Currency pair in foreign exchange market – In the realm of international finance, currency pairs play a pivotal role in the foreign exchange market, where traders speculate on the relative value of different currencies. Delving into the intricacies of currency pairs, this comprehensive guide unravels their components, dynamics, and significance in the global financial landscape.
Currency pairs represent the exchange rate between two currencies, with the first currency being the base currency and the second currency being the quote currency. The value of a currency pair fluctuates constantly, influenced by a myriad of economic and political factors. Traders seek to profit from these fluctuations by buying and selling currency pairs at opportune moments.
Currency Pair Definition
In the foreign exchange market, a currency pair refers to the exchange rate between two different currencies. It represents the value of one currency in terms of another, indicating how many units of the second currency are required to purchase one unit of the first currency.
Common Currency Pairs
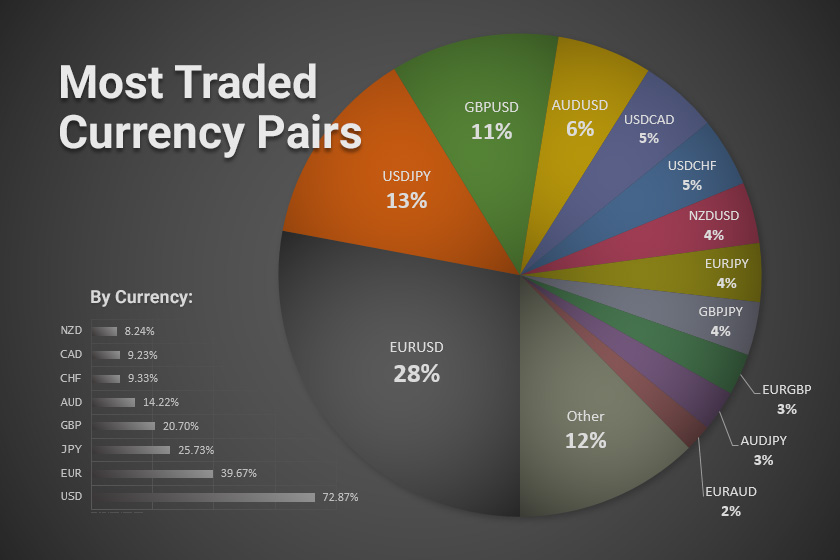
Some of the most commonly traded currency pairs in the forex market include:
- EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar)
- USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen)
- GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar)
- AUD/USD (Australian Dollar/US Dollar)
- USD/CHF (US Dollar/Swiss Franc)
Currency Pair Components

A currency pair is a combination of two currencies used in the foreign exchange market. It represents the exchange rate between the two currencies, indicating how much of one currency is needed to purchase one unit of the other.
Every currency pair consists of two currencies:
- Base Currency: The currency placed first in the pair. Its value is considered the standard against which the quote currency is measured.
- Quote Currency: The currency placed second in the pair. Its value is expressed in terms of the base currency, indicating how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency.
Currency Pair Quotation
In the foreign exchange market, currency pairs are quoted in a specific format. The first currency listed in the pair is called the base currency, and the second currency is called the quote currency. The price of a currency pair represents how much of the quote currency is required to buy one unit of the base currency.
Discover the crucial elements that make meaning of a foreign exchange market the top choice.
Pip (Point in Percentage), Currency pair in foreign exchange market
The pip (point in percentage) is the smallest unit of measurement for currency pair price changes. It is typically the fourth decimal place for most currency pairs. For example, if the EUR/USD currency pair moves from 1.1000 to 1.1001, it has moved by one pip.
For descriptions on additional topics like foreign exchange rate today black market, please visit the available foreign exchange rate today black market.
Currency Pair Trading
Currency pair trading involves the simultaneous buying of one currency and selling of another in the foreign exchange market. It is one of the most common trading strategies in forex, allowing traders to speculate on the relative value of two currencies.
Process of Currency Pair Trading
The process of currency pair trading involves the following steps:
- Selecting a Currency Pair: Traders choose a currency pair to trade based on factors such as market conditions, economic indicators, and technical analysis.
- Determining the Trade Direction: Traders decide whether to buy or sell the currency pair based on their analysis of the market and their expectations for the future value of the currencies.
- Placing the Order: Traders place an order with their broker to buy or sell the currency pair at a specific price.
- Managing the Trade: Once the order is executed, traders may choose to monitor the trade and make adjustments as needed, such as setting stop-loss or take-profit orders.
- Closing the Trade: Traders close the trade when they have achieved their profit target or when they believe the market conditions have changed significantly.
Factors Affecting Currency Pair Value
Currency pair values are influenced by a multitude of economic and political factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for successful currency pair trading.
Supply and demand, interest rates, and economic data play significant roles in determining currency pair prices. Let’s delve into each factor in detail.
Supply and Demand
The law of supply and demand dictates that when the demand for a currency increases relative to its supply, its value rises. Conversely, when supply exceeds demand, its value falls. Factors like economic growth, political stability, and interest rate differentials can affect the supply and demand of currencies.
Interest Rates
Interest rates are a major determinant of currency pair values. Higher interest rates make a currency more attractive to investors, increasing its demand and value. Conversely, lower interest rates can lead to a decline in demand and value.
Economic Data
Economic data releases, such as GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment rates, provide insights into the health of an economy. Strong economic data can boost demand for a currency, while weak data can lead to its depreciation.
Currency Pair Analysis Techniques
Currency pair analysis involves examining the price movements of currency pairs to identify trading opportunities. There are two main approaches to currency pair analysis: technical analysis and fundamental analysis.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis involves studying historical price charts to identify patterns and trends that can indicate future price movements. Common technical analysis methods include:
– Trend analysis: Identifying the overall direction of the price movement, whether it is uptrending, downtrending, or sideways.
– Support and resistance levels: Identifying areas where the price has consistently bounced off, indicating potential buying or selling opportunities.
– Moving averages: Smoothing out price fluctuations to identify underlying trends.
– Oscillators: Indicators that measure the momentum or overbought/oversold conditions of a currency pair.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis involves evaluating the economic factors that affect the value of currencies. These factors include:
– Economic growth: The rate at which an economy is growing, which affects the demand for its currency.
– Inflation: The rate at which prices are rising, which can erode the value of a currency.
– Interest rates: The cost of borrowing money, which can attract or deter foreign investment and affect the value of a currency.
– Political stability: The stability of a country’s government and its policies, which can impact investor confidence and the value of its currency.
– Central bank policies: The actions of a country’s central bank, such as setting interest rates and managing the money supply, can significantly affect the value of its currency.
By combining technical and fundamental analysis, traders can gain a comprehensive understanding of the factors affecting currency pair prices and make informed trading decisions.
Currency Pair Trading Strategies: Currency Pair In Foreign Exchange Market

Currency pair trading involves a wide range of strategies, each with its unique approach to capitalizing on market movements. Understanding these strategies is crucial for traders to make informed decisions and develop effective trading plans.
The choice of trading strategy depends on factors such as risk tolerance, time horizon, and market conditions. Some of the most common trading strategies used in currency pair trading include scalping, day trading, swing trading, and position trading.
Scalping
Scalping is a high-frequency trading strategy that involves making numerous small trades throughout the day, aiming to profit from tiny price fluctuations. Scalpers typically hold positions for only a few seconds or minutes, relying on tight spreads and high trading volume to generate profits.
Day Trading
Day trading involves opening and closing positions within the same trading day, aiming to capture short-term market movements. Day traders typically focus on intraday price patterns and technical analysis to identify potential trading opportunities. They may hold positions for several hours or even the entire trading day.
Swing Trading
Swing trading involves holding positions for a few days or weeks, capturing medium-term price trends. Swing traders typically use technical analysis to identify potential turning points in the market and aim to profit from larger price swings.
Position Trading
Position trading involves holding positions for months or even years, aiming to profit from long-term market trends. Position traders typically focus on fundamental analysis and economic factors to identify potential trading opportunities and may use a combination of technical and fundamental analysis to make trading decisions.
Currency Pair Risk Management
In the realm of currency pair trading, risk management stands as a crucial pillar for safeguarding one’s financial well-being. It entails employing strategies and tools to mitigate potential losses and maximize gains.
Remember to click foreign exchange market timings to understand more comprehensive aspects of the foreign exchange market timings topic.
A key risk management tool is the stop-loss order, which automatically exits a trade when the price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses. Conversely, take-profit orders automatically close a trade when a certain profit target is reached, securing gains.
Other Risk Management Tools
- Trailing stop-loss orders: Adjust the stop-loss level as the trade moves in a favorable direction, protecting profits while allowing for potential further gains.
- Hedging: Opening opposing positions in different currency pairs to reduce overall exposure to market fluctuations.
- Position sizing: Determining the appropriate trade size based on available capital and risk tolerance, ensuring that potential losses do not exceed acceptable limits.
- Risk-reward ratio: Calculating the potential reward relative to the potential risk, guiding decisions on whether to enter or exit a trade.
- Risk appetite: Assessing one’s tolerance for financial losses, which influences risk management strategies and trading decisions.
Currency Pair Market Trends
Currency pair markets are constantly evolving, influenced by a myriad of factors. Understanding current trends and their underlying causes is crucial for informed trading decisions.
Global economic events play a significant role in shaping currency pair prices. Economic growth, inflation rates, interest rate changes, and political stability all have a direct impact on the value of currencies.
Impact of Global Economic Events
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth in a country leads to increased demand for its currency, resulting in appreciation.
- Inflation Rates: High inflation erodes the value of a currency, leading to depreciation.
- Interest Rate Changes: Central bank decisions to raise or lower interest rates affect the attractiveness of a currency for investment, influencing its value.
- Political Stability: Political uncertainty and instability can negatively impact a currency’s value due to reduced investor confidence.
Currency Pair Market Outlook
The currency pair market is a vast and ever-evolving landscape, offering both opportunities and challenges for traders. With the increasing interconnectedness of global economies, the demand for currency exchange is expected to continue to grow, providing a fertile ground for currency pair trading.
Potential Opportunities
The currency pair market presents several potential opportunities for traders:
- High Liquidity: Currency pairs are among the most liquid financial assets, enabling traders to enter and exit positions quickly and efficiently.
- 24/7 Trading: The currency pair market operates 24 hours a day, 5 days a week, providing traders with ample trading opportunities.
- Volatility: Currency pairs can experience significant price fluctuations, offering traders the potential for substantial profits.
Challenges
Despite its potential, currency pair trading also poses certain challenges:
- Complexity: The currency pair market is influenced by a wide range of factors, making it complex to analyze and predict price movements.
- Leverage: While leverage can amplify profits, it can also lead to significant losses if not managed properly.
- Risk: Currency pair trading involves inherent risk, as the value of currencies can fluctuate rapidly.
Overall, the currency pair market outlook remains positive, with ample opportunities for traders who are willing to navigate its complexities and manage risks effectively.
Wrap-Up
The currency pair market is a dynamic and ever-evolving arena, presenting both opportunities and challenges for traders. By understanding the fundamental principles of currency pairs, traders can navigate the complexities of the foreign exchange market and make informed decisions to maximize their potential returns.
