Economics definition of foreign exchange market delves into the fascinating world of currency exchange, where global trade and finance converge. This intricate network of markets facilitates the conversion of currencies, enabling businesses and individuals to engage in cross-border transactions, investments, and financial activities.
Understanding the economics definition of foreign exchange market empowers us to navigate the complexities of international commerce, unravel the factors influencing currency values, and harness the opportunities presented by this dynamic and ever-evolving financial landscape.
Definition of Foreign Exchange Market

The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market, is a global marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
The forex market is used by businesses, governments, and individuals to exchange currencies for a variety of reasons, including international trade, investment, and speculation.
Types of Forex Markets
There are two main types of forex markets: the spot market and the forward market.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of foreign exchange artinya.
- The spot market is where currencies are traded for immediate delivery.
- The forward market is where currencies are traded for delivery at a future date.
Role of Forex Markets
Forex markets play a vital role in international trade and finance. They provide a way for businesses to exchange currencies so that they can buy and sell goods and services from other countries.
Forex markets also provide a way for investors to diversify their portfolios and hedge against currency risk.
Check what professionals state about foreign exchange market upsc and its benefits for the industry.
Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market
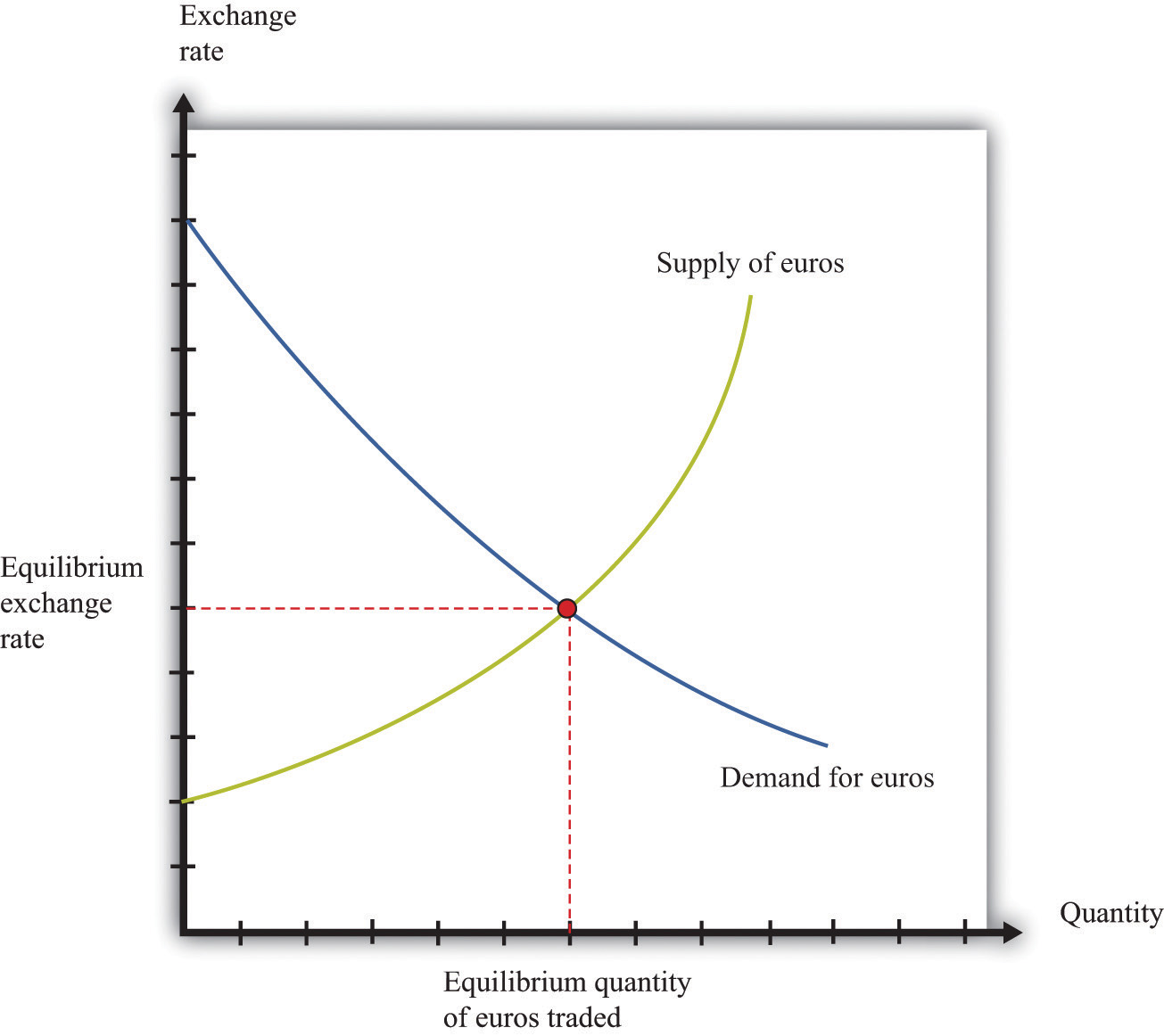
The foreign exchange market, the world’s largest financial market, involves a diverse range of participants, each with unique roles and motivations.
Major participants include banks, corporations, institutional investors, central banks, and individual traders. Their actions collectively influence market dynamics, affecting exchange rates and overall market stability.
Banks
Banks play a central role in the forex market, facilitating transactions and providing liquidity. They act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, matching orders and facilitating currency exchanges.
Banks also speculate on currency movements, seeking to profit from exchange rate fluctuations. Their large trading volumes can significantly impact market direction.
Corporations
Corporations engage in foreign exchange transactions for various reasons, including international trade, investment, and hedging against currency risk.
When companies import or export goods, they need to exchange currencies to settle payments. Corporations also invest in foreign markets, requiring currency conversions. Additionally, they may use forex hedging strategies to mitigate the impact of currency fluctuations on their operations.
Institutional Investors
Institutional investors, such as hedge funds, mutual funds, and pension funds, actively participate in the forex market, seeking to generate returns and manage risk.
These investors employ sophisticated trading strategies and utilize large capital pools to capitalize on market movements. Their trades can influence exchange rates and contribute to market volatility.
Central Banks
Central banks, responsible for managing a country’s monetary policy, intervene in the forex market to influence exchange rates and maintain economic stability.
Central banks buy or sell currencies to control the value of their own currency relative to others. Their actions can significantly impact market dynamics and affect the global economy.
Individual Traders
Individual traders, known as retail traders, participate in the forex market with varying degrees of experience and capital.
Retail traders often trade for speculative purposes, attempting to profit from short-term currency fluctuations. Their collective actions can contribute to market volatility, particularly during periods of high uncertainty.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Rates
The foreign exchange market is a dynamic and ever-changing environment. A multitude of factors can influence the value of currencies, making it crucial to understand the underlying forces that drive these fluctuations.
Economic Factors
- Interest rates: Central banks set interest rates to control inflation and economic growth. Higher interest rates attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the domestic currency and strengthening its value.
- Economic growth: A strong economy attracts foreign investment and boosts demand for the domestic currency. Conversely, a weak economy can lead to currency depreciation.
- Inflation: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of a currency, reducing its value relative to other currencies.
- Trade balance: A country with a trade surplus (exports exceeding imports) typically sees its currency appreciate, while a trade deficit (imports exceeding exports) can lead to depreciation.
Political Factors
- Political stability: Political uncertainty and instability can lead to currency depreciation as investors seek safer havens.
- Government policies: Changes in fiscal or monetary policy, such as tax cuts or interest rate adjustments, can impact currency values.
- International relations: Diplomatic tensions or conflicts between countries can affect currency exchange rates.
Social Factors
- Culture: Cultural events or changes in consumer preferences can impact demand for certain currencies.
- Natural disasters: Natural disasters can disrupt economic activity and affect currency values.
- Demographics: Changes in population demographics, such as aging or migration, can influence the supply and demand for currencies.
Supply and Demand, Economics definition of foreign exchange market
Ultimately, foreign exchange rates are determined by the forces of supply and demand. When demand for a currency exceeds supply, its value appreciates. Conversely, when supply exceeds demand, the currency depreciates.
Factors affecting supply and demand include:
- Speculation: Currency traders speculate on future exchange rate movements, which can influence supply and demand.
- Hedging: Businesses and individuals hedge against currency risks by buying or selling currencies in the forward market, which affects supply and demand in the spot market.
- Central bank intervention: Central banks can intervene in the foreign exchange market to stabilize currency values or achieve specific economic goals.
Foreign Exchange Market Operations
The foreign exchange market facilitates the exchange of currencies, enabling international trade and investment. Various types of transactions occur within this market, including spot and forward contracts, which are essential for managing currency risk and facilitating global economic activities.
Currency Trading
Currency trading involves the exchange of one currency for another, typically with the goal of profiting from fluctuations in exchange rates. The most common type of currency trading is spot trading, where currencies are exchanged at the current market rate for immediate delivery.
Forward contracts, on the other hand, allow traders to lock in an exchange rate for a future date, hedging against potential currency fluctuations. This is particularly useful for businesses that need to make future payments or receive payments in a foreign currency.
Remember to click foreign exchange market share to understand more comprehensive aspects of the foreign exchange market share topic.
Leverage and Risk Management
Leverage is a tool used in forex trading that allows traders to increase their potential profits by borrowing funds from a broker. However, it also amplifies potential losses, so it’s crucial to use leverage wisely and employ appropriate risk management techniques.
Risk management strategies include setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, diversifying trades across different currency pairs, and using technical analysis to identify potential trading opportunities and market trends.
Regulation and Supervision of the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is a complex and interconnected global network, making regulation and supervision crucial for ensuring market integrity and protecting investors.
Regulatory Bodies
- Central Banks: Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the US and the European Central Bank, play a significant role in regulating the forex market by setting monetary policy and intervening in currency markets to stabilize exchange rates.
- Financial Conduct Authorities: Regulatory bodies like the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) in the US oversee forex brokers and exchanges, ensuring compliance with regulations and protecting investors from fraud and manipulation.
- International Organizations: The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) provides a forum for central banks to cooperate on forex market issues and promotes best practices in regulation.
Measures for Market Integrity
- Anti-Money Laundering and Know-Your-Customer (KYC) Regulations: These measures aim to prevent the use of the forex market for illegal activities, such as money laundering and terrorist financing.
- Transparency and Reporting Requirements: Regulators require forex brokers and exchanges to disclose their trading activities and provide regular reports to ensure transparency and accountability.
- Risk Management Frameworks: Regulators set standards for risk management practices to minimize systemic risks and protect investors from excessive losses.
Challenges and Controversies
Despite regulatory efforts, the forex market faces challenges and controversies:
- Complexity and Global Reach: The global nature of the forex market makes it difficult for regulators to effectively monitor and enforce regulations across different jurisdictions.
- Cross-Border Transactions: Forex transactions often involve multiple countries, which can create jurisdictional issues and make it challenging to enforce regulations.
- Unlicensed Brokers: Unregulated or unlicensed brokers can operate outside the regulatory framework, posing risks to investors and undermining market integrity.
Emerging Trends and Innovations in the Foreign Exchange Market: Economics Definition Of Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is constantly evolving, with new technologies and innovations shaping its dynamics. These advancements have revolutionized the way currencies are traded, creating opportunities and challenges for market participants.
Electronic Trading Platforms
Electronic trading platforms have transformed the forex market, enabling traders to execute trades in real-time from anywhere with an internet connection. These platforms provide access to a wider range of currency pairs, increased liquidity, and reduced transaction costs.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is playing an increasingly significant role in the forex market, with algorithms analyzing vast amounts of data to identify trading opportunities and make automated decisions. AI-powered trading bots can execute trades based on pre-defined parameters, providing traders with the ability to monitor multiple markets simultaneously.
Blockchain Technology and Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the settlement and clearing of foreign exchange transactions. By providing a secure and transparent ledger system, blockchain can reduce settlement times and costs while enhancing the overall efficiency of the market. Cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, are also gaining traction as an alternative to traditional fiat currencies.
Last Point
In conclusion, the economics definition of foreign exchange market unveils a multifaceted ecosystem that underpins global economic interconnectedness. Its participants, operations, and regulatory framework shape currency dynamics, facilitating international trade, investment, and financial stability. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the foreign exchange market will continue to play a pivotal role in fostering economic growth and prosperity.
