The foreign exchange market diagram provides a comprehensive overview of the global marketplace where currencies are traded. This dynamic and ever-evolving market plays a crucial role in international trade, investment, and economic stability.
The diagram illustrates the major components of the forex market, including currency pairs, market participants, and the factors that influence exchange rates. It also highlights the importance of risk management and the regulatory landscape governing forex trading.
Market Overview
The foreign exchange (forex) market is the world’s largest and most liquid financial market, facilitating the trading of currencies between countries and institutions. It plays a crucial role in international trade and investment, enabling businesses to conduct cross-border transactions and individuals to travel abroad. The daily trading volume in the forex market exceeds $5 trillion, making it significantly larger than the stock, bond, and commodity markets combined.
Major Players
The forex market involves a wide range of participants, including:
- Central banks: Manage their countries’ exchange rates and monetary policies.
- Commercial banks: Facilitate currency exchange for their clients.
- Investment banks: Engage in speculative trading and provide liquidity to the market.
- Hedge funds: Use sophisticated strategies to capitalize on currency fluctuations.
- Retail traders: Individuals who trade currencies for profit.
Currency Pairs and Trading
The foreign exchange market operates through the trading of currency pairs. A currency pair represents the exchange rate between two different currencies. The first currency in the pair is known as the base currency, while the second is known as the quote currency.
When trading currency pairs, traders speculate on the relative value of one currency against another. If a trader believes that the base currency will strengthen against the quote currency, they will buy the base currency and sell the quote currency. Conversely, if they believe that the base currency will weaken against the quote currency, they will sell the base currency and buy the quote currency.
Major Currency Pairs
The most commonly traded currency pairs are known as major currency pairs. These pairs include the following:
- EUR/USD (Euro/US dollar)
- USD/JPY (US dollar/Japanese yen)
- GBP/USD (British pound/US dollar)
- USD/CHF (US dollar/Swiss franc)
- AUD/USD (Australian dollar/US dollar)
- NZD/USD (New Zealand dollar/US dollar)
- USD/CAD (US dollar/Canadian dollar)
Major currency pairs are typically the most liquid, meaning that they have the highest trading volume and the tightest spreads. This makes them the most popular choice for traders of all levels.
Market Participants and Roles
The foreign exchange market is a vast and complex network of buyers and sellers from various backgrounds and with diverse objectives. These participants play distinct roles in shaping market dynamics and facilitating the exchange of currencies.
Understanding the different types of market participants and their functions is crucial for navigating the forex market effectively.
Types of Market Participants
The primary participants in the foreign exchange market include:
- Central Banks: Central banks are government institutions responsible for managing a country’s monetary policy. They intervene in the forex market to influence exchange rates, stabilize the economy, and manage foreign reserves.
- Commercial Banks: Commercial banks facilitate currency exchange for businesses and individuals. They provide a range of services, including currency conversion, wire transfers, and trade finance.
- Investment Banks: Investment banks engage in currency trading for their clients, hedge funds, and other institutional investors. They provide sophisticated trading strategies and market analysis.
- Hedge Funds: Hedge funds are investment funds that use advanced trading strategies to profit from currency fluctuations. They often employ leverage and short-selling techniques.
- Retail Traders: Retail traders are individuals who trade currencies on a smaller scale, using personal funds and typically through online platforms.
Factors Influencing Exchange Rates

Exchange rates are influenced by a complex interplay of economic and political factors that affect the supply and demand for currencies. These factors can impact the value of currencies, making them appreciate (increase in value) or depreciate (decrease in value).
Economic factors, such as economic growth, inflation, interest rates, and trade balance, play a significant role in determining exchange rates. Political factors, including government policies, political stability, and geopolitical events, can also impact currency values.
You also can investigate more thoroughly about foreign exchange market worth to enhance your awareness in the field of foreign exchange market worth.
Economic Factors
- Economic Growth: A strong economy attracts foreign investment and increases demand for the currency, leading to appreciation.
- Inflation: Higher inflation erodes the purchasing power of a currency, reducing its value against other currencies.
- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates attract foreign capital, increasing demand for the currency and leading to appreciation.
- Trade Balance: A trade surplus (exports exceeding imports) increases demand for the currency, while a trade deficit has the opposite effect.
Political Factors
- Government Policies: Fiscal and monetary policies can impact economic growth, inflation, and interest rates, indirectly influencing exchange rates.
- Political Stability: Political instability and uncertainty can reduce foreign investment and lead to currency depreciation.
- Geopolitical Events: Wars, trade disputes, and natural disasters can significantly impact currency values.
Forex Trading Strategies
Traders employ various strategies to navigate the dynamic forex market, each with its advantages and risks. Understanding these strategies is crucial for successful trading.
Trend Trading
- Identifying and trading in the direction of the prevailing market trend.
- Advantages:
- Potentially high returns when the trend continues.
- Requires less active monitoring.
- Risks:
- False signals and reversals can lead to losses.
- Requires patience and discipline to wait for profitable trades.
Range Trading
- Identifying a range of prices within which the currency pair is expected to trade.
- Advantages:
- Lower risk than trend trading.
- Can generate profits even in volatile markets.
- Risks:
- Breakouts from the range can lead to significant losses.
- Requires constant monitoring to adjust trading positions.
Scalping
- Executing multiple small trades within a short period, aiming for small but frequent profits.
- Advantages:
- Can generate consistent profits in active markets.
- Requires less capital than other strategies.
- Risks:
- High transaction costs can erode profits.
- Requires constant monitoring and quick decision-making.
Carry Trading
- Borrowing a currency with a low interest rate and investing it in a currency with a higher interest rate.
- Advantages:
- Can generate consistent profits from interest rate differentials.
- Diversifies a portfolio.
- Risks:
- Exchange rate fluctuations can lead to losses.
- Requires a significant amount of capital.
News Trading
- Trading based on the release of economic data, news events, and political announcements.
- Advantages:
- Can generate high returns if market reactions are correctly predicted.
- Requires quick decision-making and a deep understanding of market fundamentals.
- Risks:
- False signals and unexpected market reactions can lead to losses.
- Requires constant monitoring of news and economic events.
Risk Management in Forex Trading
Risk management is crucial in forex trading as it involves significant financial risk. It encompasses strategies to mitigate potential losses and protect traders’ capital.
Effective risk management practices include:
Understanding Risk Tolerance
Determining the amount of risk a trader is comfortable taking, based on their financial situation and trading goals.
Position Sizing
Limiting the size of each trade relative to the trader’s account balance to prevent substantial losses.
Stop-Loss Orders
Setting orders that automatically close trades when prices reach predetermined levels, limiting potential losses.
Take-Profit Orders
Setting orders that automatically close trades when prices reach target profit levels, locking in gains.
Hedging
Using offsetting positions to reduce exposure to risk in specific market conditions.
Risk-Reward Ratio
Calculating the potential reward for a trade relative to the potential risk to ensure favorable odds.
Diversification
Trading multiple currency pairs or asset classes to spread risk and reduce exposure to any single market.
Emotional Control
Managing emotions and avoiding impulsive trading decisions that could lead to losses.
Forex Market Regulation: The Foreign Exchange Market Diagram
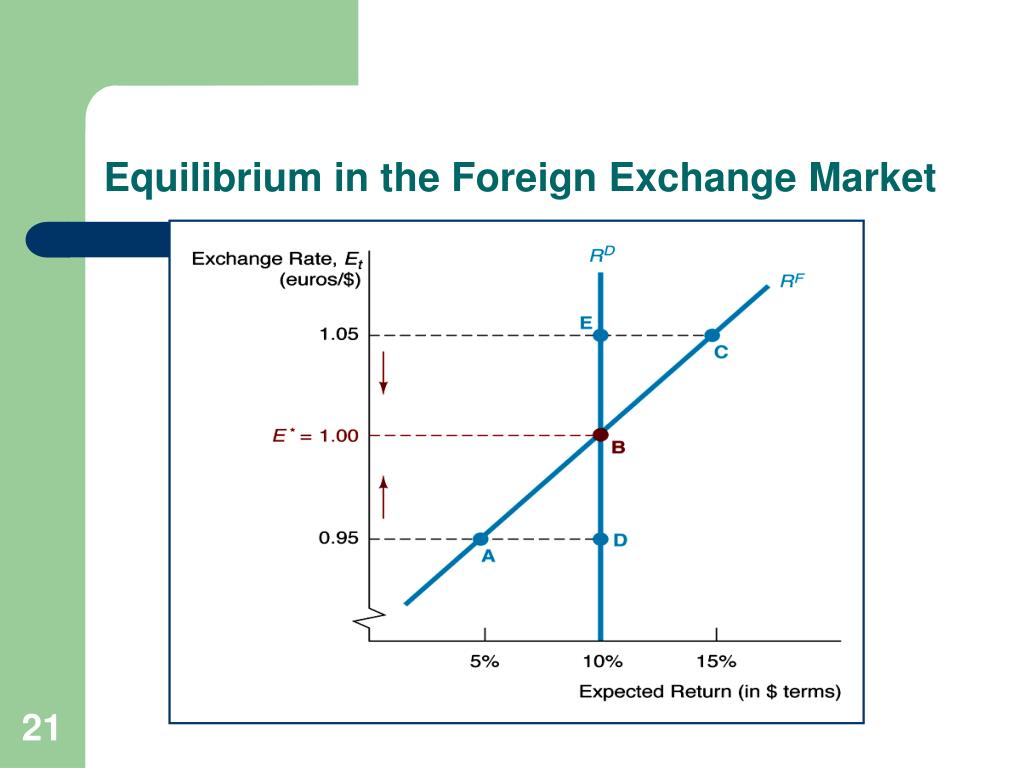
The foreign exchange market is a vast and complex global marketplace, and like any financial market, it requires regulation to ensure its stability and integrity. Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in overseeing the forex market, establishing rules and guidelines to protect traders and maintain market fairness.
Regulatory Bodies, The foreign exchange market diagram
The regulatory landscape of the forex market varies from country to country. In the United States, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) is the primary regulator of forex trading. The CFTC enforces regulations to prevent fraud, manipulation, and other illegal activities in the forex market. Other major regulatory bodies include the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the United Kingdom, the Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA) in Switzerland, and the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) in Singapore.
You also will receive the benefits of visiting foreign exchange market future today.
Impact of Regulation
Regulation has a significant impact on forex trading. Regulatory bodies set rules and guidelines that govern the activities of forex brokers, including capital requirements, risk management practices, and disclosure obligations. These regulations help to ensure that forex brokers operate in a safe and transparent manner, protecting traders from fraud and abuse.
Regulation also promotes market fairness by preventing manipulation and insider trading. Regulatory bodies have the authority to investigate and punish violations of their rules, which helps to maintain the integrity of the forex market and protect traders from unfair practices.
Remember to click foreign exchange market scams to understand more comprehensive aspects of the foreign exchange market scams topic.
Technology in Forex Trading

Technology has revolutionized the foreign exchange market, making it accessible to a wider range of participants and facilitating faster and more efficient trading.
Trading platforms have emerged as the primary interface for forex traders. These platforms provide real-time market data, charting tools, and order execution capabilities. They also offer advanced features such as technical analysis indicators, automated trading, and risk management tools.
Mobile Apps
Mobile apps have made forex trading even more convenient. Traders can now access the market and execute trades from anywhere with an internet connection. Mobile apps offer similar functionality to desktop trading platforms, including real-time quotes, charting, and order management.
Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading, also known as automated trading, involves using computer programs to execute trades based on predefined rules. Algorithms can analyze market data, identify trading opportunities, and place orders automatically. This type of trading can reduce the emotional element from trading and improve execution speed.
The Future of the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is constantly evolving, and the future holds many exciting possibilities. One of the most significant trends is the increasing use of technology. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are already being used to automate many tasks in the forex market, and this trend is only expected to continue.
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies such as blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT) are also expected to have a major impact on the forex market. These technologies could make it possible to create new types of financial instruments and to trade currencies more efficiently and securely.
Changing Market Dynamics
In addition to the impact of technology, the forex market is also being shaped by changing market dynamics. The rise of emerging markets and the increasing interconnectedness of the global economy are both contributing to the growth of the forex market.
Epilogue
In conclusion, the foreign exchange market diagram is an essential tool for understanding the complex and interconnected world of currency trading. By providing a visual representation of the market’s key elements, the diagram empowers traders, investors, and policymakers to make informed decisions and navigate the ever-changing forex landscape.
