Equilibrium in the foreign exchange market is a crucial concept that determines the value of currencies. It represents a balance between the supply and demand for currencies, influenced by various factors. Understanding this equilibrium is essential for businesses, investors, and policymakers.
The equilibrium exchange rate is determined by the interaction of supply and demand in the foreign exchange market. When the supply of a currency exceeds the demand, its value depreciates, while an excess demand leads to appreciation.
Equilibrium in the Foreign Exchange Market
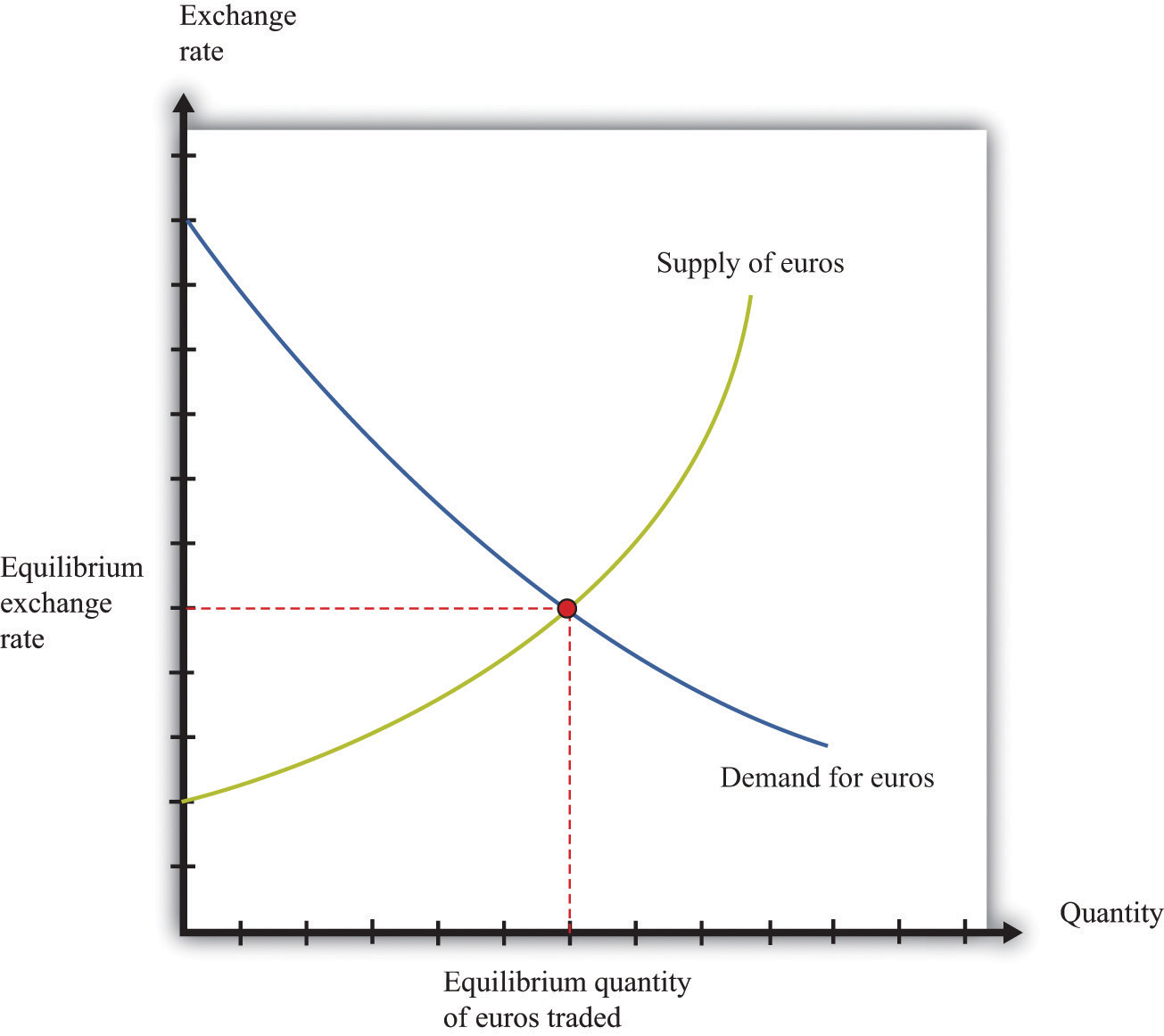
Equilibrium in the foreign exchange market occurs when the demand for a currency is equal to its supply. At this point, the exchange rate is stable and there is no tendency for it to change.
The equilibrium exchange rate is determined by a number of factors, including:
Economic Factors, Equilibrium in the foreign exchange market
- Economic growth: A country with a strong economy will typically have a stronger currency.
- Inflation: A country with high inflation will typically have a weaker currency.
- Interest rates: A country with high interest rates will typically have a stronger currency.
Political Factors
- Political stability: A country with a stable political system will typically have a stronger currency.
- Government policies: Government policies can affect the value of a currency.
Market Factors
- Demand and supply: The equilibrium exchange rate is determined by the demand for and supply of a currency.
- Speculation: Speculation can affect the value of a currency.
Determinants of Equilibrium
The equilibrium exchange rate is determined by a complex interplay of economic factors, both domestic and international. These factors can be broadly categorized into two main groups: supply and demand factors.
Finish your research with information from foreign exchange market pdf notes.
Supply and Demand
The supply of a currency in the foreign exchange market refers to the amount of that currency that is available for sale, while the demand for a currency refers to the amount of that currency that is desired for purchase. The equilibrium exchange rate is the price at which the quantity of currency supplied equals the quantity of currency demanded.
In this topic, you find that foreign exchange market definition in simple words is very useful.
The following table Artikels the major determinants of equilibrium in the foreign exchange market:
| Factor | Impact on Supply and Demand | Effect on Equilibrium Exchange Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Interest rates | Higher interest rates attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the domestic currency | Appreciation of domestic currency |
| Inflation | Higher inflation erodes the purchasing power of the domestic currency, reducing demand | Depreciation of domestic currency |
| Economic growth | Stronger economic growth increases demand for the domestic currency | Appreciation of domestic currency |
| Political stability | Political instability reduces demand for the domestic currency | Depreciation of domestic currency |
| Trade balance | A trade surplus increases demand for the domestic currency | Appreciation of domestic currency |
| Fiscal policy | Expansionary fiscal policy reduces demand for the domestic currency | Depreciation of domestic currency |
| Monetary policy | Expansionary monetary policy reduces demand for the domestic currency | Depreciation of domestic currency |
It is important to note that these factors are not mutually exclusive and can interact in complex ways. For example, a country with high interest rates may also have high inflation, which could offset the positive impact of interest rates on the exchange rate.
Check foreign-exchange market interventions will always to inspect complete evaluations and testimonials from users.
Types of Equilibrium: Equilibrium In The Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market can experience different types of equilibrium, each with unique characteristics. These types include:
- Stable equilibrium: In this type of equilibrium, the exchange rate settles at a level where the demand for and supply of a currency are equal. Any fluctuations in the exchange rate are temporary and the market quickly returns to the equilibrium level.
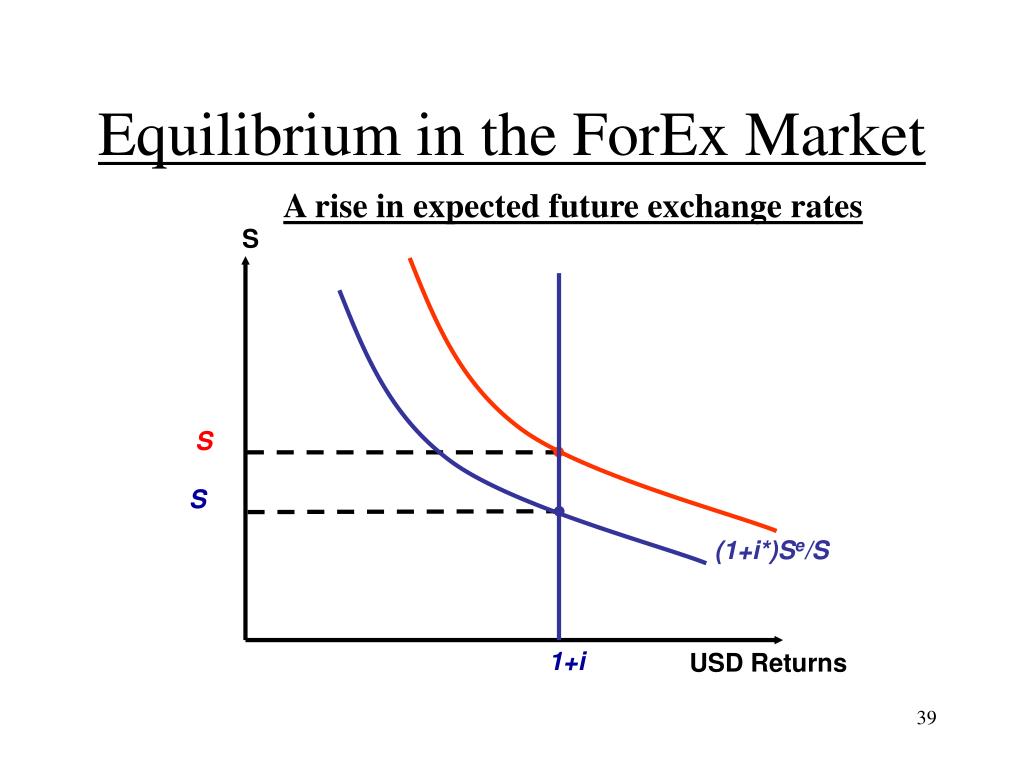
- Unstable equilibrium: In unstable equilibrium, the exchange rate is not self-correcting. If the exchange rate deviates from the equilibrium level, it tends to move further away from it, rather than returning to it. This can lead to large fluctuations in the exchange rate.
- Neutral equilibrium: In neutral equilibrium, the exchange rate is indifferent to changes in the demand and supply of a currency. The market does not have a strong tendency to return to a specific equilibrium level, and the exchange rate can fluctuate freely.
Stability of Equilibrium
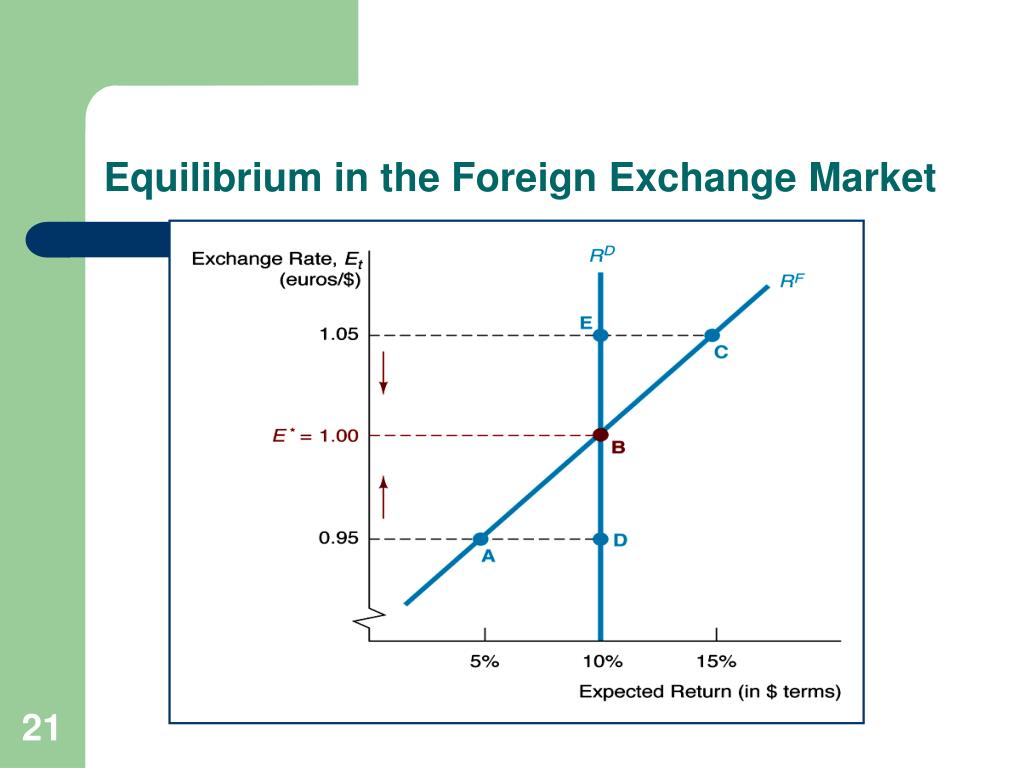
Equilibrium in the foreign exchange market is a state of balance where the supply and demand for currencies are equal. This balance can be affected by a variety of factors, including economic conditions, political events, and market sentiment.
When equilibrium is disrupted, the value of currencies can fluctuate significantly. This can have a number of consequences, including:
– Increased volatility in the foreign exchange market
– Reduced confidence in the stability of the financial system
– Negative impacts on trade and investment
Factors Affecting Stability
A number of factors can affect the stability of equilibrium in the foreign exchange market, including:
– The size and liquidity of the market
– The level of economic integration between countries
– The credibility of government policies
– The level of political stability
– The degree of market speculation
Consequences of Disruptions
Disruptions to equilibrium in the foreign exchange market can have a number of negative consequences, including:
– Increased volatility in the market
– Reduced confidence in the financial system
– Negative impacts on trade and investment
– Currency crises
Policy Implications
Equilibrium in the foreign exchange market has significant policy implications for governments and central banks. Maintaining equilibrium is crucial for economic stability and growth.
Role of Central Banks
Central banks play a pivotal role in maintaining equilibrium in the foreign exchange market. They use various monetary policy tools to influence exchange rates and ensure stability. These tools include:
- Open market operations
- Changes in reserve requirements
- Changes in the discount rate
By manipulating these tools, central banks can influence the supply and demand for foreign currencies, thereby stabilizing exchange rates.
Summary
Equilibrium in the foreign exchange market is a dynamic concept that is constantly influenced by economic, political, and social factors. Understanding the determinants of equilibrium and its implications for businesses and policymakers is crucial for navigating the complex world of currency markets.
