Foreign exchange market expensive currency – In the dynamic world of currency exchange, the valuation of currencies plays a pivotal role. This article delves into the foreign exchange market and explores the intriguing concept of expensive currencies, examining the factors that drive their value and the impact they have on economies.
The determination of an expensive currency hinges on a multitude of economic indicators and events, including interest rates, inflation, and economic growth. These factors shape the strength of a currency and influence its desirability in the global market.
Currency Valuation: Foreign Exchange Market Expensive Currency

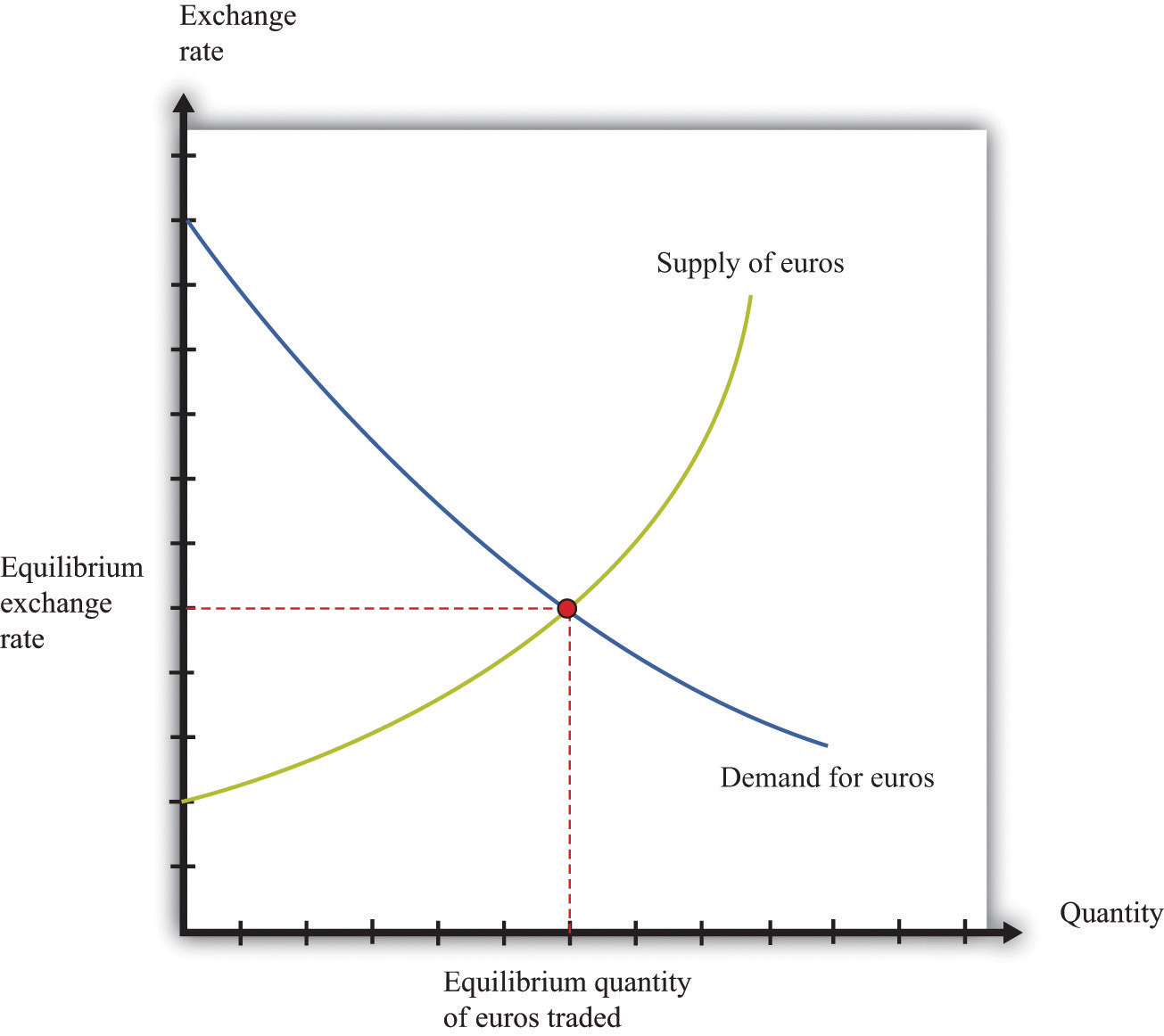
The value of a currency in the foreign exchange market is determined by a multitude of factors, both domestic and international. These factors influence the demand and supply for a particular currency, ultimately affecting its exchange rate against other currencies.
Economic indicators and events that impact currency values include:
Economic Growth
- Strong economic growth typically leads to an increase in demand for a country’s currency, as investors seek to participate in the growth potential.
- A growing economy often results in higher interest rates, which can attract foreign capital and further strengthen the currency.
Inflation, Foreign exchange market expensive currency
- High inflation can erode the value of a currency, as it reduces the purchasing power of domestic goods and services.
- Central banks may raise interest rates to combat inflation, which can make the currency more attractive to investors and support its value.
Interest Rates
- Higher interest rates tend to attract foreign capital, as investors seek higher returns on their investments.
- A country with higher interest rates may experience an appreciation of its currency, as demand for its bonds and other interest-bearing assets increases.
Political Stability
- Political stability and a favorable business environment can make a country more attractive to foreign investment.
- Uncertainty or political turmoil can lead to capital flight and a depreciation of the currency.
Current Account Balance
- A current account surplus, where exports exceed imports, can indicate a strong economy and support the value of the currency.
- A current account deficit, where imports exceed exports, can put downward pressure on the currency.
Speculation
- Currency markets can be subject to speculation, where traders buy or sell currencies based on expectations of future value changes.
- Speculation can amplify currency movements and contribute to volatility.
Determinants of Expensive Currencies
The value of a currency is determined by various factors, making some currencies more expensive than others. Understanding the characteristics and economic conditions that contribute to an expensive currency is crucial for investors, traders, and businesses.
Obtain a comprehensive document about the application of foreign exchange market open that is effective.
Interest Rates
Interest rates play a significant role in currency valuation. Higher interest rates in a country make its currency more attractive to foreign investors seeking higher returns on their investments. This increased demand for the currency leads to its appreciation against other currencies.
For descriptions on additional topics like types of foreign exchange market ppt, please visit the available types of foreign exchange market ppt.
Inflation, Foreign exchange market expensive currency
Inflation, the rate at which prices rise, affects currency value. Low inflation indicates a stable economy and encourages foreign investment, leading to currency appreciation. High inflation, on the other hand, erodes the purchasing power of a currency, making it less desirable and contributing to its depreciation.
Economic Growth
Economic growth is a key indicator of a country’s overall health and stability. A strong and growing economy attracts foreign investment, boosting demand for the currency and contributing to its appreciation. Conversely, a weak or stagnant economy can lead to currency depreciation.
Impact of Expensive Currencies
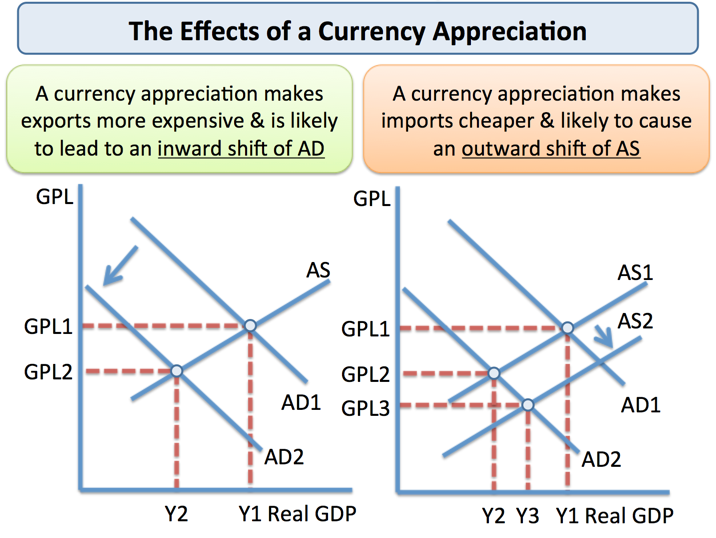
The value of a currency significantly influences a country’s economy. Expensive currencies offer certain advantages but also pose challenges.
Benefits:
When investigating detailed guidance, check out foreign exchange market phone app now.
- Lower import costs: Imports become cheaper, allowing consumers to purchase foreign goods and services at a reduced price.
- Increased purchasing power abroad: Citizens traveling overseas benefit from a stronger currency, as their money goes further in foreign countries.
- Attractiveness for foreign investment: An expensive currency indicates a stable economy, attracting foreign investors seeking opportunities.
Drawbacks:
- Reduced exports: Expensive currencies make exports more costly for foreign buyers, potentially leading to a decline in export revenue.
- Curbed tourism: Tourists from other countries may find it more expensive to visit, resulting in a decrease in tourism revenue.
- Reduced competitiveness: Businesses operating in the export sector may face challenges competing with companies from countries with weaker currencies.
Strategies for Managing Expensive Currencies
Mitigating the impact of expensive currencies requires a combination of strategies by governments and businesses. These include monetary policy, fiscal policy, and currency intervention.
Monetary policy, controlled by central banks, aims to manage the supply of money and interest rates. Increasing interest rates can attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the domestic currency and potentially leading to its appreciation.
Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy, implemented by governments, involves adjusting government spending and taxation. Reducing government spending or increasing taxes can reduce domestic demand for goods and services, leading to a decrease in imports and potentially strengthening the domestic currency.
Currency Intervention
Currency intervention involves the central bank buying or selling its own currency in the foreign exchange market. Buying domestic currency can increase its value, while selling it can lead to depreciation.
Case Studies of Expensive Currencies
To illustrate the economic implications of expensive currencies, let’s examine case studies of countries or regions that have experienced such conditions.
Switzerland
Switzerland has consistently maintained an expensive currency due to its strong economy, political stability, and safe-haven status during periods of global uncertainty. The Swiss franc has appreciated significantly against other major currencies over the years.
The strong franc has boosted the purchasing power of Swiss citizens and made Swiss exports more expensive. However, it has also challenged Swiss businesses by reducing their international competitiveness and impacting tourism revenues.
Norway
Norway’s currency, the Norwegian krone, has been expensive due to the country’s vast oil and gas reserves. The influx of foreign capital seeking to invest in these resources has strengthened the krone.
While the strong krone has provided Norwegians with a high standard of living, it has also made it more difficult for other industries to compete internationally. The government has implemented measures to mitigate these effects, such as investing in infrastructure and supporting innovation.
Japan
Japan has experienced periods of an expensive yen due to its strong economy and low interest rates. The yen’s strength has made Japanese exports less competitive and contributed to deflationary pressures within the economy.
The Japanese government has intervened in the currency market and implemented monetary policies to weaken the yen. However, these efforts have had limited success, and the yen remains relatively expensive.
Last Recap
The interplay of economic forces and government policies in managing expensive currencies is a complex and multifaceted endeavor. By understanding the determinants and potential consequences of expensive currencies, policymakers and businesses can navigate the challenges and harness the opportunities they present.
From the case studies of countries that have grappled with expensive currencies, we gain valuable insights into the economic conditions, policies, and outcomes associated with this phenomenon. These lessons serve as a guide for policymakers and businesses as they seek to mitigate the impact of expensive currencies and foster economic growth.
