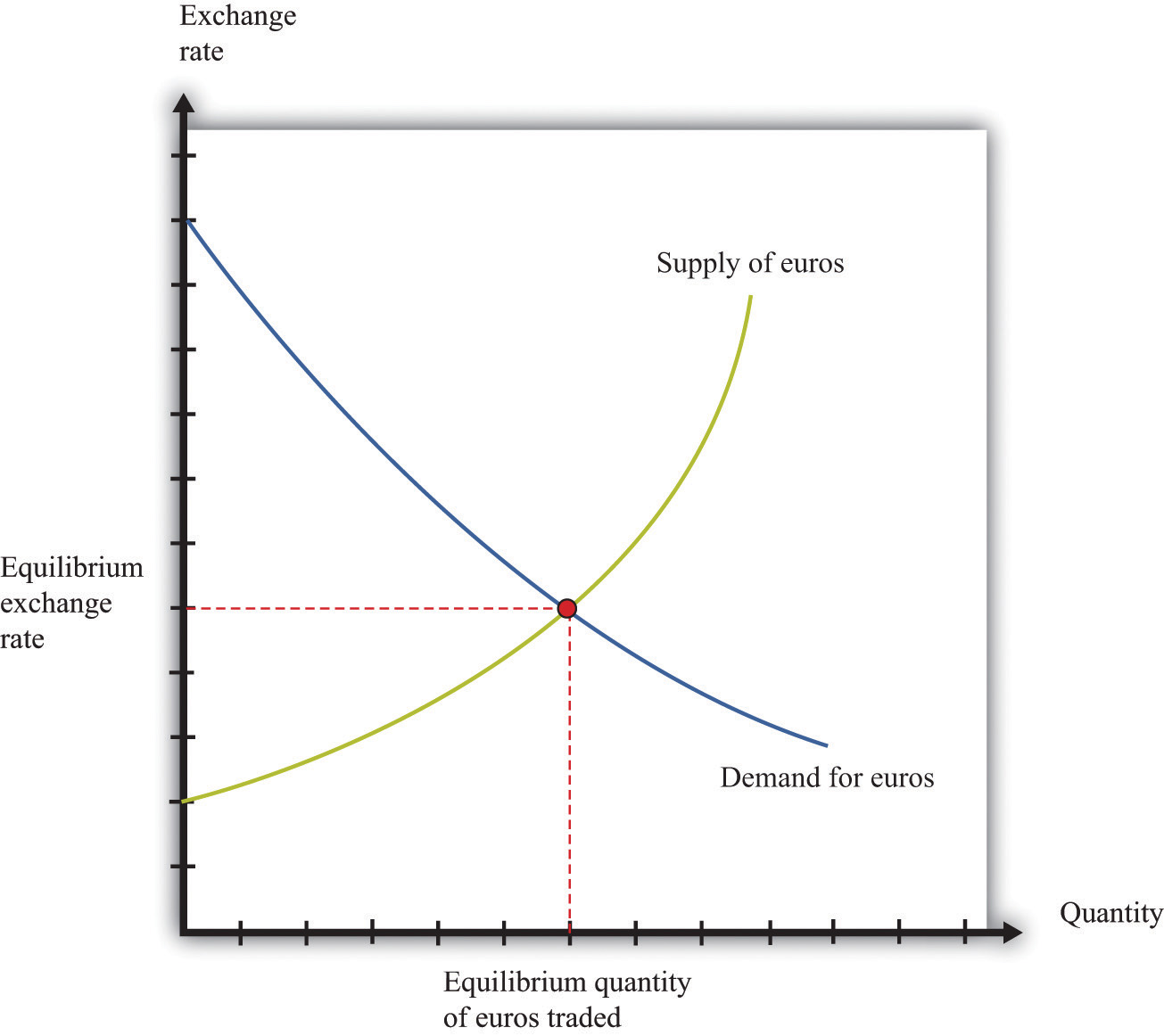
Forex transactions encompass a wide range of dealings involving the exchange of currencies. These transactions can be broadly classified into three main types: spot, forward, and swap.
Spot Transactions
Spot transactions are the most straightforward type of forex transaction, involving the immediate exchange of currencies at the prevailing market rate. Settlement typically occurs within two business days, making spot transactions ideal for short-term currency needs.
Obtain direct knowledge about the efficiency of foreign exchange market definition and meaning through case studies.
Forward Transactions
Forward transactions, also known as forward contracts, are agreements to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date. They allow businesses and investors to hedge against potential currency fluctuations and lock in exchange rates for upcoming transactions.
Swap Transactions
Swap transactions involve the simultaneous buying and selling of currencies with different maturities. These transactions are typically used for complex currency management strategies, such as arbitrage or hedging long-term currency exposures.
Investigate the pros of accepting foreign exchange market calculation in your business strategies.
Trading Strategies in Forex

The foreign exchange market offers a vast landscape for traders to employ various strategies in pursuit of profits. These strategies can be broadly categorized into two main approaches: technical analysis and fundamental analysis. Technical analysis focuses on historical price data and chart patterns to identify potential trading opportunities, while fundamental analysis delves into economic and geopolitical factors that influence currency values.
Technical Analysis Techniques
Technical analysts use a wide array of indicators and tools to analyze price charts and identify trends, support and resistance levels, and potential trading signals. Some common technical analysis techniques include:
- Trendlines: Lines drawn to connect a series of highs or lows, indicating the overall direction of a trend.
- Moving averages: Lines plotted on a chart to smooth out price fluctuations and identify potential support and resistance levels.
- Oscillators: Indicators that measure the momentum or overbought/oversold conditions of a currency pair.
- Candlesticks: Japanese candlestick charts that provide a visual representation of price action, including open, high, low, and close prices.
Fundamental Analysis Techniques
Fundamental analysts focus on economic data, news events, and geopolitical factors that can impact currency values. Some key fundamental analysis techniques include:
- Economic indicators: Data such as GDP, inflation, interest rates, and unemployment rates, which provide insights into the health of an economy.
- News events: Major economic or political events, such as central bank announcements or geopolitical crises, can have a significant impact on currency values.
- Political stability: Political instability or uncertainty can lead to currency depreciation.
- Interest rate differentials: Differences in interest rates between countries can influence the demand for currencies.
Risks and Rewards of Forex Trading
Forex trading, like any other investment opportunity, carries both potential risks and rewards. Understanding these risks and rewards is crucial for making informed decisions and developing a sound trading strategy.
Potential Risks
Forex trading involves the exchange of currencies, which are subject to constant fluctuations in value. These fluctuations can result in significant losses if not managed properly. Some of the key risks associated with forex trading include:
- Market volatility: The forex market is highly volatile, meaning currency prices can change rapidly and unpredictably. This volatility can lead to substantial losses if traders are not prepared for sudden market movements.
- Leverage: Many forex brokers offer leverage, which allows traders to trade with more capital than they have available. While leverage can amplify potential profits, it also magnifies potential losses. Traders should use leverage cautiously and only to the extent that they can afford to lose.
- Liquidity risk: Forex trading is generally a liquid market, but there can be times when it becomes difficult to buy or sell a currency pair quickly and at a desired price. This can lead to slippage, which is the difference between the expected price and the actual price at which a trade is executed.
Potential Rewards
Despite the risks, forex trading also offers the potential for significant rewards. Some of the potential benefits of forex trading include:
- High liquidity: The forex market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion. This liquidity allows traders to enter and exit positions quickly and easily.
- 24-hour trading: The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, allowing traders to take advantage of market opportunities around the clock.
- Potential for high returns: Forex trading has the potential to generate high returns, especially for traders who are skilled in analyzing market trends and managing risk.
Importance of Risk Management
Risk management is paramount in forex trading. Traders should implement a comprehensive risk management strategy to mitigate potential losses and protect their capital. This strategy should include:
- Setting stop-loss orders: Stop-loss orders are used to automatically close a position when the market price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses.
- Using leverage wisely: Traders should only use leverage to the extent that they can afford to lose. Excessive leverage can lead to significant losses.
- Diversifying trading portfolio: Diversifying across different currency pairs can help spread risk and reduce the impact of losses on any one currency.
Understanding the risks and rewards of forex trading, and implementing a sound risk management strategy, is essential for success in this dynamic and challenging market.
Final Review
In conclusion, the foreign exchange market is a complex and dynamic environment that offers both opportunities and risks for traders. By understanding the key concepts and factors that influence exchange rates, traders can develop effective trading strategies and manage their risk exposure.
