The foreign exchange market equilibrium condition is a crucial concept in international finance, determining the exchange rate at which the supply of a currency equals the demand for that currency. Understanding this condition is essential for businesses, investors, and policymakers.
Various factors influence the equilibrium exchange rate, including economic growth, interest rates, inflation, and political stability. When the market is in equilibrium, the exchange rate remains stable, facilitating smooth international trade and investment.
Market Equilibrium: Foreign Exchange Market Equilibrium Condition
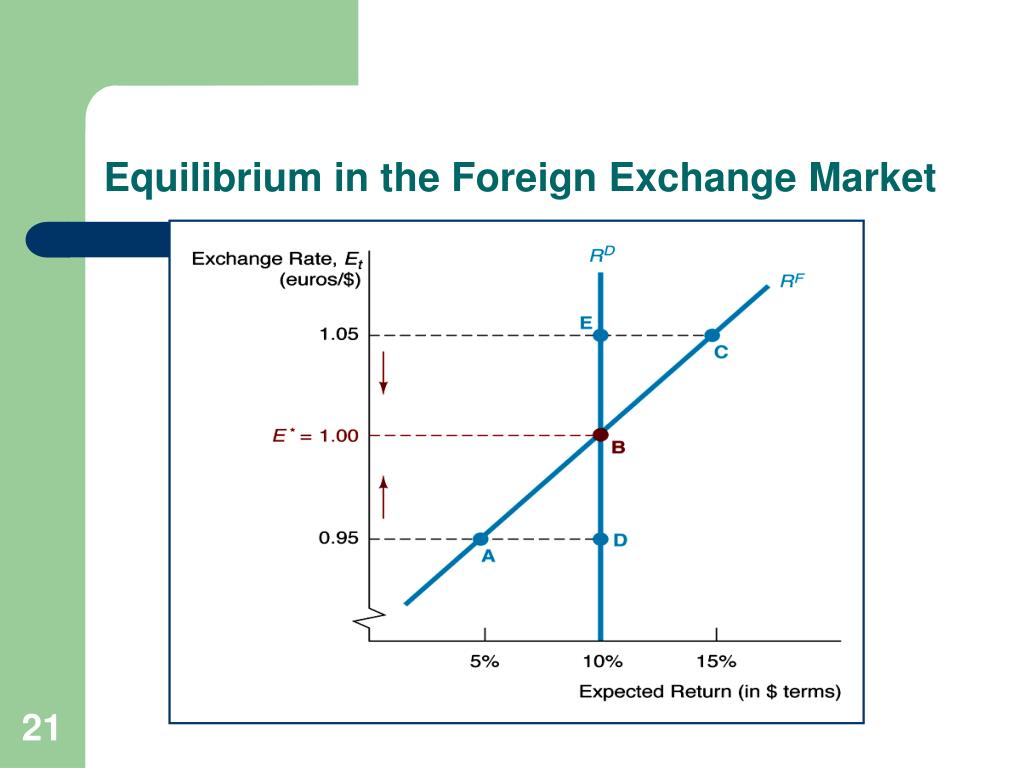
Market equilibrium is a state in which the forces of supply and demand are in balance, resulting in a stable price or exchange rate. In the foreign exchange market, equilibrium occurs when the supply of a currency equals the demand for that currency at a particular exchange rate.
Browse the multiple elements of articles on foreign exchange market to gain a more broad understanding.
The equilibrium exchange rate is determined by several factors, including economic fundamentals, interest rates, inflation rates, and political stability. When these factors change, the supply or demand for a currency may also change, leading to an adjustment in the exchange rate to restore equilibrium.
Factors Determining Equilibrium Exchange Rate
- Economic Fundamentals: Economic growth, inflation, and unemployment rates can influence the demand for a currency.
- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates tend to attract foreign capital, increasing demand for a currency.
- Inflation Rates: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of a currency, reducing its demand.
- Political Stability: Political instability can lead to a decrease in demand for a currency due to perceived risk.
Market Adjustment to Restore Equilibrium
When the market is not in equilibrium, there are forces that act to restore balance. For example:
- If the exchange rate is too high, it makes exports more expensive and imports cheaper, leading to a decrease in demand for the currency and a fall in the exchange rate.
- If the exchange rate is too low, it makes imports more expensive and exports cheaper, leading to an increase in demand for the currency and a rise in the exchange rate.
Supply and Demand in the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market, is a global decentralized market where currencies are traded. The value of a currency is determined by the forces of supply and demand. The supply of a currency refers to the amount of that currency that is available for purchase, while the demand for a currency refers to the amount of that currency that people are willing to buy.
Obtain a comprehensive document about the application of foreign exchange indonesia that is effective.
The equilibrium exchange rate is the rate at which the supply of a currency is equal to the demand for that currency. At the equilibrium exchange rate, there is no shortage or surplus of the currency in the market. Changes in supply and demand can cause the equilibrium exchange rate to change.
Discover more by delving into foreign exchange market statistics further.
Changes in Supply and Demand
An increase in the supply of a currency will cause the equilibrium exchange rate to depreciate. This is because an increase in supply means that there is more of the currency available for purchase, which makes it less valuable. Conversely, a decrease in the supply of a currency will cause the equilibrium exchange rate to appreciate. This is because a decrease in supply means that there is less of the currency available for purchase, which makes it more valuable.
An increase in the demand for a currency will cause the equilibrium exchange rate to appreciate. This is because an increase in demand means that more people are willing to buy the currency, which makes it more valuable. Conversely, a decrease in the demand for a currency will cause the equilibrium exchange rate to depreciate. This is because a decrease in demand means that fewer people are willing to buy the currency, which makes it less valuable.
Real-World Examples
There are many real-world events that can influence supply and demand in the foreign exchange market. For example, a change in interest rates can affect the demand for a currency. If a country’s interest rates increase, it becomes more attractive for investors to buy that country’s currency. This increased demand will cause the equilibrium exchange rate to appreciate.
Another event that can influence supply and demand in the foreign exchange market is a change in economic growth. If a country’s economy is growing, it will increase the demand for that country’s currency. This increased demand will cause the equilibrium exchange rate to appreciate.
Central Bank Intervention
Central banks play a crucial role in the foreign exchange market by influencing the exchange rates of their currencies. They intervene in the market to achieve various economic objectives, such as managing inflation, stabilizing the currency, and promoting economic growth.
Central bank intervention can affect the equilibrium exchange rate by altering the supply and demand for currencies. For instance, if a central bank wants to depreciate its currency, it can sell its currency in the market, increasing the supply and driving down the exchange rate. Conversely, if it wants to appreciate its currency, it can buy its currency in the market, reducing the supply and pushing up the exchange rate.
Examples of Central Bank Intervention
Central banks have intervened in the foreign exchange market in various ways. Some notable examples include:
- In 2011, the Swiss National Bank intervened heavily to prevent the Swiss franc from appreciating against the euro, setting a minimum exchange rate.
- In 2013, the Bank of Japan launched a quantitative easing program, purchasing large amounts of Japanese government bonds to weaken the yen.
- In 2015, the People’s Bank of China intervened to stabilize the yuan after it depreciated sharply.
Floating Exchange Rates
Floating exchange rates are determined by the forces of supply and demand in the foreign exchange market. In a floating exchange rate regime, the central bank does not intervene to fix the exchange rate. Instead, the exchange rate is allowed to fluctuate freely based on market conditions.
The equilibrium exchange rate in a floating exchange rate regime is the exchange rate at which the quantity of a currency supplied in the foreign exchange market is equal to the quantity demanded.
Countries that have adopted floating exchange rate regimes
- United States
- United Kingdom
- Canada
- Japan
- Eurozone
Fixed Exchange Rates
In a fixed exchange rate regime, the government or central bank sets and maintains the value of the domestic currency relative to one or more foreign currencies. This means that the exchange rate is fixed at a predetermined level and is not allowed to fluctuate freely in response to market forces.
Equilibrium Exchange Rate in a Fixed Exchange Rate Regime
In a fixed exchange rate regime, the equilibrium exchange rate is the rate that the government or central bank sets and maintains. This rate is typically determined by considering a variety of factors, including the country’s economic fundamentals, inflation rate, and balance of payments.
Examples of Countries with Fixed Exchange Rate Regimes
Several countries around the world have adopted fixed exchange rate regimes. Some notable examples include:
- Hong Kong
- Saudi Arabia
- United Arab Emirates
- Bhutan
- Brunei
Managed Exchange Rates
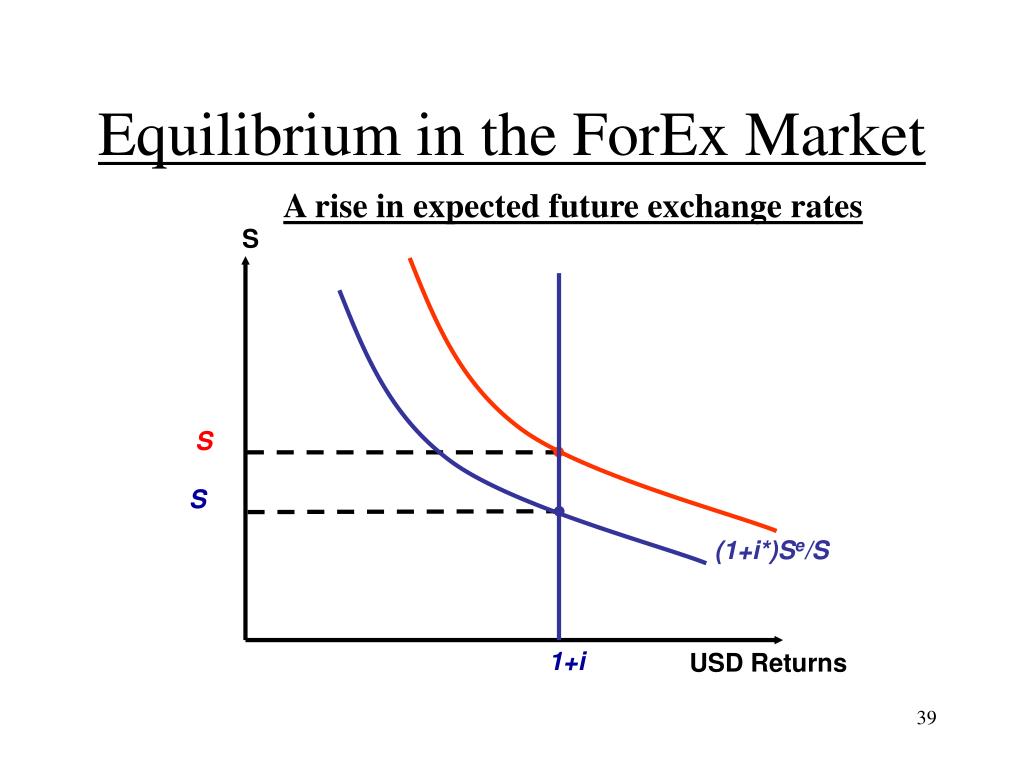
Managed exchange rates are a type of exchange rate regime in which the central bank intervenes in the foreign exchange market to influence the value of its currency. This can be done through a variety of mechanisms, such as buying or selling foreign currencies, or setting a target exchange rate and intervening to keep the exchange rate within a certain range.
The equilibrium exchange rate in a managed exchange rate regime is determined by the central bank’s intervention. The central bank will typically set a target exchange rate and intervene to keep the exchange rate within a certain range of this target. The equilibrium exchange rate will therefore be the exchange rate that the central bank is targeting.
Examples of Countries with Managed Exchange Rate Regimes
There are a number of countries that have adopted managed exchange rate regimes. Some of the most notable examples include:
- China
- Hong Kong
- Saudi Arabia
- Singapore
- United Arab Emirates
Exchange Rate Regimes and Economic Development
Exchange rate regimes play a significant role in shaping the economic development of a country. The choice of regime, whether fixed, floating, or managed, can impact economic growth, inflation, and employment.
Economic Growth
Fixed exchange rates can promote economic growth by providing stability and predictability for businesses and investors. This stability encourages investment and long-term planning, leading to economic expansion. On the other hand, floating exchange rates can introduce volatility, making it challenging for businesses to plan and invest, potentially hindering economic growth.
Inflation, Foreign exchange market equilibrium condition
Exchange rate regimes can influence inflation. Fixed exchange rates can help control inflation by anchoring the domestic currency to a stable currency, such as the US dollar. Floating exchange rates, however, can lead to higher inflation if the domestic currency depreciates against foreign currencies, making imported goods more expensive.
Employment
Exchange rate regimes can affect employment through their impact on exports and imports. Fixed exchange rates can make exports more competitive, leading to increased production and job creation in export-oriented industries. Conversely, floating exchange rates can make imports cheaper, potentially leading to job losses in domestic industries that compete with imports.
Examples
China, for example, has maintained a fixed exchange rate against the US dollar for several decades. This has contributed to its rapid economic growth by promoting stability and attracting foreign investment. In contrast, Argentina has experienced periods of high inflation and economic instability due to its history of fluctuating exchange rates.
End of Discussion
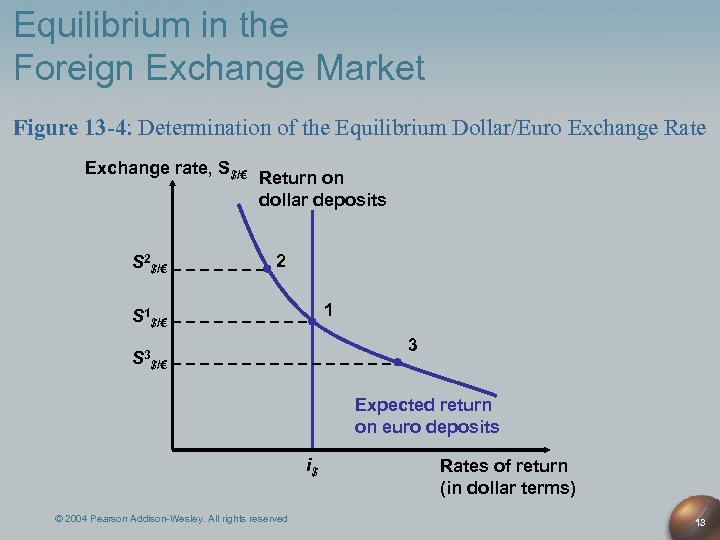
In conclusion, the foreign exchange market equilibrium condition plays a pivotal role in global economic stability. By comprehending the factors that determine this equilibrium, we can better anticipate exchange rate fluctuations and make informed decisions in the international financial arena.
