The equilibrium of foreign exchange market is a captivating subject that offers a lens into the intricate workings of global finance. This dynamic market, where currencies are traded and exchanged, plays a pivotal role in facilitating international commerce and shaping economic landscapes worldwide.
Understanding the forces that drive equilibrium in the foreign exchange market is crucial for businesses, investors, and policymakers alike. This comprehensive analysis will delve into the complexities of supply and demand, exchange rate determination, and the impact of central bank intervention, providing valuable insights into this ever-evolving arena.
Foreign Exchange Market Equilibrium
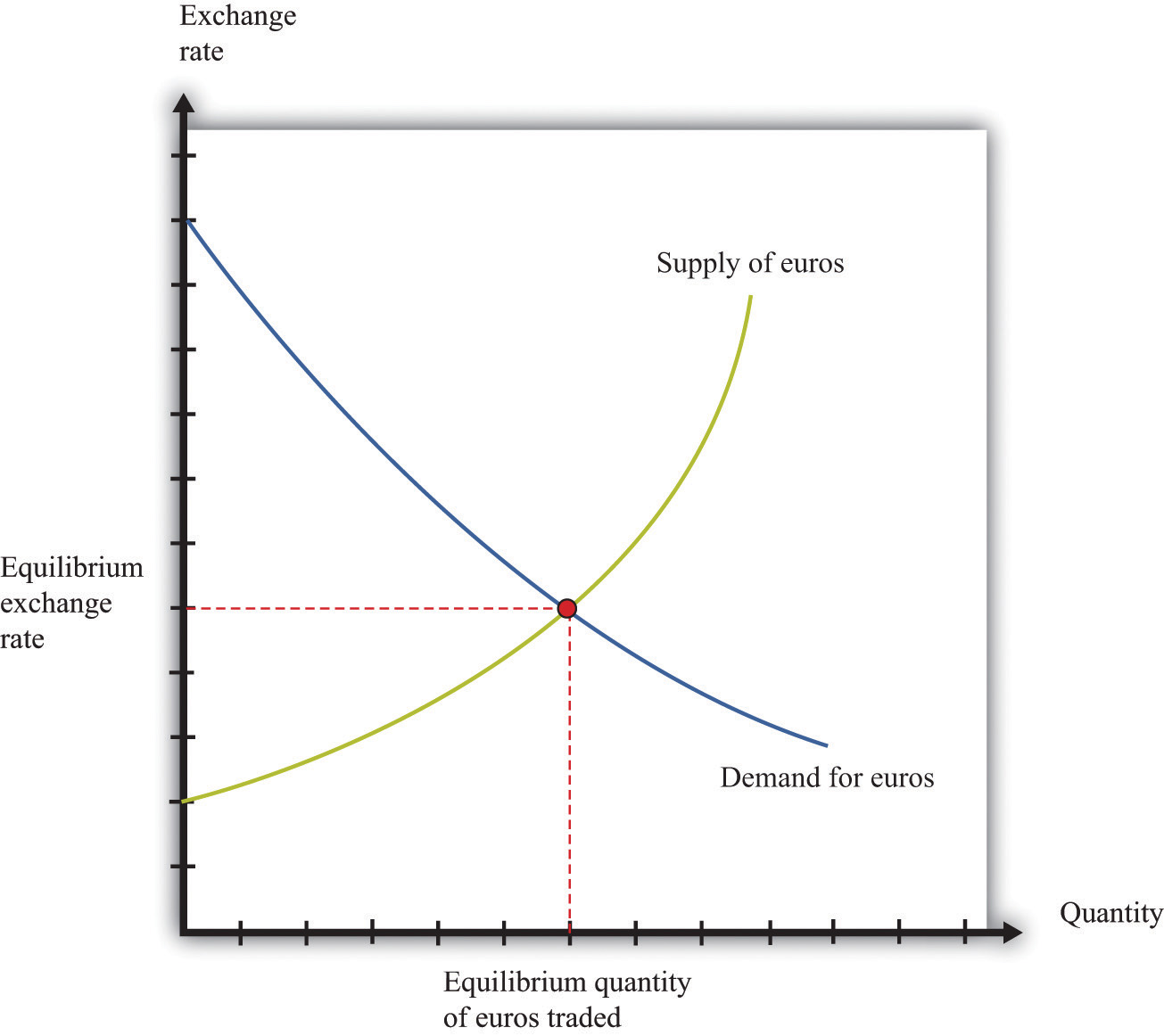
Equilibrium in the foreign exchange market occurs when the supply of a currency equals the demand for that currency. At this point, there is no pressure for the exchange rate to change.
Discover how foreign exchange market options definition has transformed methods in RELATED FIELD.
The supply of a currency is determined by the amount of that currency that is available for sale. The demand for a currency is determined by the amount of that currency that people want to buy. The supply and demand of a currency can be affected by a variety of factors, including economic conditions, political events, and interest rates.
Factors Affecting Supply and Demand
- Economic conditions: The economic conditions in a country can affect the supply and demand of its currency. For example, if a country’s economy is growing, the demand for its currency will likely increase, as more people will want to invest in that country.
- Political events: Political events can also affect the supply and demand of a currency. For example, if there is a political crisis in a country, the demand for its currency may decrease, as people may be less willing to invest in that country.
- Interest rates: Interest rates can also affect the supply and demand of a currency. For example, if a country’s interest rates are high, the demand for its currency will likely increase, as people will want to invest in that country to earn a higher return.
Exchange Rate Determination: The Equilibrium Of Foreign Exchange Market
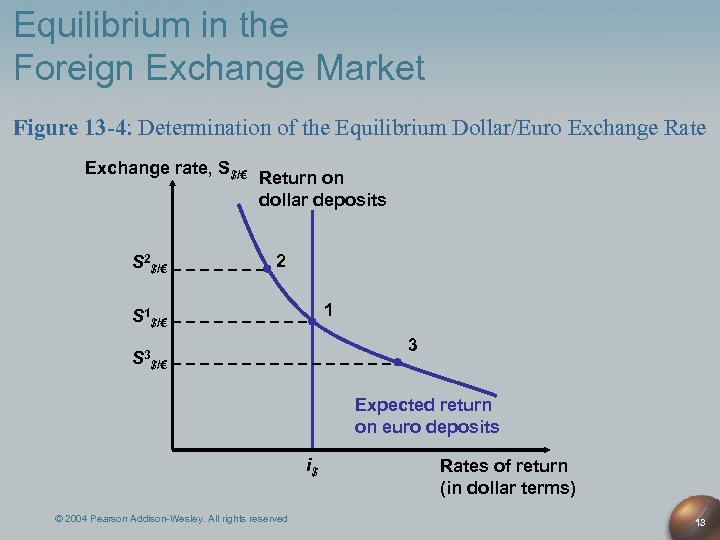
Exchange rates, the prices of one currency in terms of another, are determined in the foreign exchange market by the interaction of supply and demand. The supply of a currency is the amount that people are willing to sell at a given price, while the demand is the amount that people are willing to buy at that price. The equilibrium exchange rate is the price at which the quantity of currency supplied equals the quantity demanded.
Market Forces
The primary market forces that determine exchange rates are:
- Interest rates: Higher interest rates in a country make its currency more attractive to investors, increasing demand and raising its value.
- Inflation: Higher inflation rates reduce the purchasing power of a currency, decreasing its value.
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth in a country increases demand for its currency, raising its value.
- Political stability: Political instability or uncertainty can reduce demand for a currency, lowering its value.
- Speculation: Speculators can influence exchange rates by buying or selling currencies based on their expectations of future movements.
Factors Influencing Fluctuations
In addition to these market forces, several other factors can influence exchange rate fluctuations, including:
- Government intervention: Governments can intervene in the foreign exchange market to influence exchange rates, such as by buying or selling their own currency.
- Natural disasters or geopolitical events: Major events can impact a country’s economy and currency value.
- Technological advancements: Innovations in financial technology can affect the efficiency and speed of currency trading.
Central Bank Intervention
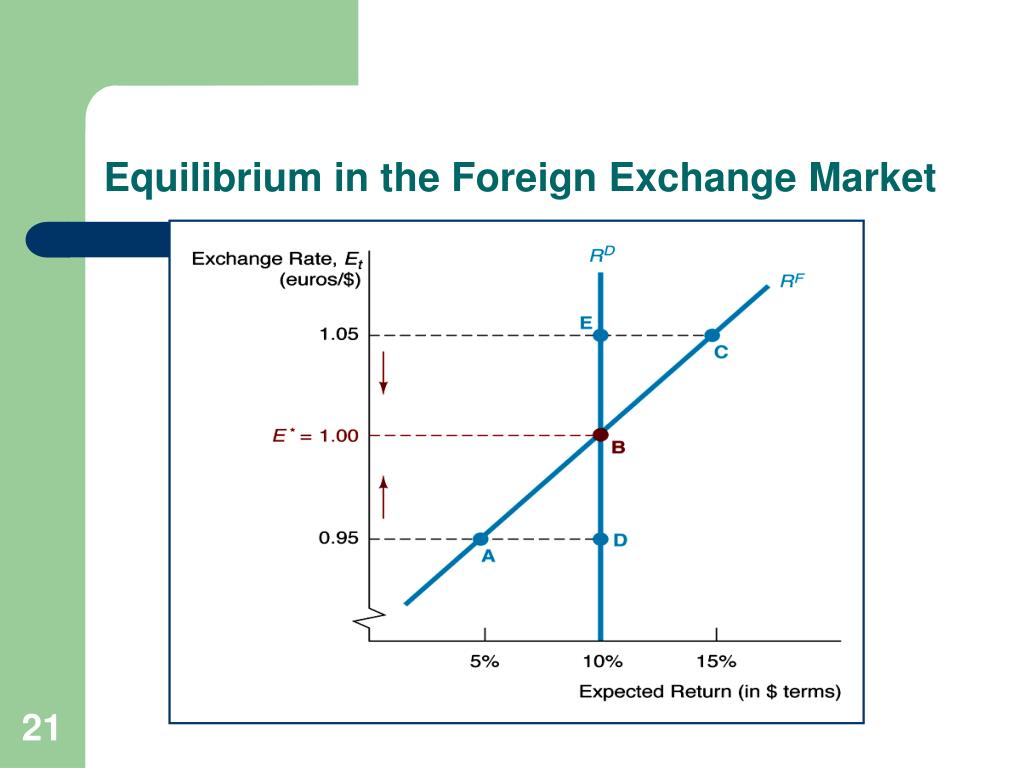
Central banks play a crucial role in the foreign exchange market by influencing exchange rates and maintaining monetary stability. They intervene to correct imbalances, manage currency volatility, and achieve specific economic goals.
Types of Central Bank Intervention
Central banks can intervene in the foreign exchange market through various mechanisms:
- Open Market Operations: Buying or selling foreign currencies in the open market to influence exchange rates.
- Currency Swaps: Temporary exchanges of currencies between central banks to adjust liquidity or stabilize exchange rates.
- Foreign Exchange Reserves: Holding foreign currencies as reserves to support the value of the domestic currency.
Consequences of Central Bank Intervention
Central bank intervention can have significant consequences, including:
- Temporary Effects: Intervention can provide short-term relief but may not resolve underlying imbalances in the long run.
- Market Distortion: Intervention can create artificial demand or supply, distorting the natural equilibrium of the market.
- Reduced Confidence: Excessive intervention can erode market confidence and increase volatility in the long term.
Exchange Rate Regimes
An exchange rate regime refers to the system by which a country manages the value of its currency relative to other currencies. Different types of exchange rate regimes exist, each with its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of regime depends on various factors.
Examine how foreign exchange market today can boost performance in your area.
Fixed Exchange Rate Regime
Under a fixed exchange rate regime, the government or central bank maintains the value of its currency at a fixed rate against a single currency or a basket of currencies. This is typically achieved through intervention in the foreign exchange market by buying or selling its own currency.
Advantages:
- Price stability and predictability in international trade
- Reduced exchange rate volatility
Disadvantages:
- Loss of monetary policy independence
- Potential for speculative attacks and currency crises
Floating Exchange Rate Regime, The equilibrium of foreign exchange market
In a floating exchange rate regime, the value of the currency is determined by the forces of supply and demand in the foreign exchange market, with no intervention from the central bank.
Advantages:
- Monetary policy independence
- Flexibility to adjust to economic shocks
Disadvantages:
- Increased exchange rate volatility
- Potential for currency overvaluation or undervaluation
Managed Float Regime
A managed float regime combines elements of both fixed and floating exchange rate regimes. The central bank intervenes in the foreign exchange market to influence the value of the currency but allows it to fluctuate within a specified range.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of foreign exchange market currency of.
Advantages:
- Balance between monetary policy independence and exchange rate stability
- Flexibility to respond to market conditions
Disadvantages:
- Requires significant central bank intervention
- Can be difficult to manage effectively
Factors Influencing Exchange Rate Regime Choice
The choice of exchange rate regime depends on various factors, including:
- Level of economic development
- Trade openness
- Inflation rate
- Capital mobility
- Political and economic stability
Currency Crises
A currency crisis occurs when a country’s currency rapidly loses value against other currencies, often due to a combination of economic and political factors. This can have severe consequences for the country’s economy and its citizens.
Currency crises can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Speculation: When investors believe a currency is overvalued, they may sell it in large quantities, leading to a drop in its value.
- Economic imbalances: A country with a large trade deficit or high levels of government debt may be more vulnerable to a currency crisis.
- Political instability: Political turmoil or uncertainty can lead to a loss of confidence in a country’s currency.
The consequences of a currency crisis can be severe, including:
- Inflation: A rapid decline in the value of a currency can lead to higher prices for goods and services.
- Economic recession: Currency crises can lead to a loss of confidence in the economy, resulting in a decrease in investment and economic growth.
- Social unrest: Currency crises can cause financial hardship and social unrest, leading to protests and political instability.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the equilibrium of foreign exchange market is a complex and ever-changing landscape that is shaped by a multitude of factors. Understanding the dynamics of this market is essential for navigating the complexities of global trade and making informed decisions in the face of currency fluctuations.
