Foreign exchange instruments in capital market – In the dynamic world of capital markets, foreign exchange instruments emerge as indispensable tools, enabling seamless international trade, investment, and risk management. Dive into this comprehensive guide to explore the diverse types, functions, and intricacies of foreign exchange instruments, empowering you to navigate these markets with confidence and precision.
Foreign Exchange Instruments in Capital Market
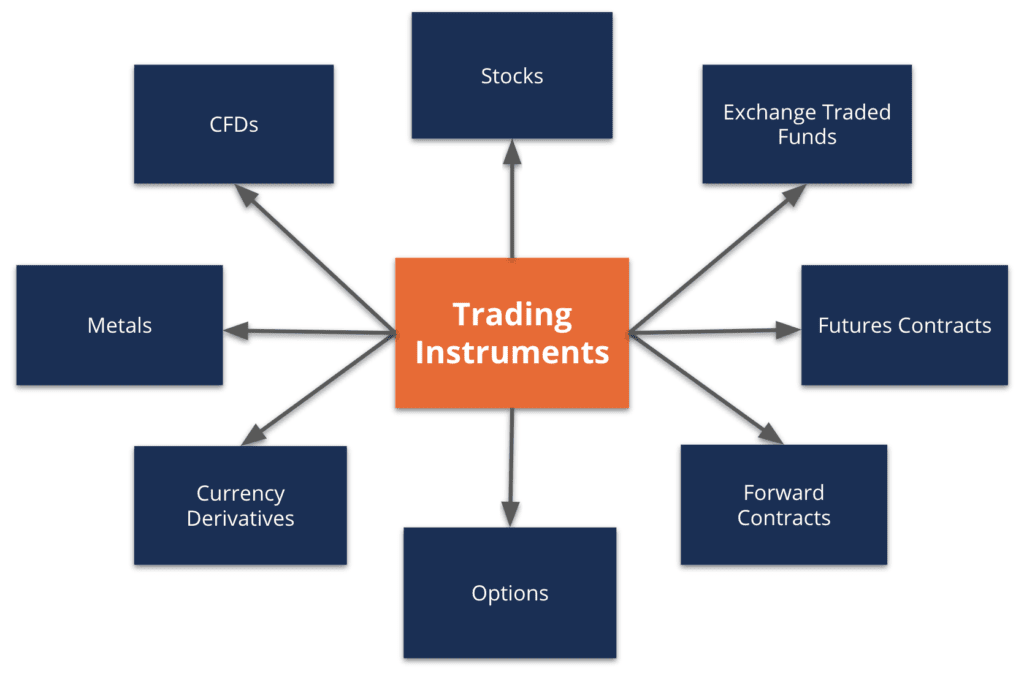
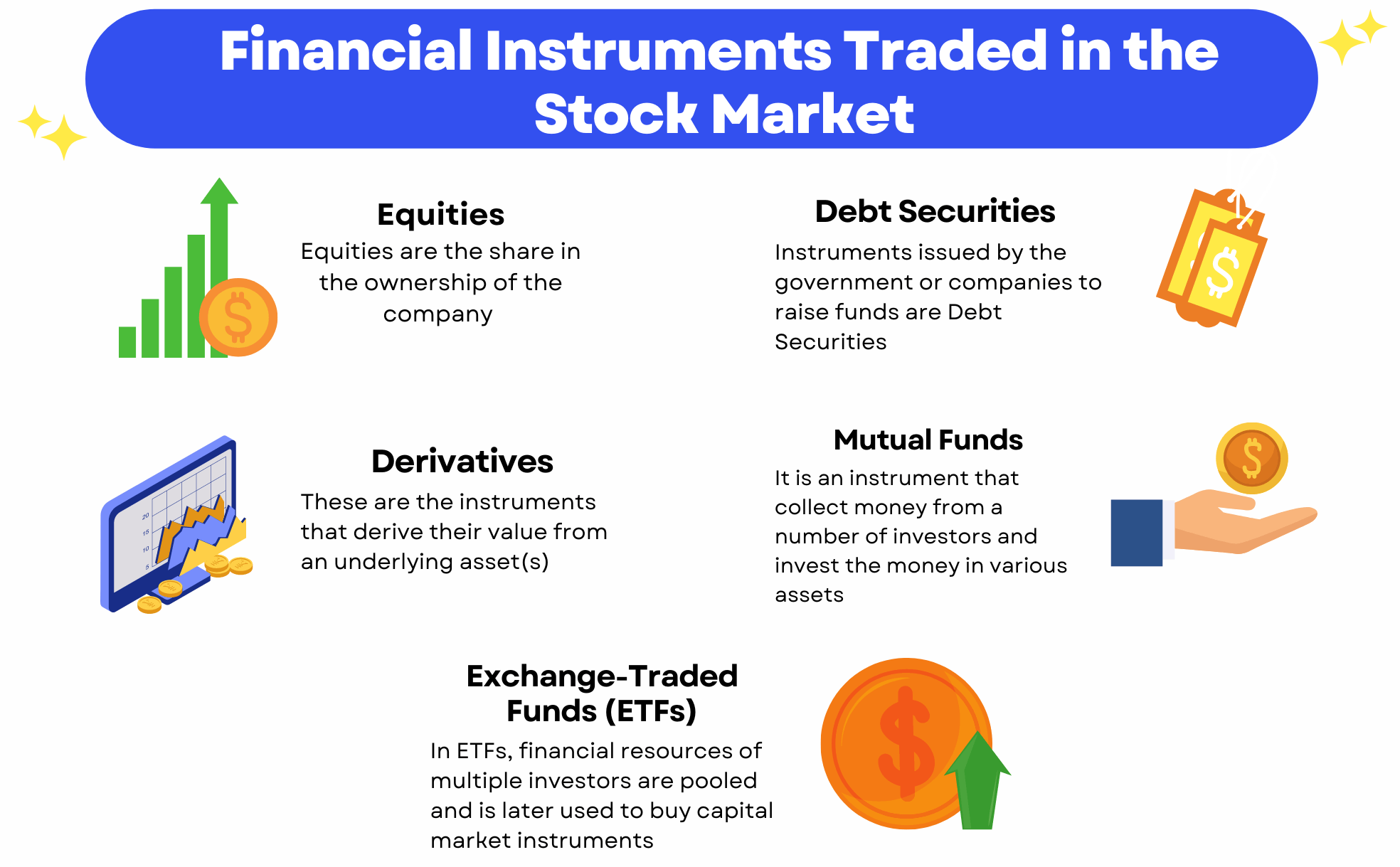
Foreign exchange instruments are financial instruments that facilitate the exchange of currencies between different countries. These instruments are used for various purposes, including international trade, investment, and speculation. There are several types of foreign exchange instruments, each with its own characteristics and risks.
Spot Transactions, Foreign exchange instruments in capital market
- Spot transactions involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the current market rate. These transactions are typically used for commercial purposes, such as settling international trade invoices.
- Example: A US importer purchases goods from a European exporter and agrees to pay in euros. The importer will need to exchange US dollars for euros at the spot rate to make the payment.
Forward Contracts
- Forward contracts are agreements to exchange currencies at a specified future date and rate. These contracts are used to lock in an exchange rate for a future transaction, reducing the risk of exchange rate fluctuations.
- Example: A US company expects to receive a payment in euros in six months. The company can enter into a forward contract to sell euros at a fixed rate, ensuring it receives a predetermined amount of US dollars regardless of the future spot rate.
Currency Options
- Currency options give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specified amount of currency at a specified price on or before a certain date. These instruments are used to speculate on exchange rate movements or to hedge against currency risk.
- Example: An investor believes the euro will appreciate against the US dollar. The investor can purchase a call option on the euro, giving them the right to buy euros at a fixed price in the future. If the euro does appreciate, the investor can exercise the option and profit from the difference between the fixed price and the spot rate.
Currency Swaps
- Currency swaps are agreements to exchange the principal and interest payments of two loans denominated in different currencies. These instruments are used to reduce the cost of borrowing or to hedge against currency risk.
- Example: A US company with a loan denominated in euros can swap its loan with a European company with a loan denominated in US dollars. This allows both companies to reduce their exposure to exchange rate fluctuations.
Risks and Benefits of Using Foreign Exchange Instruments
- Risks: Exchange rate fluctuations, counterparty risk, and liquidity risk are some of the risks associated with using foreign exchange instruments.
- Benefits: Foreign exchange instruments can provide several benefits, including reducing exchange rate risk, hedging against currency fluctuations, and speculating on exchange rate movements.
Role of Foreign Exchange Instruments in Capital Markets
Foreign exchange instruments play a crucial role in facilitating international trade and investment. They enable the exchange of currencies between countries, allowing businesses and individuals to engage in cross-border transactions.
Managing Currency Risk
Foreign exchange instruments also provide a means to manage currency risk. Currency risk arises when the value of one currency fluctuates against another. Businesses and investors can use foreign exchange instruments to hedge against this risk, ensuring that they are not adversely affected by currency fluctuations.
Role of Central Banks
Central banks play a significant role in the foreign exchange market. They intervene in the market to influence the value of their currency, often with the aim of promoting economic stability. Central banks also hold reserves of foreign currencies, which they can use to intervene in the market or support their own currency.
Market Participants in Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is a global marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $5 trillion. The foreign exchange market is open 24 hours a day, 5 days a week, and it is used by a wide range of participants, including banks, corporations, governments, and individual investors.
Types of Participants
- Banks: Banks are the largest participants in the foreign exchange market. They act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers of currencies, and they provide a variety of services, such as currency trading, foreign exchange hedging, and foreign exchange risk management.
- Corporations: Corporations use the foreign exchange market to manage their foreign exchange risk. This risk arises when a corporation has operations in multiple countries and is exposed to fluctuations in currency exchange rates.
- Governments: Governments use the foreign exchange market to manage their foreign exchange reserves. These reserves are used to support the value of the country’s currency and to intervene in the foreign exchange market when necessary.
- Individual investors: Individual investors use the foreign exchange market to speculate on currency movements. They can do this by buying and selling currencies through a variety of brokers.
Role of Participants
The different types of participants in the foreign exchange market play a vital role in the functioning of the market. Banks provide liquidity to the market and facilitate the exchange of currencies. Corporations use the market to manage their foreign exchange risk. Governments use the market to manage their foreign exchange reserves. And individual investors use the market to speculate on currency movements.
Interactions between Participants
The interactions between participants in the foreign exchange market are complex and dynamic. Banks compete with each other to provide the best prices and services to their clients. Corporations and governments use banks to manage their foreign exchange risk. And individual investors use banks to speculate on currency movements. These interactions help to create a liquid and efficient market that is essential for the global economy.
Do not overlook explore the latest data about foreign exchange market mechanism.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Rates

The value of a currency in relation to other currencies is determined by a multitude of factors, both economic and political. These factors can influence the supply and demand for a currency, thereby affecting its exchange rate.
In this topic, you find that foreign exchange market vs financial is very useful.
Economic Factors
Economic factors that can impact foreign exchange rates include:
- Interest rates: Higher interest rates tend to attract foreign investment, increasing the demand for a currency and strengthening its value.
- Inflation: High inflation can erode the value of a currency, reducing its purchasing power and making it less attractive to investors.
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth indicates a healthy economy, which can attract foreign investment and strengthen the currency.
- Trade balance: A country with a trade surplus (exports exceeding imports) typically has a stronger currency, as there is more demand for its currency to purchase exports.
Political Factors
Political factors can also influence foreign exchange rates:
- Political stability: Political uncertainty or instability can lead to a decline in investor confidence and a weaker currency.
- Government policies: Government policies, such as tax changes or trade restrictions, can impact the attractiveness of a country for investment and affect its currency’s value.
- International relations: Tensions or conflicts between countries can lead to increased risk perception, weakening the currency of the affected countries.
Supply and Demand
The exchange rate of a currency is ultimately determined by supply and demand. When there is more demand for a currency than supply, its value increases. Conversely, when there is more supply than demand, the currency’s value decreases.
Check what professionals state about meaning of arbitrage in foreign exchange market and its benefits for the industry.
Factors that can affect supply and demand include:
- Speculation: Currency traders can buy and sell currencies based on expectations of future changes in their value, influencing supply and demand.
- Carry trade: Investors may borrow in one currency with a low interest rate and invest in another currency with a higher interest rate, creating demand for the higher-yielding currency.
- Hedging: Businesses may use currency derivatives to reduce the risk of exchange rate fluctuations, affecting supply and demand for currencies.
Central Bank Intervention
Central banks can intervene in the foreign exchange market to influence the value of their currency. They can:
- Buy or sell currencies: Central banks can buy or sell currencies in the open market to increase or decrease the supply of a currency, thereby affecting its exchange rate.
- Set interest rates: Central banks can raise or lower interest rates to influence the demand for a currency, as discussed earlier.
- Impose capital controls: Central banks may restrict the flow of capital into or out of a country, limiting the supply or demand for a currency.
Foreign Exchange Market Regulation
The foreign exchange market, being a global and decentralized market, requires a regulatory framework to ensure its stability and transparency. This framework involves a combination of national regulations, international agreements, and the involvement of international organizations.
At the national level, central banks and financial regulatory authorities play a crucial role in regulating the foreign exchange market. They establish rules and regulations governing the conduct of foreign exchange transactions, including reporting requirements, risk management practices, and anti-money laundering measures.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations also play a significant role in regulating the foreign exchange market. The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) serves as a global forum for central banks, promoting cooperation and coordination on various aspects of foreign exchange market regulation. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) monitors global economic and financial developments, including foreign exchange market trends, and provides policy advice to member countries.
Challenges of Regulating the Foreign Exchange Market
Regulating the foreign exchange market poses several challenges. The global and decentralized nature of the market makes it difficult to implement and enforce regulations consistently across jurisdictions. Additionally, the rapid pace of technological advancements, including the rise of electronic trading platforms and cryptocurrencies, creates new challenges for regulators.
Final Thoughts: Foreign Exchange Instruments In Capital Market
As we conclude our exploration of foreign exchange instruments in capital markets, it is evident that these instruments play a pivotal role in facilitating global economic activity. Their versatility and complexity demand a thorough understanding of their risks and benefits, as well as the regulatory landscape that governs their operations. By embracing the insights gained from this guide, investors and businesses can harness the power of foreign exchange instruments to optimize their capital market strategies and navigate the ever-evolving financial landscape with greater success.
