Step into the dynamic realm of foreign exchange, where currencies dance and global economies intertwine. Define foreign exchange market and its importance unveils the intricacies of this vital marketplace, exploring its role in international trade, investment, and risk management. Brace yourself for a journey that unravels the secrets of currency exchange and its profound impact on our interconnected world.
The foreign exchange market, a bustling hub of financial activity, serves as a platform for exchanging currencies between nations, facilitating global commerce and investment. Its significance extends beyond mere transactions, influencing economic growth, managing financial risks, and fostering global interconnectedness.
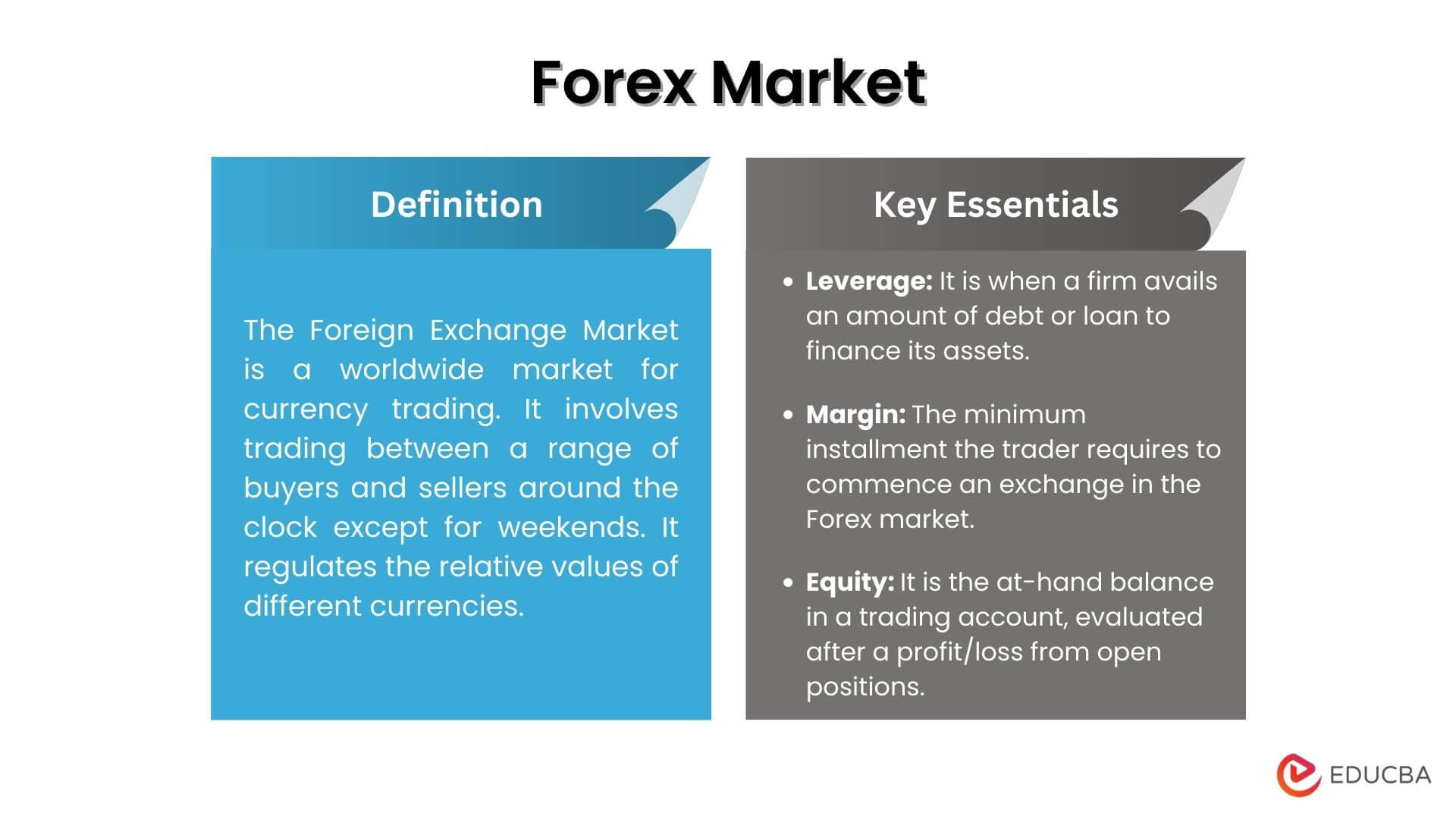
Definition of Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market or FX market, is a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion. The forex market is open 24 hours a day, 5 days a week, and currencies are traded in pairs.
Role of Currencies in the Foreign Exchange Market
Currencies are the medium of exchange in the foreign exchange market. They are used to facilitate international trade and investment. The value of a currency is determined by supply and demand. When there is more demand for a currency, its value will increase. When there is less demand for a currency, its value will decrease.
Types of Currencies Traded
There are many different types of currencies traded in the foreign exchange market. The most commonly traded currencies are the US dollar, the euro, the Japanese yen, the British pound, and the Swiss franc. These currencies are known as “major currencies”. There are also many other currencies traded in the foreign exchange market, including “minor currencies” and “exotic currencies”.
Importance of Foreign Exchange Market: Define Foreign Exchange Market And Its Importance

The foreign exchange market is a vital component of the global financial system. It enables the smooth flow of international trade and investment, facilitates economic growth, and provides risk management tools for businesses and investors.
Facilitating International Trade
The foreign exchange market plays a crucial role in facilitating international trade. When businesses import or export goods and services, they need to convert their currency into the currency of the other country. The foreign exchange market provides a platform for these currency conversions, ensuring that businesses can make and receive payments in different currencies.
For example, if a U.S. company wants to import goods from Japan, it will need to convert its U.S. dollars into Japanese yen. The foreign exchange market allows the company to do this quickly and efficiently, ensuring that the transaction can proceed smoothly.
Facilitating Global Investment and Economic Growth
The foreign exchange market also facilitates global investment. When investors invest in foreign stocks, bonds, or real estate, they need to convert their currency into the currency of the country where the investment is made. The foreign exchange market provides a mechanism for these currency conversions, making it easier for investors to diversify their portfolios and access investment opportunities worldwide.
Global investment can lead to economic growth by providing capital for businesses to expand, create jobs, and innovate. The foreign exchange market supports this process by making it easier for investors to access global investment opportunities.
Check foreign exchange market close time to inspect complete evaluations and testimonials from users.
Risk Management
The foreign exchange market also plays a vital role in risk management. Businesses and investors often use foreign exchange hedging strategies to reduce the risk of currency fluctuations. By using these strategies, they can protect themselves from losses that could occur if the value of a currency changes unexpectedly.
Check what professionals state about the concept of foreign exchange market and its benefits for the industry.
For example, a U.S. company that exports goods to Europe may use a currency forward contract to lock in the exchange rate for future payments. This protects the company from the risk that the euro will weaken against the U.S. dollar, which could reduce the value of its export earnings.
Notice foreign exchange market background for recommendations and other broad suggestions.
Participants in Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market involves various entities known as participants. These participants engage in currency transactions for different purposes, influencing the market’s dynamics and exchange rates.
Banks
Banks are the primary participants in the foreign exchange market. They act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers of currencies, facilitating currency exchange and international payments. Banks maintain large reserves of foreign currencies to meet customer demands and participate in interbank trading.
Corporations
Multinational corporations and businesses with international operations actively participate in the foreign exchange market. They engage in currency exchange to facilitate international trade, make investments abroad, and manage their foreign exchange risks.
Individual Investors
Individual investors, including retail traders and hedge funds, also participate in the foreign exchange market. They speculate on currency movements and seek to profit from exchange rate fluctuations.
Central Banks, Define foreign exchange market and its importance
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States or the European Central Bank, play a significant role in the foreign exchange market. They intervene in the market to manage exchange rates, influence monetary policy, and maintain financial stability.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Rates
Foreign exchange rates are influenced by a myriad of economic and political factors. These factors can impact the value of currencies and lead to fluctuations in exchange rates.
Economic Factors
Economic factors play a significant role in determining foreign exchange rates. These include:
- Interest rates: Higher interest rates in a country can attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the country’s currency and leading to appreciation.
- Inflation: High inflation can erode the purchasing power of a currency, making it less attractive to foreign investors and leading to depreciation.
- Economic growth: A strong economy with positive growth prospects can attract foreign investment and support currency appreciation.
- Trade balance: A positive trade balance (exports exceeding imports) can increase demand for a country’s currency, leading to appreciation.
Political Factors
Political factors can also impact foreign exchange rates. These include:
- Political stability: Political instability and uncertainty can deter foreign investment and lead to currency depreciation.
- Government policies: Government policies, such as exchange rate controls or fiscal policies, can influence the supply and demand for a currency.
- International relations: Diplomatic tensions or conflicts between countries can affect foreign exchange rates.
Examples:
- In 2022, the US dollar strengthened against many other currencies due to the Federal Reserve raising interest rates to combat inflation.
- In 2016, the British pound depreciated significantly after the UK voted to leave the European Union, creating political uncertainty.
Foreign Exchange Market Instruments
The foreign exchange market is a global marketplace where currencies are traded. To facilitate these transactions, a variety of financial instruments have been developed.
Spot Contracts
Spot contracts are the most basic type of foreign exchange instrument. They involve the immediate exchange of one currency for another at the current market rate. Spot contracts are typically used for small transactions and for businesses that need to convert currencies quickly.
Forward Contracts
Forward contracts are agreements to exchange currencies at a specified rate on a future date. They are used to hedge against the risk of exchange rate fluctuations. Forward contracts are typically used for larger transactions and for businesses that need to plan their currency needs in advance.
Currency Options
Currency options give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specified amount of currency at a specified rate on a future date. Currency options are used to speculate on exchange rate movements or to hedge against the risk of exchange rate fluctuations.
Foreign Exchange Market Regulation
The foreign exchange market is a highly regulated environment to ensure its stability, transparency, and fairness. Central banks and other regulatory bodies play crucial roles in establishing and enforcing these regulations.
Central Bank Role
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States or the European Central Bank, are responsible for managing monetary policy and overseeing the foreign exchange market. They set interest rates, intervene in the market to stabilize exchange rates, and regulate the activities of banks and other financial institutions involved in foreign exchange trading.
Regulatory Bodies
In addition to central banks, various regulatory bodies around the world are responsible for overseeing the foreign exchange market. These include the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the United Kingdom, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) in the United States, and the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) in the European Union. These bodies set rules and regulations to prevent market manipulation, ensure transparency, and protect investors.
Examples of Regulations
- Anti-Money Laundering and Know Your Customer (KYC) Regulations: These regulations require financial institutions to verify the identity of their clients and monitor transactions for suspicious activity.
- Capital Adequacy Requirements: These regulations set minimum capital requirements for banks and other financial institutions involved in foreign exchange trading to ensure their financial stability.
- Market Conduct Rules: These regulations prohibit market manipulation, insider trading, and other unethical practices that could disrupt the market.
Final Wrap-Up

In conclusion, the foreign exchange market stands as a cornerstone of the global economy, enabling international trade, facilitating investment, and mitigating financial risks. Its dynamic nature, influenced by a myriad of economic and political factors, underscores the complexity and interconnectedness of our global financial system. Understanding define foreign exchange market and its importance empowers us to navigate the ever-evolving landscape of currency exchange and its profound impact on businesses, economies, and individuals alike.
