Foreign exchange market affect currency – As the foreign exchange market takes center stage, it’s crucial to understand its profound impact on currency values. This intricate global marketplace, where currencies are traded 24/7, plays a pivotal role in shaping the financial landscape and influencing economic outcomes worldwide.
The interplay of fundamental factors, central bank actions, speculation, cross-border trade, and risk management creates a dynamic and ever-evolving environment that can both empower and challenge businesses, investors, and governments alike.
Market Dynamics
Foreign exchange markets are influenced by a complex interplay of fundamental factors, including economic, political, and social conditions. These factors shape the supply and demand for currencies, ultimately determining their values.
Supply and Demand
The value of a currency is determined by the interaction of supply and demand in the foreign exchange market. When the demand for a currency exceeds its supply, its value rises (appreciates). Conversely, when the supply of a currency exceeds its demand, its value falls (depreciates).
Enhance your insight with the methods and methods of project report on foreign exchange market in india pdf.
Economic Events
Economic events, such as changes in interest rates, inflation, and economic growth, can significantly impact currency values. For example, a country with higher interest rates will attract foreign investment, increasing demand for its currency and leading to appreciation.
Political Events
Political events, such as elections, changes in government, and geopolitical tensions, can also influence currency markets. Political instability or uncertainty can lead to a loss of confidence in a currency, causing its value to depreciate.
Get the entire information you require about definition and functions of foreign exchange market on this page.
Central Bank Influence

Central banks play a crucial role in managing foreign exchange markets through monetary policy decisions that influence currency values. They act as the gatekeepers of a country’s financial system, overseeing interest rates, money supply, and foreign exchange reserves.
Monetary policy decisions, particularly interest rate adjustments, have a significant impact on currency values. When a central bank raises interest rates, it makes the currency more attractive to foreign investors seeking higher returns. This increased demand for the currency leads to its appreciation against other currencies.
Quantitative Easing and Unconventional Monetary Policies
In recent years, central banks have employed unconventional monetary policies, such as quantitative easing (QE), to stimulate economic growth. QE involves the central bank purchasing large quantities of government bonds and other assets, which increases the money supply and lowers long-term interest rates.
QE can have a complex impact on foreign exchange rates. Initially, it can lead to currency depreciation as investors sell the currency to purchase higher-yielding assets. However, in the long run, QE can support economic growth and inflation, which can make the currency more attractive and lead to appreciation.
Obtain recommendations related to foreign exchange market derivatives that can assist you today.
Speculation and Market Sentiment: Foreign Exchange Market Affect Currency

Speculation and market sentiment play a significant role in driving currency movements. Speculators are individuals or institutions that engage in foreign exchange trading with the primary aim of profiting from short-term fluctuations in currency prices. Their actions can influence the direction and volatility of currency pairs.
Market sentiment, on the other hand, refers to the collective mood and attitude of market participants towards a particular currency or currency pair. It is often influenced by economic news, political events, and psychological factors. Positive market sentiment can lead to increased demand for a currency, while negative sentiment can result in selling pressure.
Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Currency traders use a variety of analytical techniques to make trading decisions. Technical analysis involves studying historical price charts and patterns to identify potential trading opportunities. Fundamental analysis focuses on economic data, interest rates, and political events to assess the underlying value of a currency.
Market Psychology and Herd Mentality, Foreign exchange market affect currency
Market psychology and herd mentality can also significantly impact currency markets. Traders often follow the actions of others, leading to self-fulfilling prophecies and exaggerated market movements. For example, if a large number of traders believe that a currency is undervalued, they may buy it, which in turn drives up its price.
Cross-Border Trade and Investment
Cross-border trade and foreign exchange markets are intertwined, as international trade necessitates currency exchange to facilitate transactions between countries. Trade imbalances occur when the value of a country’s exports differs from its imports, affecting currency demand and supply. Similarly, foreign direct investment (FDI) involves the flow of capital across borders, influencing currency exchange rates by increasing demand for the host country’s currency.
Currency Exchange Rates and International Trade
Currency exchange rates play a crucial role in facilitating international trade by determining the relative prices of goods and services across countries. A weaker currency makes exports cheaper and imports more expensive, potentially boosting exports and curbing imports. Conversely, a stronger currency has the opposite effect.
Currency Exchange Rates and Foreign Direct Investment
Foreign direct investment can impact currency exchange rates by increasing demand for the host country’s currency. When foreign investors purchase assets or establish businesses in a country, they need to exchange their currency for the local currency, increasing demand and potentially appreciating its value.
Risk Management and Currency Hedging
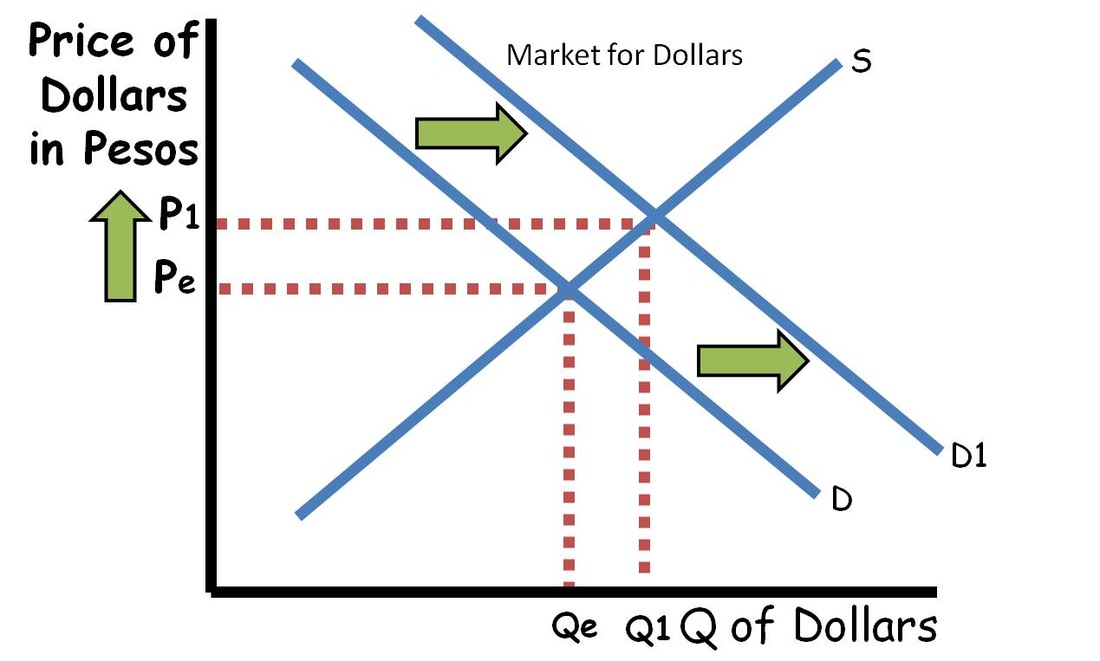
Currency risk, stemming from fluctuations in exchange rates, poses significant challenges for businesses and investors operating in the global economy. Managing this risk is crucial to safeguard profits, protect investments, and maintain financial stability.
Currency Hedging Strategies
To mitigate currency risk, businesses and investors employ various hedging strategies:
- Forward Contracts: Legally binding agreements to buy or sell a specific currency at a predetermined exchange rate on a future date. This locks in the exchange rate, eliminating uncertainty.
- Currency Options: Contracts that give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a specified exchange rate within a defined period. This provides flexibility and potential profit opportunities.
- Currency Swaps: Agreements to exchange one currency for another at an agreed-upon exchange rate on a specific date, followed by a reverse exchange at a later date. This allows for risk management without direct currency exposure.
The effectiveness of a hedging strategy depends on factors such as the type of risk being hedged, the expected duration of the exposure, and the availability of hedging instruments in the market.
Ending Remarks
In the ever-changing tapestry of the global economy, the foreign exchange market stands as a testament to the interconnectedness of nations and the profound impact of currency values on our daily lives. Understanding the dynamics that shape this complex marketplace is essential for navigating the complexities of international trade, investment, and risk management in today’s interconnected world.
