Demand and supply in foreign exchange market – At the heart of the foreign exchange market lies the interplay of demand and supply, a dynamic duo that shapes currency values and influences global economies. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the complexities of this vast and ever-evolving marketplace.
The foreign exchange market, a global arena where currencies are traded, serves as a vital facilitator of international trade and investment. Within this dynamic realm, the demand for and supply of foreign currencies constantly interact, determining exchange rates and influencing economic outcomes.
Market Structure

The foreign exchange market (forex market) is the global marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with an estimated daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
The forex market is a decentralized market, meaning that there is no central exchange where all trades take place. Instead, trades are executed over-the-counter (OTC) between two parties. This makes the forex market very liquid, as there are always buyers and sellers willing to trade.
Key Participants
The key participants in the forex market include:
- Banks
- Hedge funds
- Corporations
- Retail traders
Banks are the largest participants in the forex market, accounting for over 50% of all trades. They trade currencies for their own accounts, as well as for their clients.
Hedge funds are investment funds that use sophisticated trading strategies to generate profits. They are often active in the forex market, as they can use leverage to amplify their returns.
Corporations trade currencies to hedge against foreign exchange risk. This risk arises when a company has operations in multiple countries and is exposed to fluctuations in currency exchange rates.
Remember to click the primary participants of the foreign exchange market are imf and world bank to understand more comprehensive aspects of the the primary participants of the foreign exchange market are imf and world bank topic.
Retail traders are individuals who trade currencies for their own accounts. They typically trade smaller amounts of money than institutional traders.
Role of Central Banks
Central banks play an important role in the forex market. They are responsible for setting monetary policy, which can have a significant impact on currency exchange rates.
Central banks also intervene in the forex market to smooth out fluctuations in currency exchange rates. They do this by buying or selling currencies in the market.
Determinants of Demand and Supply
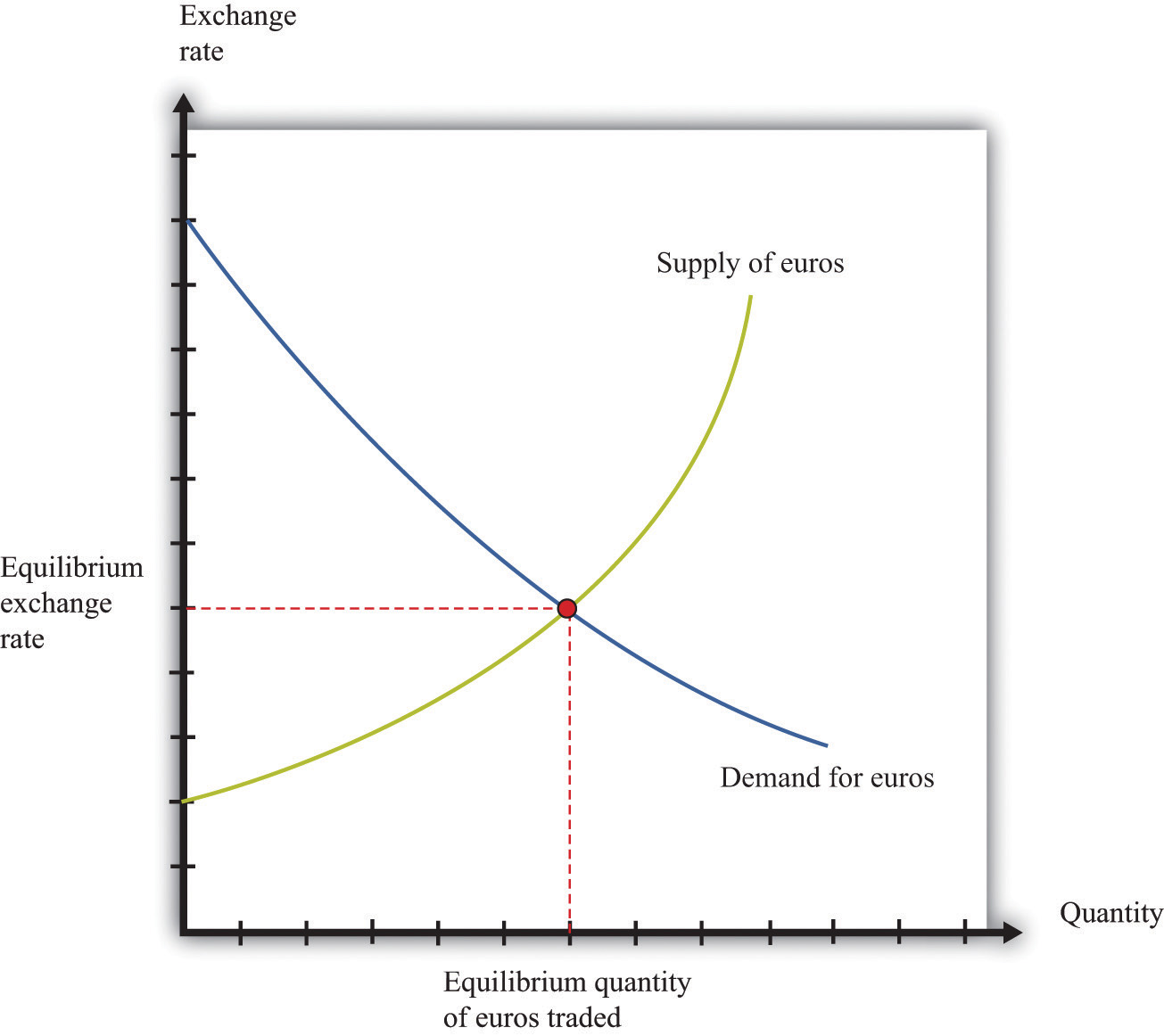
The demand for and supply of foreign currency are determined by various factors. These factors influence the quantity of currency that individuals, businesses, and governments are willing to buy or sell at a given exchange rate.
Understanding these determinants is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of the foreign exchange market and predicting exchange rate movements.
You also will receive the benefits of visiting foreign exchange market future today.
Factors Determining Demand for Foreign Currency, Demand and supply in foreign exchange market
- Imports and Exports: The demand for foreign currency increases when a country imports more goods and services than it exports, creating a need to purchase foreign currency to pay for the imports.
- Foreign Investment: When domestic investors invest in foreign assets, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, they demand foreign currency to make these investments.
- Tourism and Travel: Individuals traveling abroad demand foreign currency to cover expenses in foreign countries.
- Speculation: Currency traders and speculators buy foreign currency in anticipation of its value increasing, leading to increased demand.
Factors Determining Supply of Foreign Currency
- Exports and Imports: When a country exports more goods and services than it imports, it creates a surplus of foreign currency, increasing its supply.
- Foreign Investment: When foreign investors invest in domestic assets, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, they supply foreign currency to make these investments.
- Tourism and Travel: Individuals visiting domestic destinations supply foreign currency to cover expenses.
- Central Bank Intervention: Central banks can intervene in the foreign exchange market to buy or sell foreign currency to influence its value, affecting the supply.
Interaction of Factors and Exchange Rate Determination
The interaction of demand and supply forces determines the exchange rate. When demand for foreign currency exceeds supply, the exchange rate tends to increase, making the foreign currency more expensive. Conversely, when supply exceeds demand, the exchange rate tends to decrease, making the foreign currency cheaper.
These factors are constantly fluctuating, influenced by economic, political, and social events, leading to changes in the exchange rate and the dynamics of the foreign exchange market.
Exchange Rate Dynamics
Exchange rate dynamics refer to the changes in the value of a currency relative to other currencies over time. The exchange rate is the price of one currency in terms of another. It is influenced by various factors, including economic conditions, political events, and market sentiment.
There are different types of exchange rate regimes, each with its own mechanisms for determining the exchange rate.
Types of Exchange Rate Regimes
- Fixed Exchange Rate Regime: In this regime, the government or central bank fixes the exchange rate at a predetermined level against a single currency or a basket of currencies. The central bank intervenes in the foreign exchange market to maintain the fixed rate.
- Managed Float Regime: In this regime, the government or central bank allows the exchange rate to fluctuate within a target range. The central bank intervenes in the market to prevent the exchange rate from moving outside the target range.
- Free Float Regime: In this regime, the exchange rate is determined solely by the forces of demand and supply in the foreign exchange market. The central bank does not intervene in the market.
The exchange rate is determined differently in each type of regime. In a fixed exchange rate regime, the central bank sets the exchange rate and intervenes in the market to maintain it. In a managed float regime, the central bank intervenes in the market to keep the exchange rate within a target range. In a free float regime, the exchange rate is determined by the interaction of supply and demand in the market.
Factors Causing Exchange Rate Volatility
Several factors can cause exchange rate volatility, including:
- Economic Conditions: Changes in economic growth, inflation, and interest rates can affect the demand for a currency and, consequently, its exchange rate.
- Political Events: Political instability, wars, and elections can create uncertainty and affect the exchange rate.
- Market Sentiment: Speculators and investors can drive exchange rate movements based on their expectations about future economic conditions or political events.
- Carry Trade: This is a strategy where investors borrow in one currency with a low interest rate and invest in another currency with a higher interest rate. It can create demand for the higher-yielding currency and lead to exchange rate volatility.
Market Equilibrium

Market equilibrium in the foreign exchange market occurs when the quantity of a currency demanded is equal to the quantity supplied. At this point, there is no excess demand or supply, and the exchange rate is considered to be in balance.
Obtain direct knowledge about the efficiency of major participants of foreign exchange market through case studies.
Factors that can shift the equilibrium exchange rate
Several factors can cause the equilibrium exchange rate to shift, including:
- Changes in economic growth
- Changes in interest rates
- Changes in inflation rates
- Changes in political stability
- Changes in global demand for a particular currency
Effects of a change in the equilibrium exchange rate
A change in the equilibrium exchange rate can have several effects on the economy, including:
- Impact on exports and imports
- Impact on investment
- Impact on inflation
- Impact on economic growth
Market Intervention
Market intervention refers to actions taken by central banks to influence the foreign exchange market. Central banks intervene in the market by buying or selling currencies to achieve specific economic goals.
The main goals of market intervention include:
- Stabilizing the exchange rate
- Managing inflation
- Influencing capital flows
Types of Market Intervention
There are two main types of market intervention:
- Direct intervention: Involves the central bank directly buying or selling currencies in the foreign exchange market.
- Indirect intervention: Involves the central bank using other monetary policy tools, such as interest rate adjustments, to influence the exchange rate.
Benefits of Market Intervention
Potential benefits of market intervention include:
- Smoothing out exchange rate fluctuations
- Preventing excessive currency appreciation or depreciation
- Supporting economic growth and stability
Costs of Market Intervention
Potential costs of market intervention include:
- Reduced market efficiency
- Loss of central bank reserves
- Moral hazard (encouraging market participants to rely on central bank intervention)
Ending Remarks: Demand And Supply In Foreign Exchange Market
In conclusion, demand and supply play a pivotal role in shaping the dynamics of the foreign exchange market. By understanding the factors that influence these forces, market participants can gain valuable insights into currency movements and make informed decisions in this complex and ever-changing environment.
