Foreign exchange market definition in simple words – Delving into the realm of finance, let’s unravel the foreign exchange market, a global hub where currencies dance to the rhythm of supply and demand. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the intricacies of this financial arena in a language that resonates with clarity and simplicity.
The foreign exchange market, often abbreviated as Forex, serves as a marketplace where currencies are traded, facilitating international commerce and investments. Its participants, ranging from central banks to individual traders, play pivotal roles in shaping currency values and influencing global economic dynamics.
Introduction: Foreign Exchange Market Definition In Simple Words
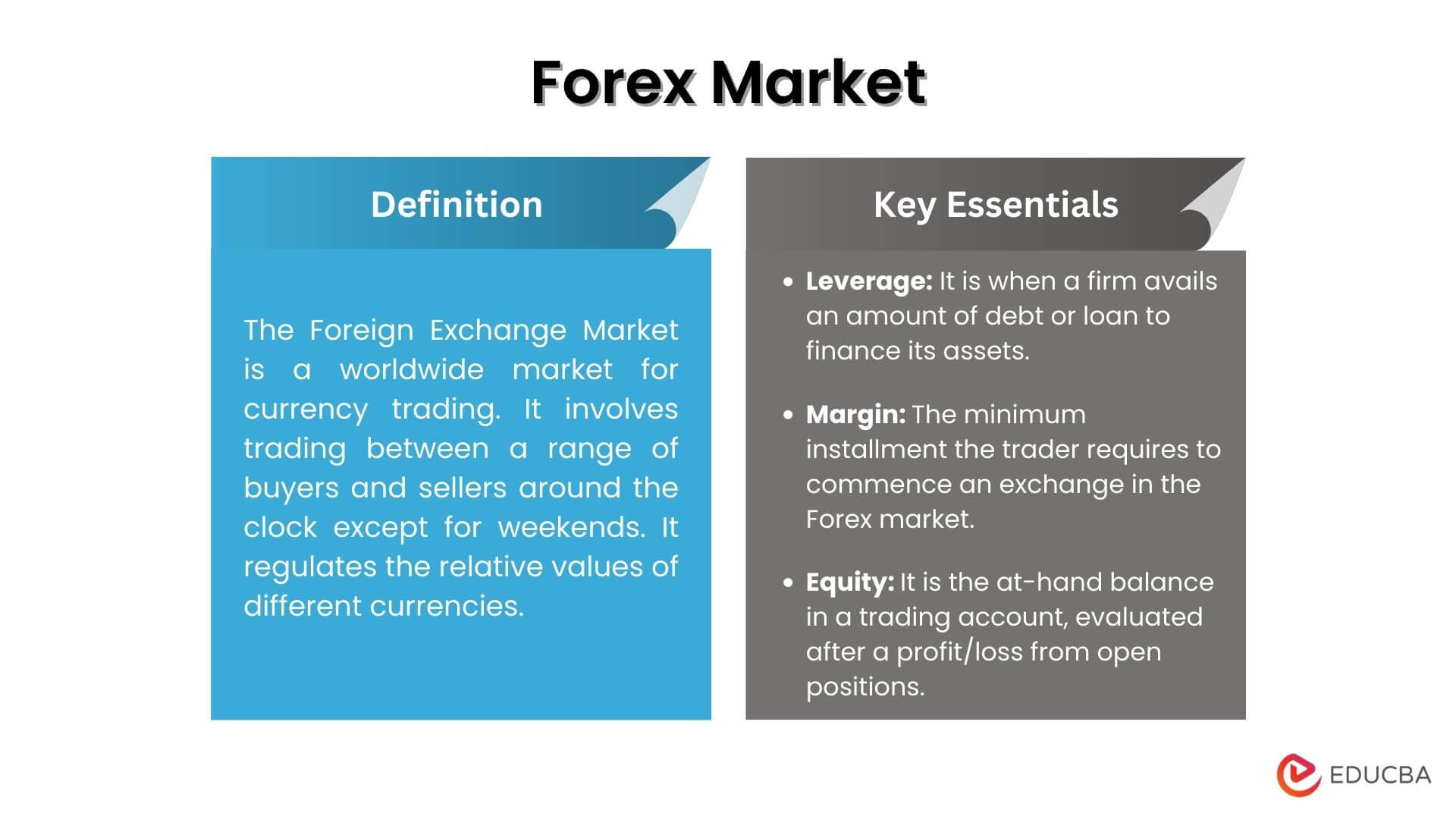
The foreign exchange market, also known as forex or FX, is a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
The purpose of the foreign exchange market is to facilitate the exchange of currencies for various purposes, including international trade, investment, and tourism. It allows businesses and individuals to convert their currencies into other currencies at a market-determined exchange rate.
Key Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market, the largest and most liquid financial market globally, involves various participants with diverse roles and motivations. Understanding these participants is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of the market.
Central Banks
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve, play a significant role in the foreign exchange market. They manage their countries’ monetary policies, including exchange rate interventions, to influence the value of their currencies and achieve economic stability.
Commercial Banks
Commercial banks facilitate foreign exchange transactions for their corporate and individual clients. They offer services such as currency conversion, hedging, and trade finance, earning profits from the spread between buying and selling prices.
Investment Funds, Foreign exchange market definition in simple words
Investment funds, including hedge funds and mutual funds, actively trade currencies to generate returns for their investors. They use various strategies, such as carry trade and currency speculation, to profit from currency movements.
Corporations
Multinational corporations engage in foreign exchange transactions to facilitate international trade and investments. They need to convert currencies to pay for imports, settle international contracts, and manage currency risks.
Retail Traders
Retail traders, including individuals and small businesses, participate in the foreign exchange market through online trading platforms. They speculate on currency movements to make profits, often using leverage to amplify their returns.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Rates
Foreign exchange rates, which determine the value of one currency against another, are influenced by a complex interplay of economic and political factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses, investors, and anyone involved in international trade.
Economic factors play a significant role in shaping exchange rates. Interest rates, inflation, economic growth, and trade balance all have a direct impact on currency values. For instance, a country with high interest rates tends to attract foreign investment, increasing demand for its currency and leading to its appreciation.
Interest Rates
Interest rates are a major factor that affects currency values. Higher interest rates in a country make its currency more attractive to investors, as they can earn a higher return on their investments. This increased demand for the currency leads to its appreciation.
Inflation
Inflation, or the rate at which prices rise, also plays a role in determining exchange rates. A country with high inflation will see its currency depreciate over time, as the value of goods and services in that country decreases relative to other countries.
Economic Growth
Economic growth is another important factor that influences exchange rates. A country with strong economic growth will generally see its currency appreciate, as investors are more likely to invest in a growing economy.
Trade Balance
The trade balance, or the difference between a country’s exports and imports, also affects exchange rates. A country with a positive trade balance will generally see its currency appreciate, as there is more demand for its goods and services than there is for its imports.
Get the entire information you require about foreign exchange market major functions on this page.
Political Factors
Political factors can also have a significant impact on exchange rates. Political instability, government policies, and geopolitical events can all cause currency values to fluctuate.
Political Stability
Political stability is a key factor that affects currency values. A country with a stable political environment is more likely to attract foreign investment, which can lead to appreciation of its currency.
Government Policies
Government policies can also have a significant impact on exchange rates. For example, a government that implements policies that encourage economic growth may see its currency appreciate.
Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events, such as wars, natural disasters, and trade disputes, can also cause currency values to fluctuate. For example, a war in a major oil-producing country may lead to an increase in the price of oil, which can cause the currencies of oil-importing countries to depreciate.
Obtain access to open market foreign currency exchange rates in pakistan to private resources that are additional.
Types of Foreign Exchange Transactions

The foreign exchange market encompasses a wide range of transactions involving the exchange of currencies. These transactions vary in purpose, mechanics, and the parties involved.
Here are some common types of foreign exchange transactions:
Spot Transactions
- In spot transactions, currencies are exchanged at the current market rate, known as the spot rate.
- The settlement of spot transactions typically occurs within two business days, making them suitable for immediate currency needs.
Forward Transactions
- Forward transactions involve the exchange of currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date.
- These transactions are used to hedge against currency fluctuations and lock in exchange rates for future payments or receipts.
Swap Transactions
- Swap transactions are agreements to exchange currencies at different points in time, typically with the intention of reducing transaction costs or managing currency exposure.
- Swap transactions can be tailored to meet specific needs, such as currency swaps, interest rate swaps, or cross-currency swaps.
Options Transactions
- Options transactions give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a specified price on or before a certain date.
- Options are used to manage currency risk, speculate on exchange rate movements, or hedge against potential losses.
Non-Deliverable Forwards (NDFs)
- NDFs are forward contracts that do not result in the physical delivery of the underlying currency.
- NDFs are used to speculate on exchange rate movements or hedge against currency risk in countries with restrictions on foreign exchange transactions.
Foreign Exchange Market Risks
Participating in the foreign exchange market entails potential risks that traders must be aware of. These risks stem from the dynamic nature of currency values, influenced by various economic and political factors. Understanding these risks is crucial for successful navigation of the forex market.
There are several ways to mitigate these risks, such as:
- Conducting thorough research and analysis of market trends and economic indicators.
- Diversifying investments across different currencies and asset classes.
- Utilizing risk management tools such as stop-loss orders and hedging strategies.
Currency Risk
Currency risk, also known as exchange rate risk, arises from fluctuations in the value of one currency relative to another. This risk is inherent in any foreign exchange transaction, as the value of the currencies involved can change rapidly, potentially leading to losses or gains.
To mitigate currency risk, traders can:
- Choose currency pairs with relatively stable exchange rates.
- Monitor economic and political news that may affect currency values.
- Use hedging strategies, such as forward contracts or options, to lock in exchange rates.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk stems from changes in interest rates, which can impact the value of currencies. When interest rates rise in one country relative to another, it can lead to an appreciation of the currency with higher interest rates, as investors seek higher returns.
Traders can mitigate interest rate risk by:
- Monitoring central bank announcements and economic data that may affect interest rates.
- Choosing currency pairs with similar interest rate trends.
- Using interest rate swaps or other hedging instruments to manage exposure to interest rate fluctuations.
Political Risk
Political risk refers to the potential for political events or instability to impact currency values. Political events, such as elections, coups, or changes in government policies, can lead to currency fluctuations and market volatility.
To mitigate political risk, traders can:
- Monitor political news and events that may affect currency values.
- Avoid trading in currencies of countries with high political instability.
- Use hedging strategies, such as currency options or forward contracts, to protect against political risks.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk refers to the difficulty or inability to buy or sell a currency at a reasonable price. This risk is particularly relevant in thinly traded currencies or during periods of market volatility.
Traders can mitigate liquidity risk by:
- Choosing currency pairs with high liquidity.
- Trading during periods of high market activity.
- Using limit orders or other order types that allow for greater control over execution prices.
Role of the Foreign Exchange Market in International Trade

The foreign exchange market plays a pivotal role in facilitating international trade by enabling the exchange of currencies between countries. This exchange allows businesses to import and export goods and services, as well as make payments for investments and other transactions across borders.
Learn about more about the process of foreign exchange market deals in in the field.
Exchange rate fluctuations can significantly impact international trade. When the value of a country’s currency appreciates (increases) against another, its exports become more expensive for foreign buyers, potentially leading to a decrease in demand. Conversely, a depreciation (decrease) in the value of a country’s currency can make its exports more competitive and boost demand.
Impact of Exchange Rate Fluctuations on Trade
- Exports: When a country’s currency appreciates, its exports become more expensive for foreign buyers, reducing demand and potentially leading to a decline in exports.
- Imports: When a country’s currency depreciates, its imports become cheaper, increasing demand and potentially leading to a rise in imports.
- Balance of Trade: Exchange rate fluctuations can affect a country’s balance of trade (the difference between its exports and imports). An appreciation can lead to a trade deficit (more imports than exports), while a depreciation can contribute to a trade surplus (more exports than imports).
Future Trends in the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is constantly evolving, and a number of emerging trends are likely to shape its future. These trends include the increasing use of technology, the globalization of trade and investment, and the rise of emerging market economies.
The increasing use of technology is making it easier for individuals and businesses to trade foreign exchange. Online trading platforms have made it possible to trade currencies from anywhere in the world, and mobile trading apps have made it even easier to access the market. As a result, the number of participants in the foreign exchange market is likely to continue to grow.
The globalization of trade and investment is also increasing the demand for foreign exchange. As businesses expand their operations into new countries, they need to exchange currencies to pay for goods and services. The rise of emerging market economies is also contributing to the growth of the foreign exchange market. As these economies develop, they are increasingly participating in global trade and investment, which is creating demand for their currencies.
These trends are likely to have a significant impact on the future of the foreign exchange market. The increasing use of technology is likely to make the market more efficient and accessible, while the globalization of trade and investment is likely to increase the demand for foreign exchange. The rise of emerging market economies is also likely to create new opportunities for investors.
Regulatory Changes
Regulators are also playing a more active role in the foreign exchange market. In recent years, a number of new regulations have been introduced to improve the transparency and stability of the market. These regulations are likely to continue to evolve in the future, as regulators seek to keep pace with the changing landscape of the foreign exchange market.
Ultimate Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of the foreign exchange market, it’s evident that this intricate system plays a crucial role in fostering international trade, facilitating investments, and impacting economies worldwide. Understanding its mechanisms and dynamics empowers individuals and businesses alike to navigate the ever-changing landscape of global finance.
