The foreign exchange market equilibrium price, a cornerstone of international finance, plays a pivotal role in determining the exchange rates between currencies. It represents the point at which supply and demand for a currency pair meet, creating a balance that facilitates efficient trading and maintains market stability.
Factors such as economic conditions, political events, and market sentiment influence the equilibrium price, shaping the dynamics of the foreign exchange market.
Define Foreign Exchange Market Equilibrium Price
In the foreign exchange market, equilibrium price refers to the exchange rate at which the supply of a currency equals the demand for that currency.
For descriptions on additional topics like conclusion for the foreign exchange market, please visit the available conclusion for the foreign exchange market.
At the equilibrium price, there is no excess supply or demand for the currency, and the market is in balance. This price is determined by the interaction of buyers and sellers in the market and is constantly fluctuating due to changes in economic factors, such as interest rates, inflation, and economic growth.
Examples of Equilibrium Prices
Here are some examples of equilibrium prices in different currency pairs:
- USD/JPY: 110.00
- EUR/USD: 1.1000
- GBP/USD: 1.2500
These equilibrium prices represent the exchange rates at which there is no excess supply or demand for the respective currencies in the market.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Market Equilibrium Price

The equilibrium price in the foreign exchange market is influenced by a range of economic, political, and market-related factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for traders and investors to make informed decisions.
Economic Factors
- Interest rates: Higher interest rates in one country make its currency more attractive to investors, leading to an appreciation in its value.
- Inflation: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of a currency, making it less valuable and leading to depreciation.
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth indicates a stable and attractive economy, which can boost the value of its currency.
Political Factors, Foreign exchange market equilibrium price
- Political stability: Political instability can create uncertainty and risk, leading to a depreciation of the currency.
- Government policies: Government policies, such as exchange rate controls or fiscal stimulus, can significantly impact the equilibrium price.
- International relations: Diplomatic tensions or conflicts between countries can affect currency values.
Market-Related Factors
- Supply and demand: The equilibrium price is determined by the interaction of supply and demand for a particular currency.
- Market sentiment: Market sentiment, such as optimism or pessimism, can influence the demand for currencies and affect their equilibrium price.
- Speculation: Currency speculators can create temporary fluctuations in equilibrium prices through buying and selling based on market expectations.
Role of Supply and Demand in Determining Equilibrium Price
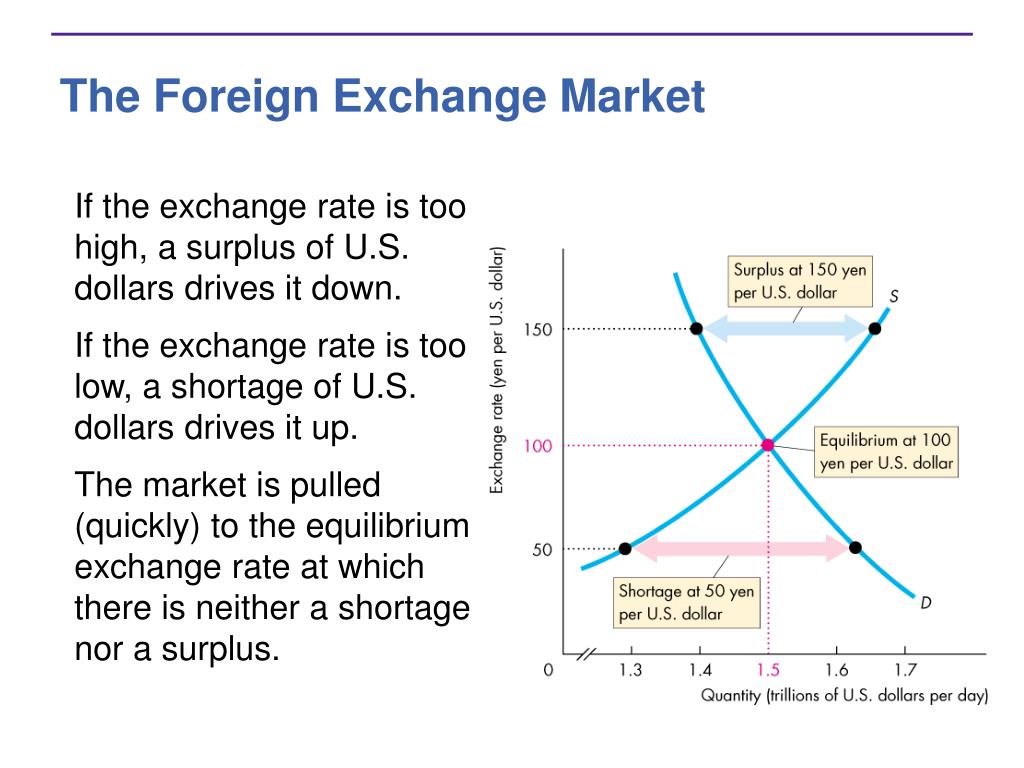
In the foreign exchange market, the equilibrium price is the price at which the quantity of currency supplied equals the quantity of currency demanded. The equilibrium price is determined by the interaction of supply and demand in the market.
The supply of a currency is the amount of that currency that is available for sale. The demand for a currency is the amount of that currency that people want to buy. The equilibrium price is the price at which the quantity of currency supplied equals the quantity of currency demanded.
Changes in Supply and Demand
Changes in supply and demand can affect the equilibrium price. An increase in supply will lead to a decrease in the equilibrium price, while a decrease in supply will lead to an increase in the equilibrium price. An increase in demand will lead to an increase in the equilibrium price, while a decrease in demand will lead to a decrease in the equilibrium price.
Impact of Exchange Rate Fluctuations on Equilibrium Price
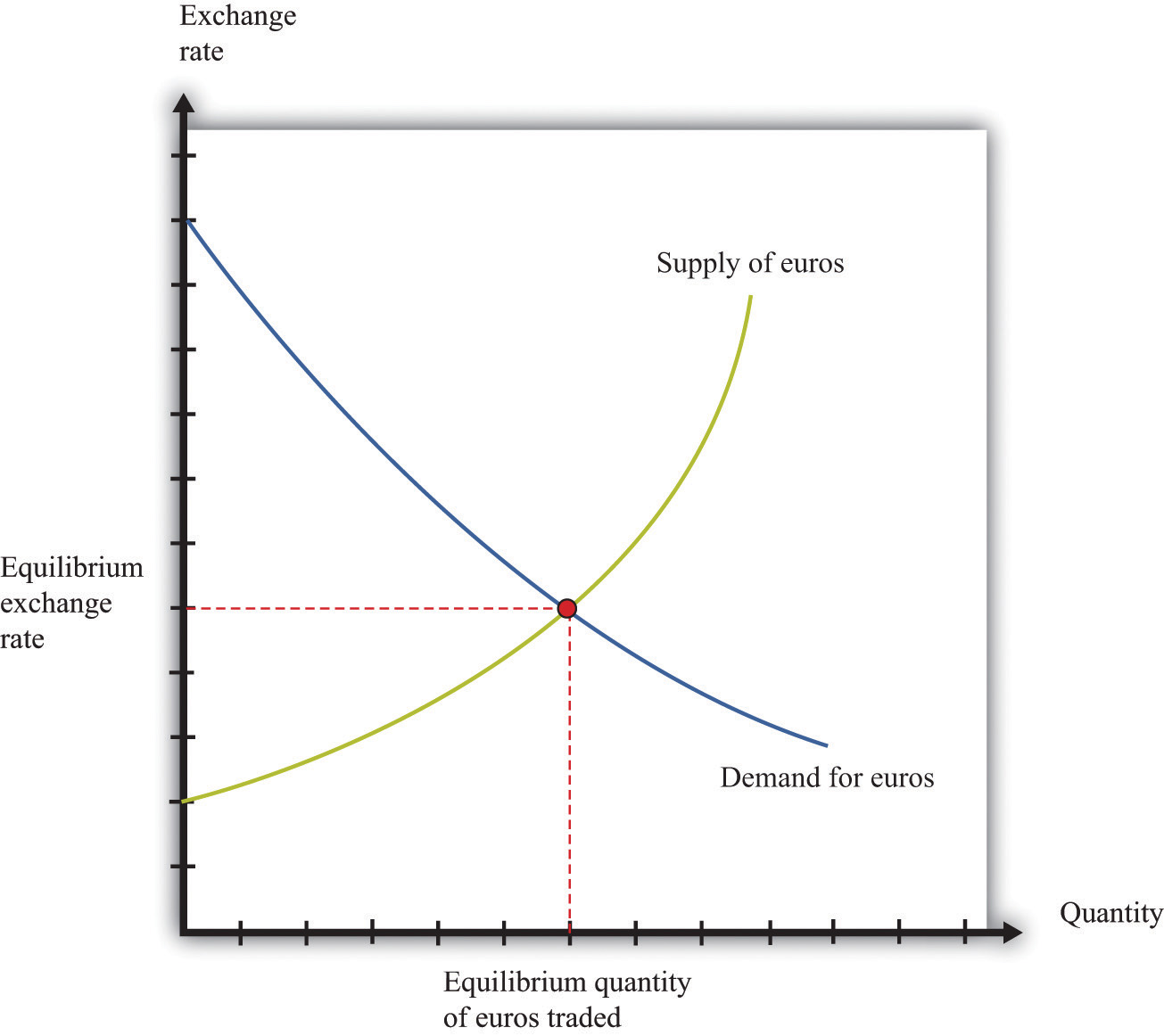
Exchange rate fluctuations have a significant impact on the equilibrium price of currencies in the foreign exchange market. When the exchange rate of a currency increases, it becomes more expensive to buy goods and services from countries that use that currency. This can lead to a decrease in demand for the currency, which can in turn lead to a decrease in its equilibrium price.
Browse the implementation of the foreign exchange market basics in real-world situations to understand its applications.
Conversely, when the exchange rate of a currency decreases, it becomes less expensive to buy goods and services from countries that use that currency. This can lead to an increase in demand for the currency, which can in turn lead to an increase in its equilibrium price.
For descriptions on additional topics like foreign exchange market graph ap econ, please visit the available foreign exchange market graph ap econ.
Examples
- In 2015, the value of the US dollar increased against the value of the euro. This made it more expensive for Europeans to buy goods and services from the United States, which led to a decrease in demand for the euro and a decrease in its equilibrium price.
- In 2016, the value of the British pound decreased against the value of the US dollar. This made it less expensive for Americans to buy goods and services from the United Kingdom, which led to an increase in demand for the pound and an increase in its equilibrium price.
Importance of Equilibrium Price in the Foreign Exchange Market
Equilibrium price in the foreign exchange market is crucial for maintaining stability and facilitating efficient trading. It represents the point where the quantity of a currency supplied equals the quantity demanded at a specific exchange rate.
Stability and Predictability
Equilibrium price provides stability and predictability to the foreign exchange market. It prevents extreme fluctuations in exchange rates, which can disrupt international trade and investment. By establishing a fair and stable price, businesses and individuals can plan their transactions with confidence.
Efficient Trading
Equilibrium price facilitates efficient trading by matching the needs of buyers and sellers. When the exchange rate is at equilibrium, there is no shortage or surplus of currency. This allows market participants to trade at a price that reflects the true value of the currency, reducing transaction costs and increasing market liquidity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the foreign exchange market equilibrium price is a crucial concept that underpins the global financial system. It provides a framework for understanding currency fluctuations and facilitates efficient trading, ensuring the smooth functioning of international commerce and investment.
