Foreign exchange market definition simple: the foreign exchange market, also known as forex, is a global marketplace where currencies are traded. It’s the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion. Forex trading involves the buying and selling of currencies, with the aim of making a profit from fluctuations in their exchange rates.
The foreign exchange market is a complex and dynamic environment, influenced by a wide range of economic, political, and social factors. However, understanding the basics of forex trading can help you to make informed decisions about your investments.
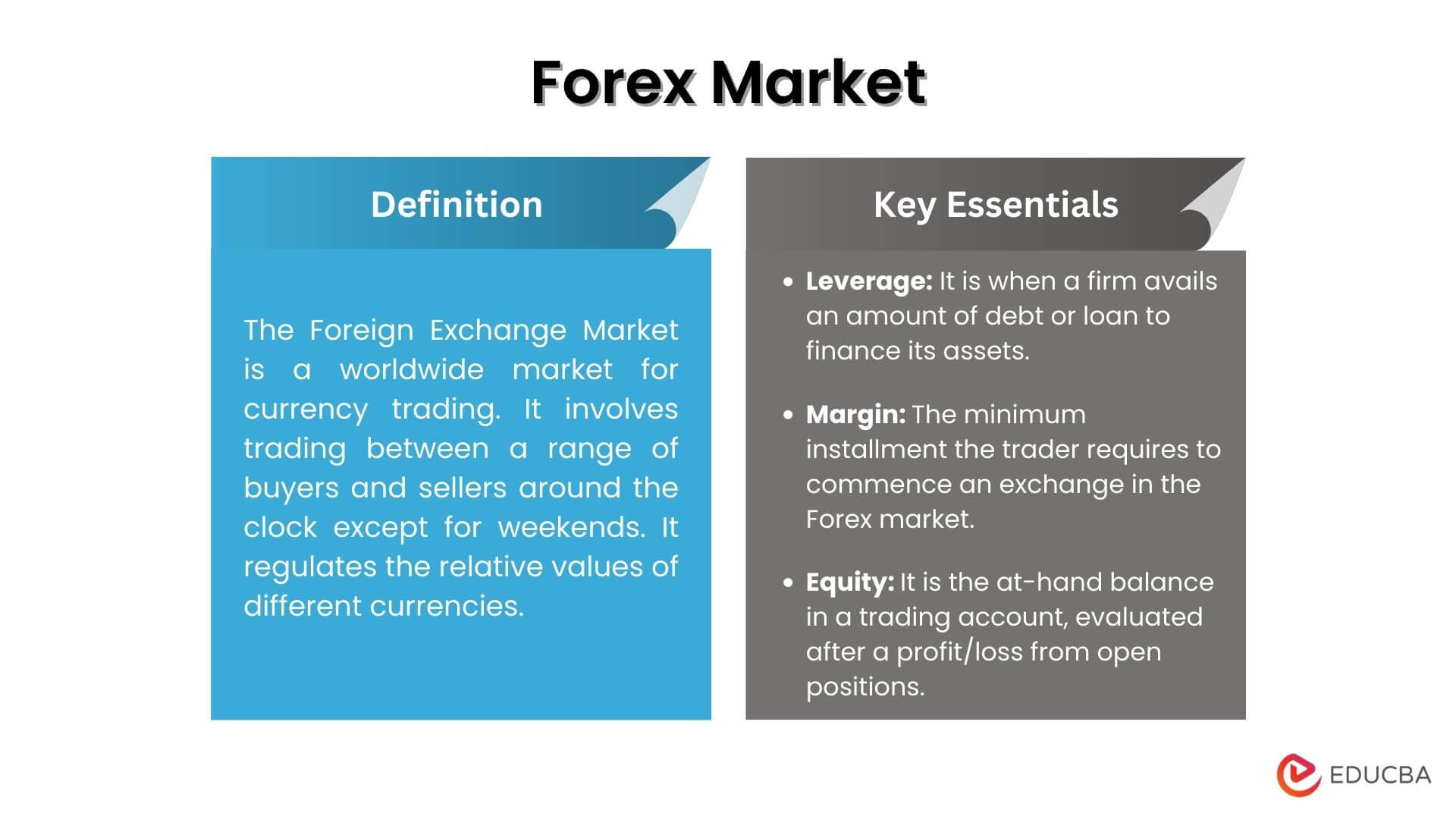
Definition of Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market, is a global decentralized market where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with an estimated daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
Foreign exchange plays a crucial role in international trade and finance. It allows businesses and individuals to buy and sell goods and services across borders, and to invest in foreign markets. The foreign exchange market also helps to determine the value of currencies relative to each other.
Discover more by delving into foreign exchange market topics for project further.
Types of Foreign Exchange Markets
There are three main types of foreign exchange markets:
- Spot market: The spot market is where currencies are traded for immediate delivery.
- Forward market: The forward market is where currencies are traded for delivery at a future date.
- Swap market: The swap market is where currencies are exchanged for a different currency at a future date, with the two currencies being exchanged back at a later date.
Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market: Foreign Exchange Market Definition Simple

The foreign exchange market is a vast and complex ecosystem, with a diverse range of participants playing crucial roles. These participants can be broadly categorized into four main groups: banks, central banks, corporations, and individual investors. Each group has its unique motivations and objectives, shaping the dynamics of the foreign exchange market.
Banks are the primary players in the foreign exchange market, facilitating the majority of currency transactions. They act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, providing liquidity and ensuring the smooth functioning of the market. Banks also engage in proprietary trading, speculating on currency movements to generate profits.
Central Banks
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States or the European Central Bank, play a significant role in the foreign exchange market. They are responsible for managing their respective countries’ monetary policies, which can have a profound impact on currency values. Central banks intervene in the foreign exchange market to stabilize currencies, manage inflation, and support economic growth.
Corporations
Corporations are another major participant in the foreign exchange market. They engage in currency transactions to facilitate international trade, manage currency risk, and optimize their financial operations. Corporations often use forward contracts or other hedging instruments to mitigate the impact of currency fluctuations on their profits.
Individual Investors
Individual investors also participate in the foreign exchange market, albeit to a lesser extent than banks, central banks, and corporations. They may trade currencies for speculative purposes, seeking to profit from currency movements. Individual investors typically use retail brokers to access the foreign exchange market.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Rates

The foreign exchange market is a dynamic and ever-changing landscape, with a myriad of factors influencing the value of currencies. These factors can be broadly categorized into two main groups: economic and political.
For descriptions on additional topics like foreign exchange market primary function, please visit the available foreign exchange market primary function.
Economic factors that affect foreign exchange rates include interest rates, inflation, trade balances, and economic growth. Interest rates, for example, play a significant role in determining the attractiveness of a currency for investment. Higher interest rates tend to attract foreign capital, leading to an appreciation of the currency. Inflation, on the other hand, can erode the value of a currency over time, making it less desirable for investors.
Trade Balances
Trade balances, which measure the difference between a country’s exports and imports, can also impact foreign exchange rates. A country with a large trade deficit, for example, may see its currency depreciate as foreign demand for its goods and services decreases. Conversely, a country with a large trade surplus may see its currency appreciate as foreign demand for its exports increases.
Political Stability
Political stability is another important factor that can influence foreign exchange rates. Political instability, such as wars, coups, or changes in government, can create uncertainty and risk for investors, leading to a depreciation of the currency. Conversely, political stability and a favorable investment climate can attract foreign capital and lead to an appreciation of the currency.
Foreign Exchange Transactions
Foreign exchange transactions involve the exchange of currencies between parties. These transactions are crucial for international trade, investment, and travel.
The process of executing foreign exchange transactions involves several steps, including determining the exchange rate, agreeing on the amount to be exchanged, and settling the transaction.
Spot Transactions
Spot transactions are the most common type of foreign exchange transaction. They involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the current market rate.
Forward Contracts
Forward contracts are agreements to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date. They are used to hedge against currency fluctuations.
Currency Swaps
Currency swaps are agreements to exchange currencies for a specific period and then exchange them back at the end of the period.
Types of Orders in Foreign Exchange Trading
There are different types of orders used in foreign exchange trading, including:
- Market orders: These orders are executed immediately at the best available market price.
- Limit orders: These orders are executed only when the market price reaches a specified level.
- Stop orders: These orders are used to trigger a trade when the market price reaches a specified level.
The type of order used will affect the execution of the foreign exchange transaction.
Understand how the union of foreign exchange market uk can improve efficiency and productivity.
Risk Management in Foreign Exchange
Foreign exchange trading involves inherent risks that can significantly impact traders and investors. Understanding and managing these risks is crucial for successful participation in the foreign exchange market.
Currency Risk
Currency risk, also known as exchange rate risk, arises from fluctuations in the exchange rates between different currencies. When the value of a currency changes against another, it can lead to gains or losses for traders holding positions in that currency.
Strategies to manage currency risk include:
- Diversification: Spreading investments across different currencies to reduce exposure to any single currency.
- Hedging: Using financial instruments like forwards or options to offset potential losses from adverse currency movements.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk refers to the impact of changes in interest rates on the value of foreign exchange contracts. When interest rates change, the value of existing contracts can be affected, leading to potential losses or gains.
Strategies to manage interest rate risk include:
- Matching maturities: Aligning the maturity dates of foreign exchange contracts with the timing of expected interest rate changes.
- Using interest rate swaps: Swapping interest rate payments with another party to mitigate the impact of interest rate fluctuations.
Counterparty Risk
Counterparty risk is the risk that the other party involved in a foreign exchange transaction may default on its obligations. This risk can arise from the insolvency or unwillingness of the counterparty to fulfill its contractual commitments.
Strategies to manage counterparty risk include:
- Due diligence: Thoroughly researching and assessing the creditworthiness of counterparties before entering into transactions.
- Using reputable brokers or exchanges: Dealing with established and regulated intermediaries that provide safeguards against counterparty default.
Foreign Exchange Market Regulation
The foreign exchange market operates within a regulatory framework designed to ensure market integrity, transparency, and risk management. These regulations cover market conduct, transparency, and risk management.
Role of Central Banks and Regulatory Bodies
Central banks and regulatory bodies play a crucial role in overseeing the foreign exchange market. They establish regulations, monitor market activities, and intervene when necessary to maintain stability and prevent excessive volatility.
- Central banks manage foreign exchange reserves and influence exchange rates through monetary policy.
- Regulatory bodies enforce regulations, investigate misconduct, and impose penalties for violations.
Market Conduct Regulations
Market conduct regulations aim to prevent unfair or manipulative practices in the foreign exchange market. These regulations include:
- Prohibitions on insider trading and front-running
- Requirements for transparency in pricing and execution
- Rules governing conflicts of interest and best execution practices
Transparency Regulations, Foreign exchange market definition simple
Transparency regulations promote fair and efficient markets by ensuring that market participants have access to accurate and timely information. These regulations include:
- Requirements for reporting large currency transactions
- Disclosure of trading activity and positions
- Publication of market data and analysis
Risk Management Regulations
Risk management regulations aim to minimize the risks associated with foreign exchange trading. These regulations include:
- Capital adequacy requirements for financial institutions
- Limits on leverage and position sizes
- Stress testing and contingency planning requirements
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, the foreign exchange market is a vast and complex system that plays a vital role in the global economy. By understanding the basics of forex trading, you can gain access to a potentially lucrative investment opportunity.
